Introduction to Routing and Packet Forwarding
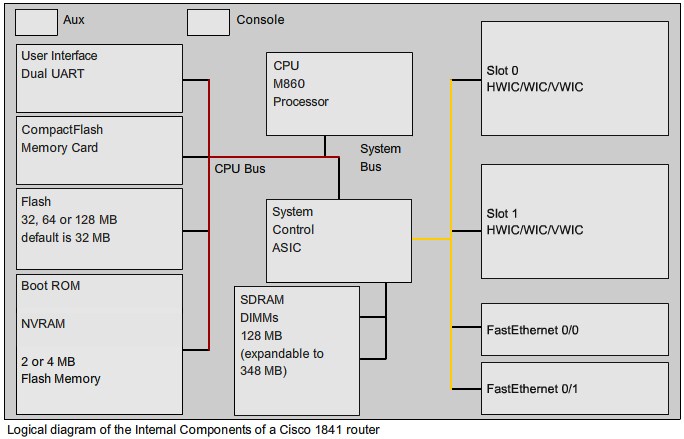
Inside the Router
Routers are Computers
Router CPU and Memory
 1800 Router Inside. PSU,HWIC,HWIC,Fan,Ram,NVRAM,AIM,CPU from left to right, top to bottom |
|
|
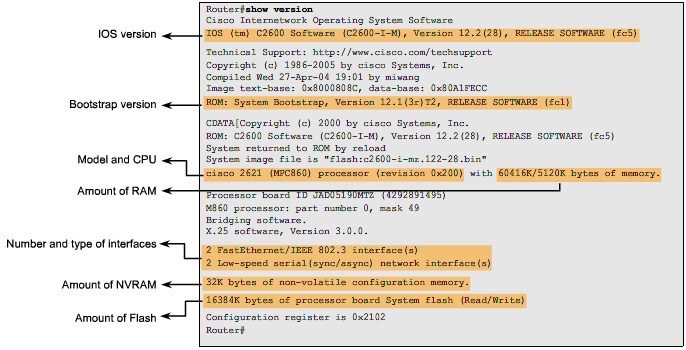
Internetwork Operating System
Der findes forskellige IOS'er der har forskellige freatures.
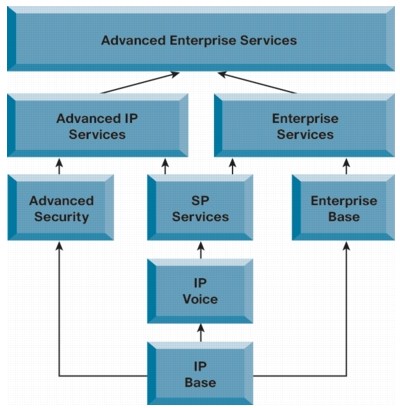 Cisco IOS packaging framework |
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/prod/collateral/iosswrel/ps8802/ps10587/ps10591/ps10621/qa_c67_561940.html
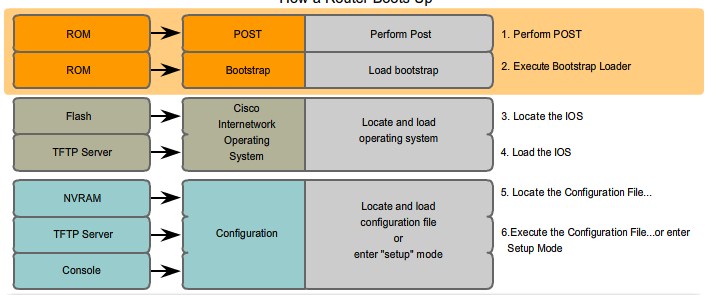
Router Boot-up Process
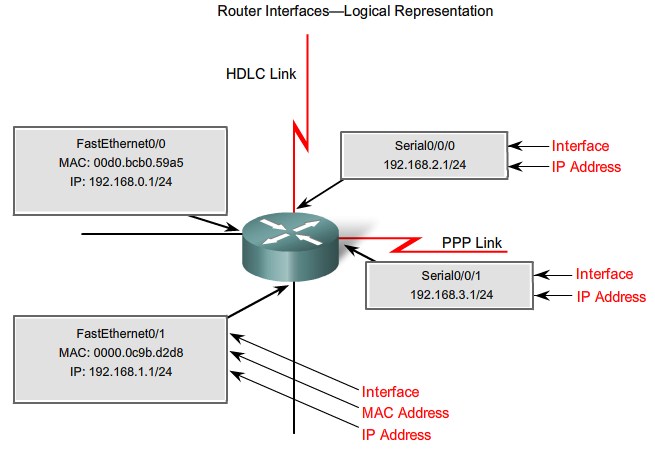
Router interfaces
 Interfaces. RJ45, Cisco Smart Serial Connector
PPP, Frame Relay, and HDLC (High-Level Data Link Control)
|
|
|
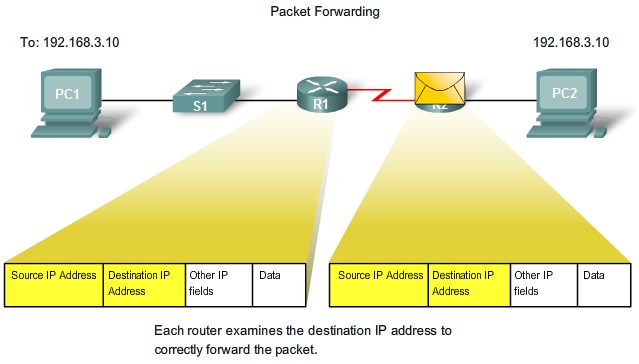
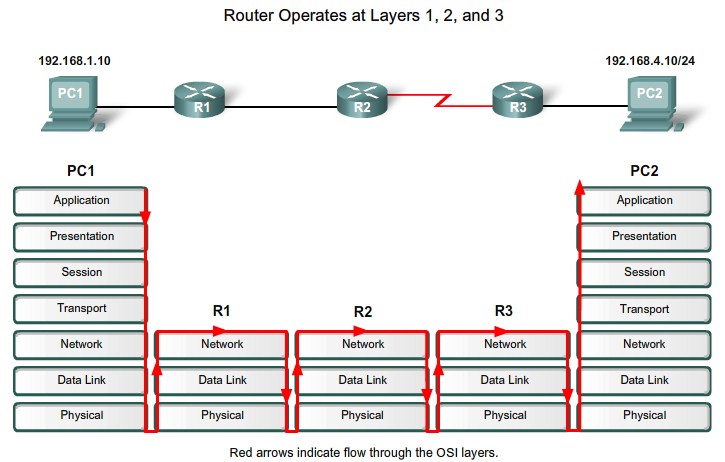
Routers and the Network Layer
CLI Configuration and Addressing
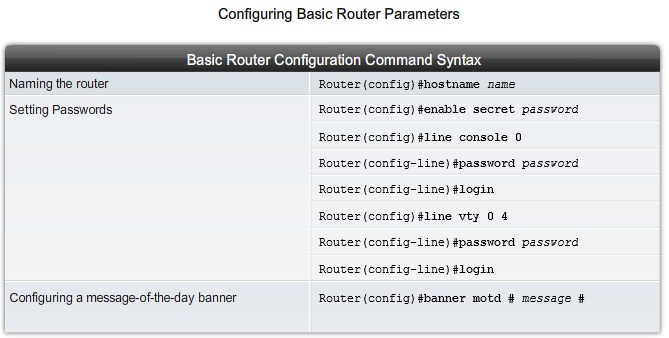
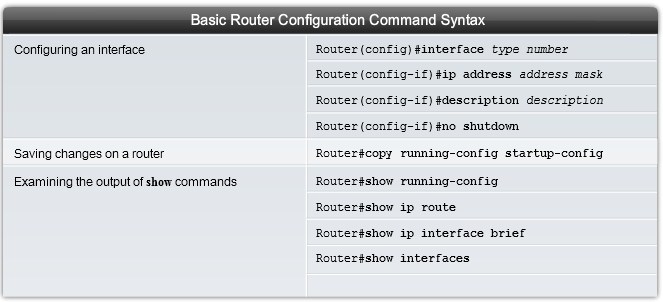
Basic Router Configuration
Building the Routing Table
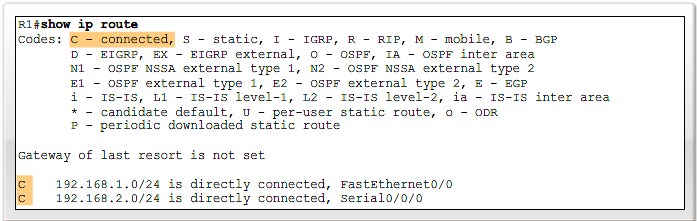
Introducing the Routing Table
|
|
|
Vis en Route Print på windåse...
|
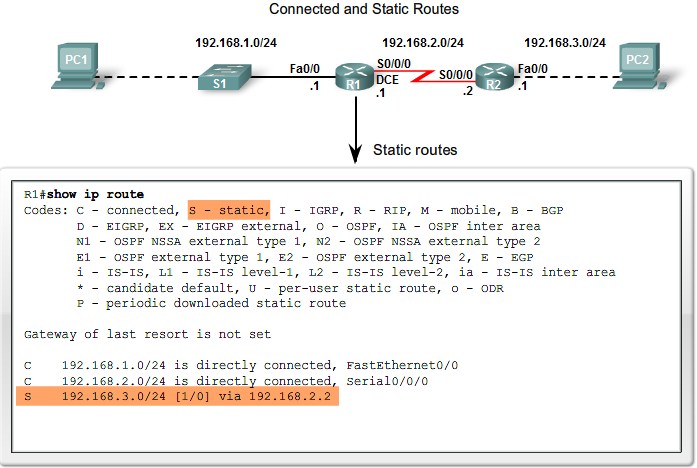
Static Routing
|
|
|
Use Static routes when:
- A network consists of only a few routers
- A network is connected to the Internet only through a single ISP
- A large network is configured in a hub-and-spoke topology
|
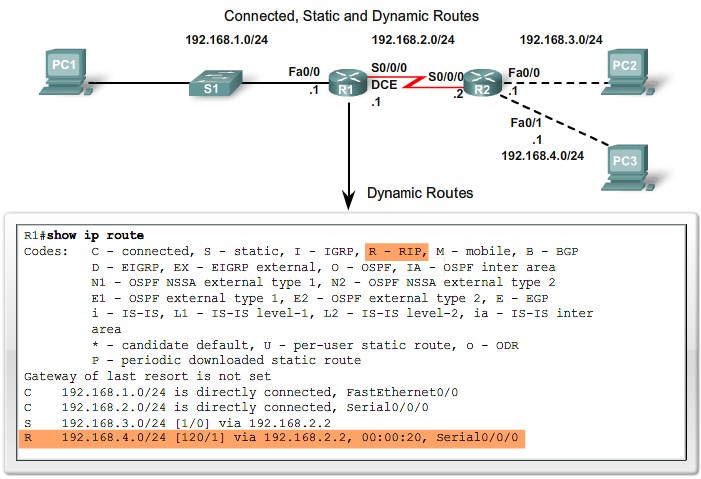
Dynamic Routing
|
|
Jobs of Dynamic Routing Protocols
- Network Discovery
- Maintaining Routing Tables
IP Routing Protocols
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
- IGRP (Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
- EIGRP (Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol)
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
- IS-IS (Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System)
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
|
Path Determination and Switching Functions
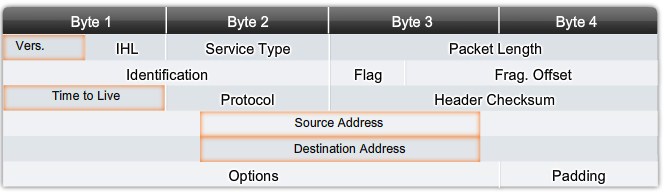
Packet Fields and Frame Fields
|
|
- Version - Version number (4 bits); predominant version is IP version 4 (IPv4)
- IP header length - Header length in 32-bit words (4 bits)
- Precedence and type of service - How the datagram should be handled (8 bits); the first 3 bits are precedence bits (this use has been superseded by Differentiated Services Code Point [DSCP], which uses the first 6 bits [last 2 reserved])
- Packet length - Total length (header + data) (16 bits)
- Identification - Unique IP datagram value (16 bits)
- Flags - Controls fragmenting (3 bits)
- Fragment offset - Supports fragmentation of datagrams to allow differing maximum transmission units (MTUs) in the Internet (13 bits)
- Time to Live (TTL) - Identifies how many routers can be traversed by the datagram before being dropped (8 bits)
- Protocol - Upper-layer protocol sending the datagram (8 bits)
- Header checksum - Integrity check on the header (16 bits)
- Source IP address - 32-bit source IP address (32 bits)
- Destination IP address - 32-bit destination IP address (32 bits)
- IP options - Network testing, debugging, security, and others (0 or 32 bits, if any)
|
|
|
Best Path and Metric
Equal Cost Load Balancing
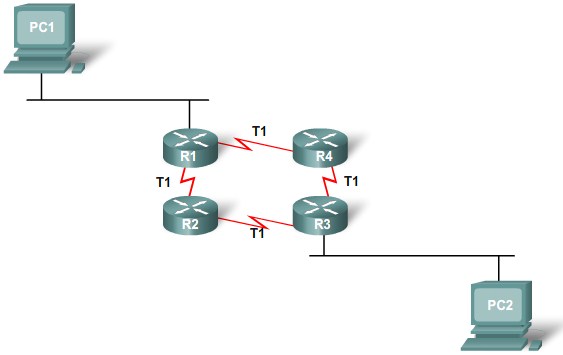 Equal Cost Load Balancing EIGRP - Unequal Cost Paths
|
Switching Function
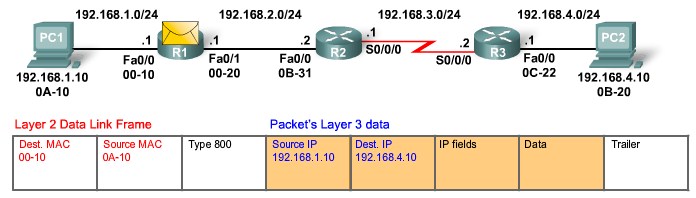 A Day in the Life of a Packet |
Summary