From Teknologisk videncenter
Basic Wireless Concepts and Configuration
The Wireless LAN
Why Use Wireless?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wireless LAN Standards
|
|
|
|
|
|
- ITU-R regulates allocation of RF bands.
- IEEE specifies how RF is modulated to carry information.
- Wi-Fi ensures that vendors make devices that are interoperable.
|
Wireless Infratructure Components
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CSMA/CA - Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Avoidance
(RTS/CTS) - CSMA/CA feature called request to send/clear to send
|
|
|
Wireless Operation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Planning the Wireless LAN
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wireless LAN Security
Threats to Wireless Security
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wireless Security Protocols
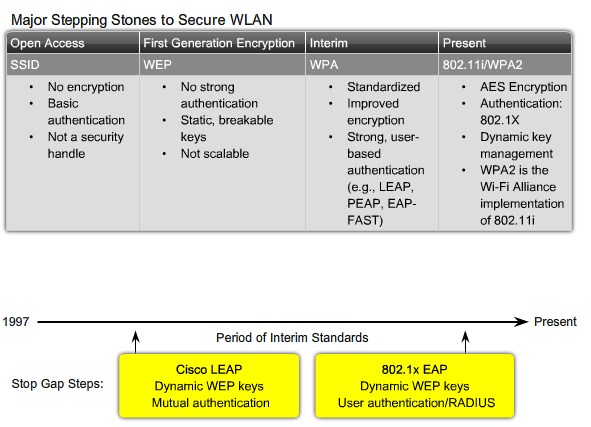 Wireless Security Protocols |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Securing a Wireless LAN
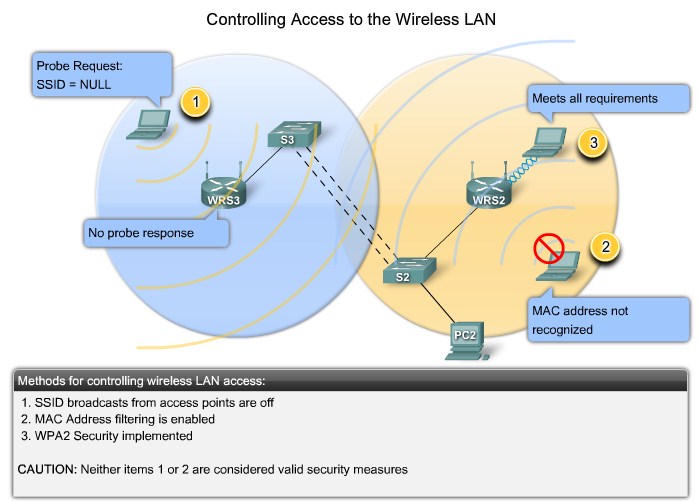 Controlling Access to the Wireless LAN |
Configuring Wireless LAN Access
Configuring the Wireless Access Point
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
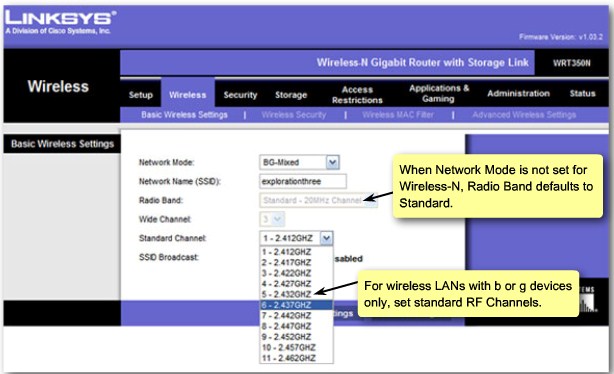 Configure standard channel |
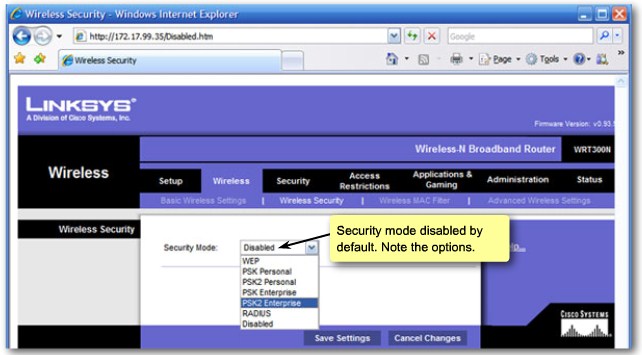 Wireless Security - Overview |
|
|
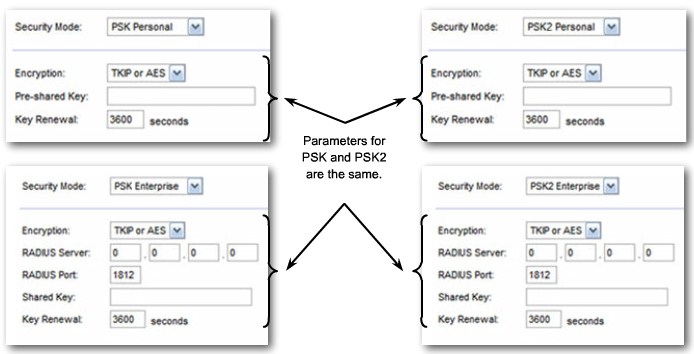 Wireless Security - Mode Parameters |
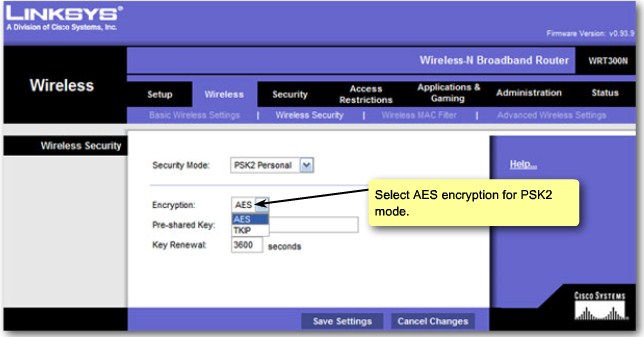 Wireless Security - Encryption |
|
|
Configuring Wireless NIC
|
|
|
|
| Configure wireless Security
|
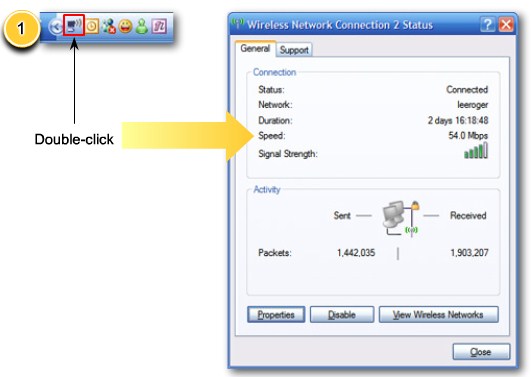 Configure wireless security step 1 |
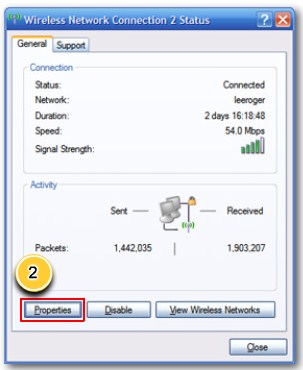 Configure wireless security step 2 |
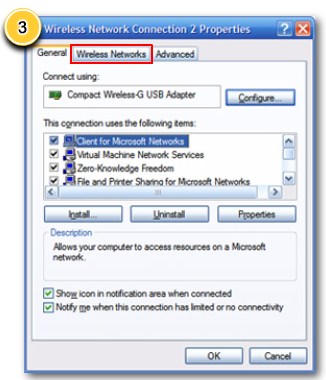 Configure wireless security step 3 |
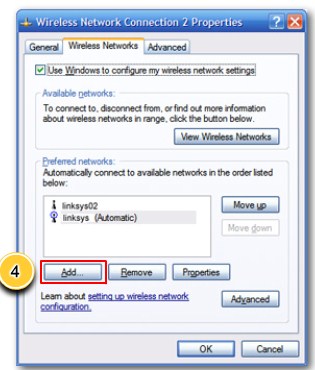 Configure wireless security step 4 |
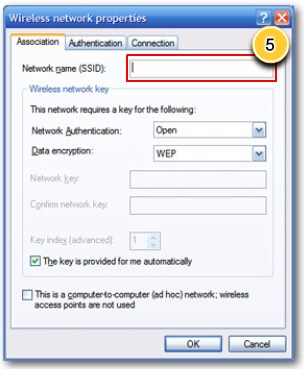 Configure wireless security step 5 |
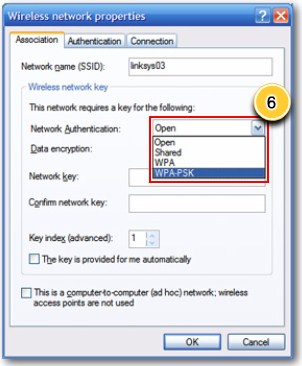 Configure wireless security step 6 |
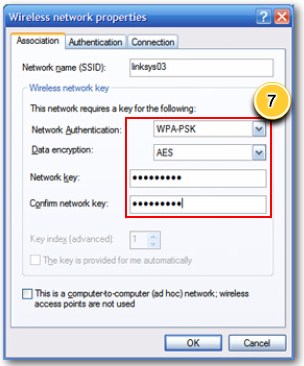 Configure wireless security step 7 |
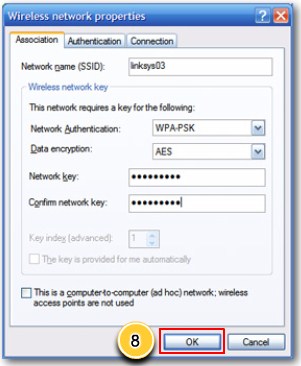 Configure wireless security step 8 |
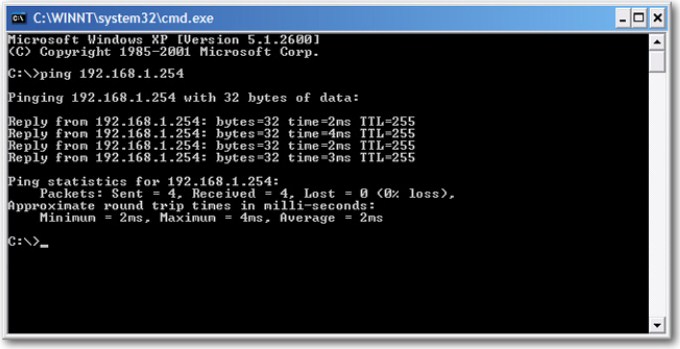 Verify Wireless connectivity |
Troubleshooting Simple WLAN Problems
Solve Access Point Radio and Firmware Issues
|
|
- Eliminate the user PC as the source of the problem.
- Confirm the network configuration on the PC using the ipconfig command. Verify that the PC has received an IP address via DHCP or is configured with a static IP address.
- Confirm that the device can connect to the wired network. Connect the device to the wired LAN and ping a known IP address.
- It may be necessary to try a different wireless NIC. If necessary, reload drivers and firmware as appropriate for the client device.
- If the wireless NIC of the client is working, check the security mode and encryption settings on the client. If the security settings do not match, the client cannot get access to the WLAN.
- How far is the PC from an access point? Is the PC out of the planned coverage area (BSA).
- Check the channel settings on the client. The client software should detect the appropriate channel as long as the SSID is correct.
- Check for the presence of other devices in the area that operate on the 2.4 GHz band.
- Confirm the physical status of devices.
- Are all the devices actually in place? Consider a possible physical security issue.
- Is there power to all devices, and are they powered on?
- Inspect links.
- Inspect links between cabled devices looking for bad connectors or damaged or missing cables.
- If the physical plant is in place, use the wired LAN to see if you can ping devices including the access point.
|
Solve Access Point Radio and Firmware Issues
|
|
|
|
|
|
Incorrect Channel Settings
|
|
|
|
|
|
Solve Access Point Radio and Firmeware Issues
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Problems with Authentication and Encryption
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|