CCNA Explorer 2 Introduction to Dynamic Routing Protocols
From Teknologisk videncenter
Introduction and Advantages
Perspective and Background
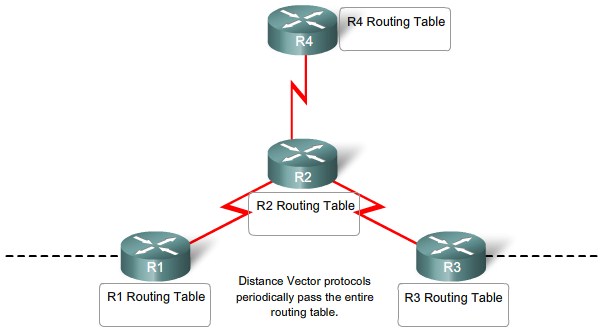
Network discovery and routing table maintenance
The purpose of a routing protocol includes:
- Discovery of remote networks
- Maintaining up-to-date routing information
- Choosing the best path to destination networks
- Ability to find a new best path if the current path is no longer available
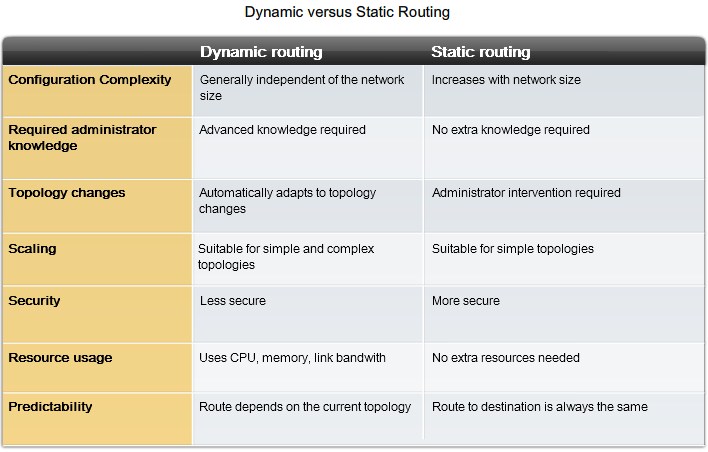
Advantages
Overview
|
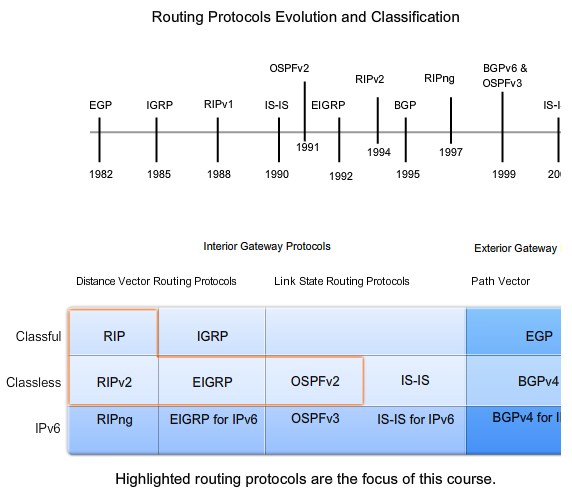
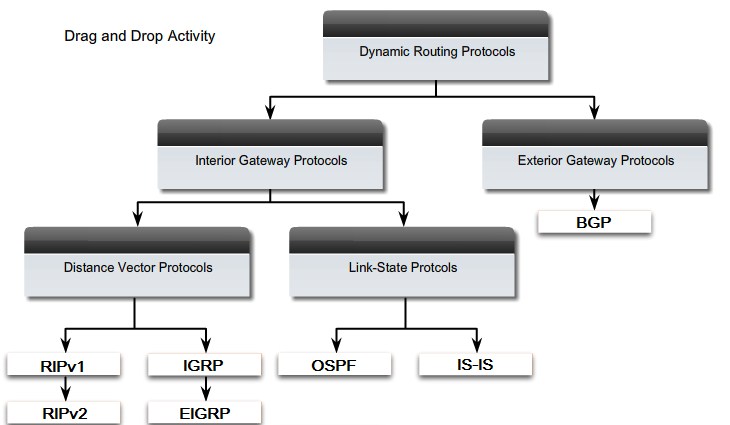
Classifying Dynamic Routing Protocols
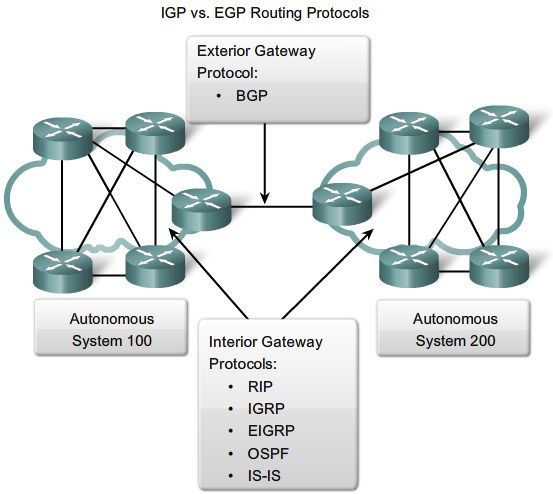
IGP and EGP
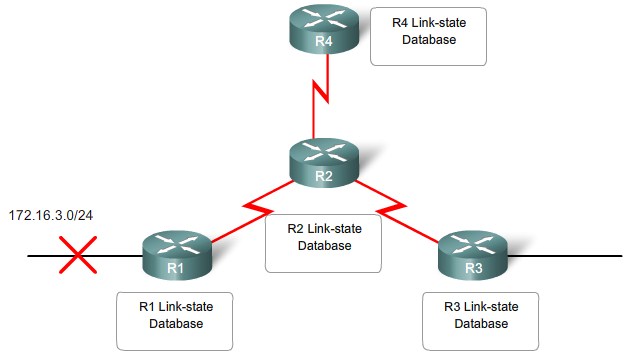
Distance Vector and Link State
Distance Vector bruger for det meste Bellman-Ford algoritmen.
Distance vector protocols work best in situations where:
- The network is simple and flat and does not require a special hierarchical design.
- The administrators do not have enough knowledge to configure and troubleshoot link-state protocols.
- Specific types of networks, such as hub-and-spoke networks, are being implemented.
- Worst-case convergence times in a network are not a concern.
Link-state protocols work best in situations where:
- The network design is hierarchical, usually occurring in large networks.
- The administrators have a good knowledge of the implemented link-state routing protocol.
- Fast convergence of the network is crucial.
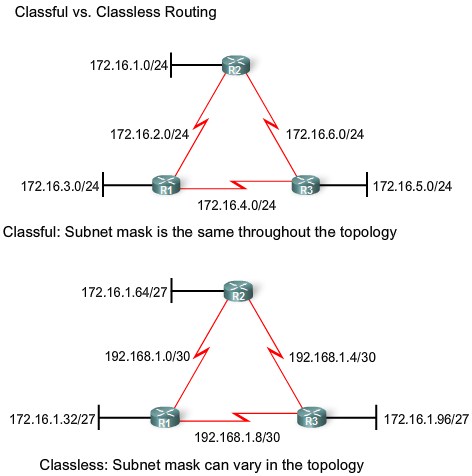
Classful and Classless
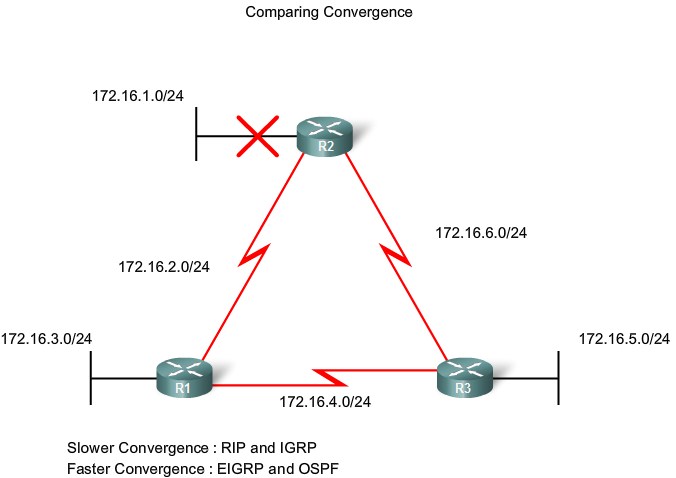
Convergence
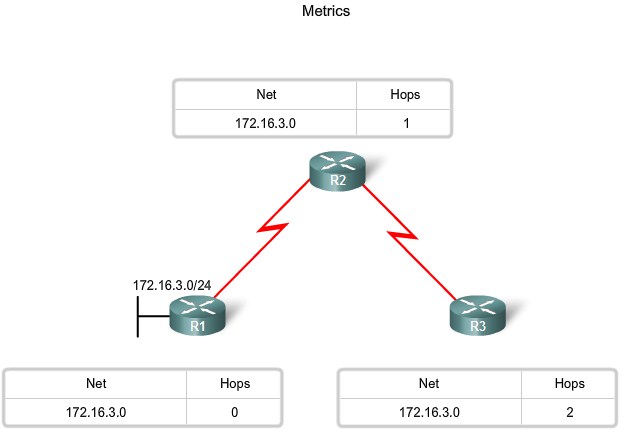
Metrics
Purpose of a Metric
Metrics and Routing Protocols
The metric for each routing protocol is:
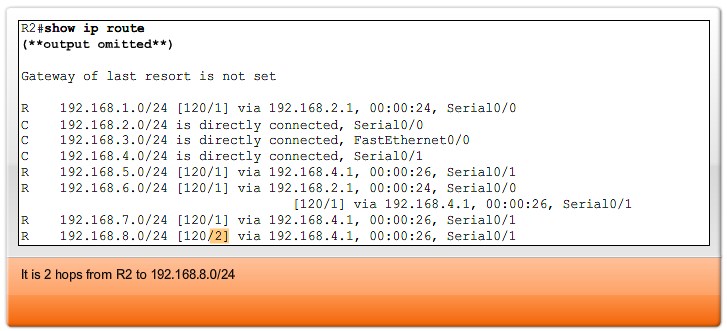
- RIP: Hop count - Best path is chosen by the route with the lowest hop count.
- IGRP and EIGRP: Bandwidth, Delay, Reliability, and Load - Best path is chosen by the route with the smallest composite metric value calculated from these multiple parameters. By default, only bandwidth and delay are used.
- IS-IS and OSPF: Cost - Best path is chosen by the route with the lowest cost. . Cisco's implementation of OSPF uses bandwidth. IS-IS is discussed in CCNP.
Metric used in IP routing protocols:
- Hop count - A simple metric that counts the number of routers a packet must traverse
- Bandwidth - Influences path selection by preferring the path with the highest bandwidth
- Load - Considers the traffic utilization of a certain link
- Delay - Considers the time a packet takes to traverse a path
- Reliability - Assesses the probability of a link failure, calculated from the interface error count or previous link failures
- Cost - A value determined either by the IOS or by the network administrator to indicate preference for a route. Cost can represent a metric, a combination of metrics or a policy.
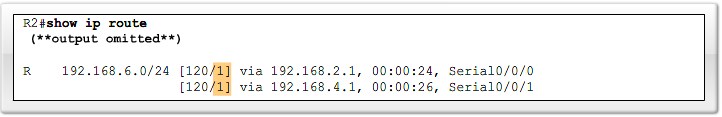
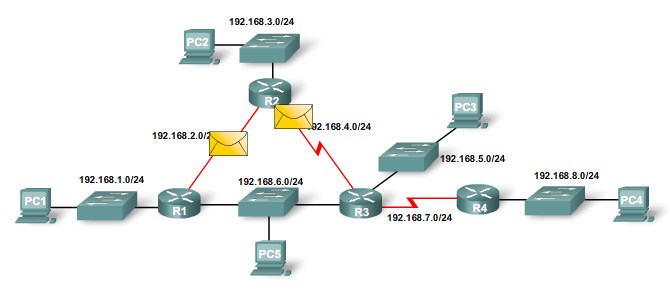
Load Balancing
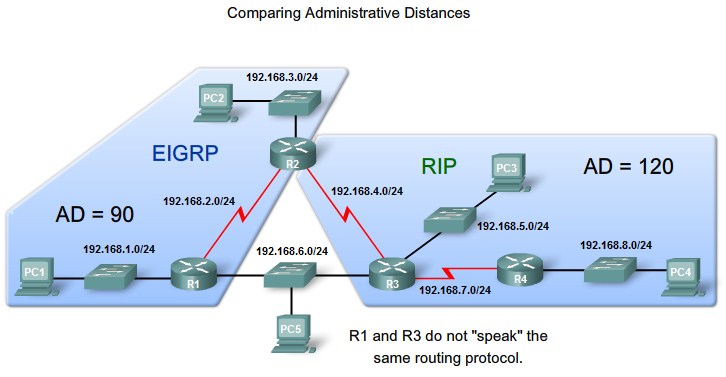
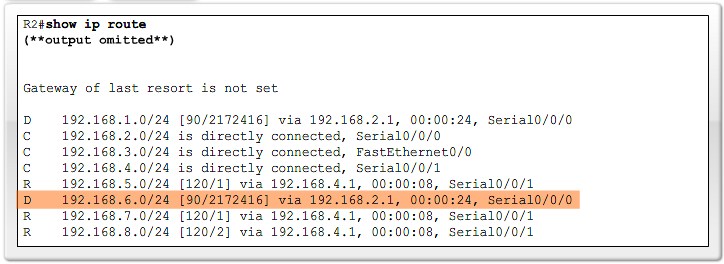
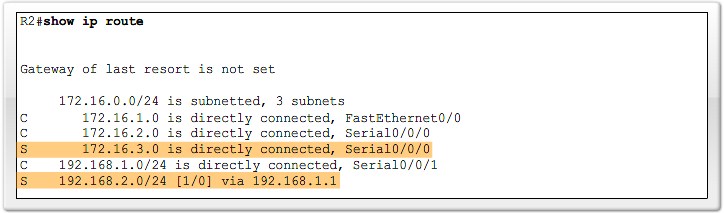
Administrativ Distance
Purpose of Administrative Distance
Cisco implementation
|