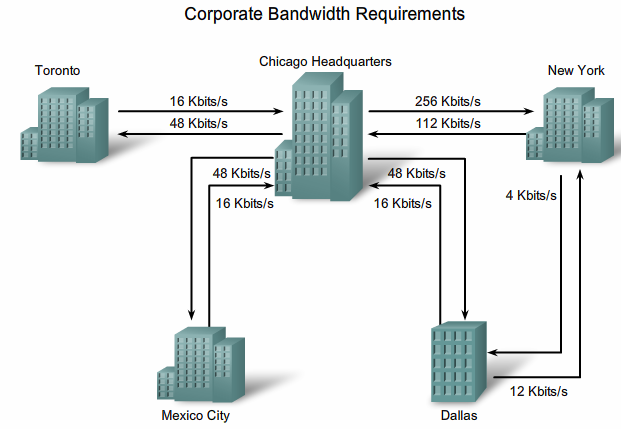
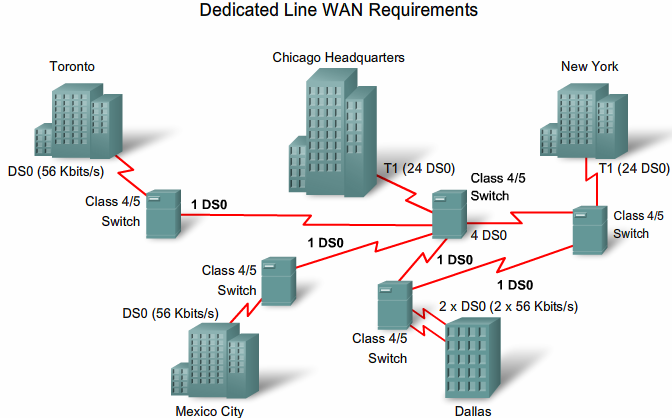
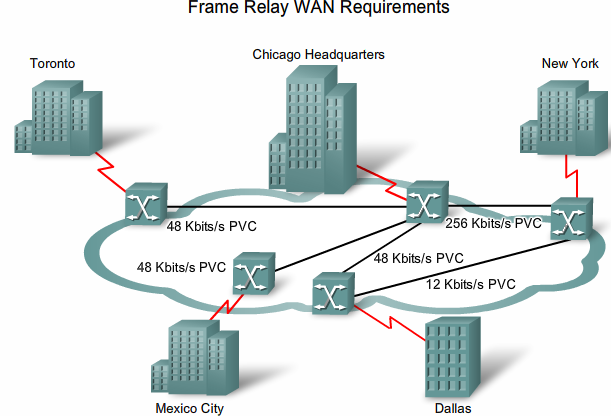
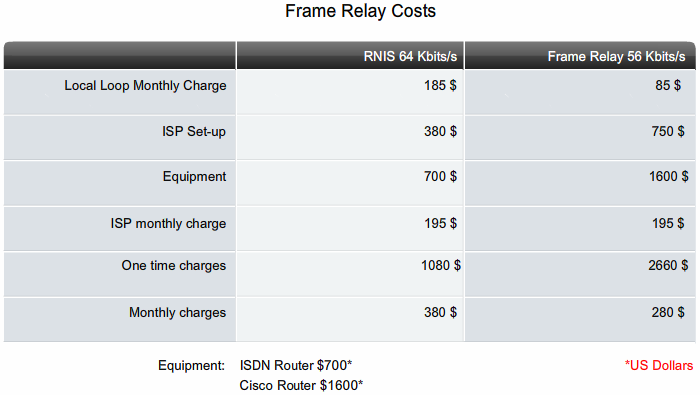
From Teknologisk videncenter
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
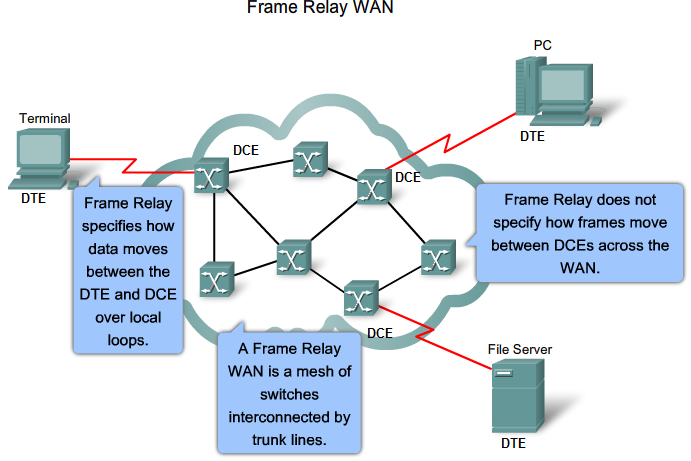
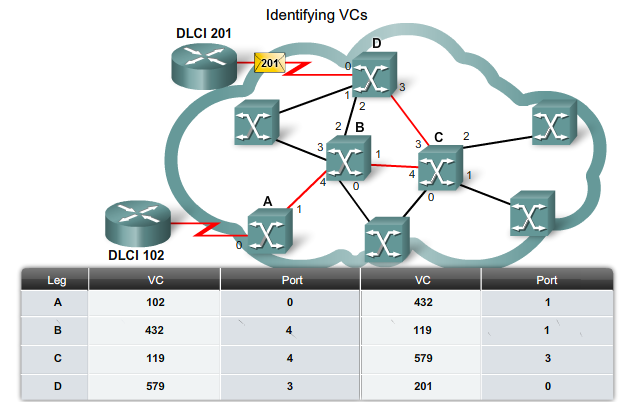
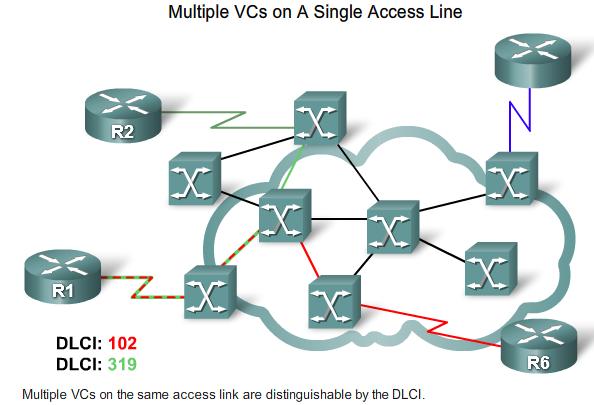
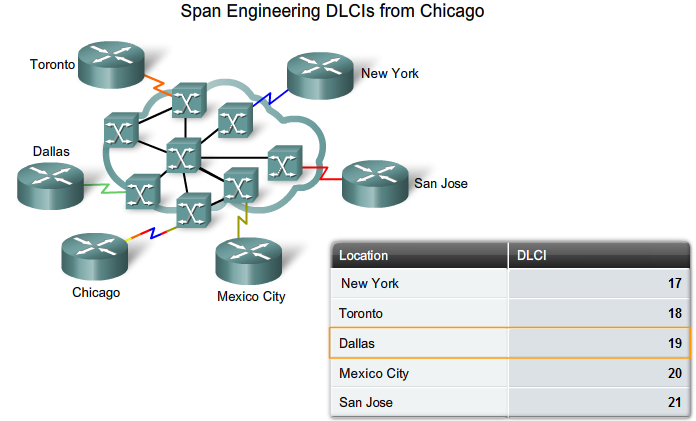
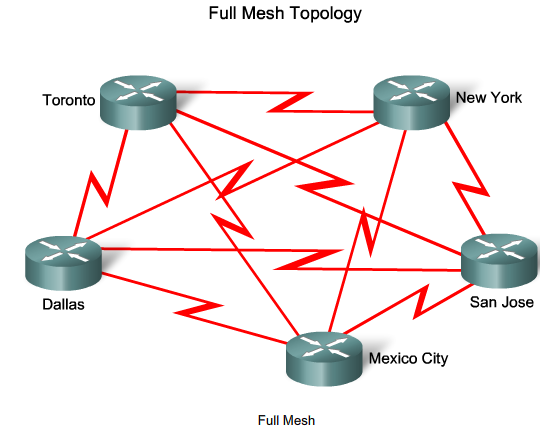
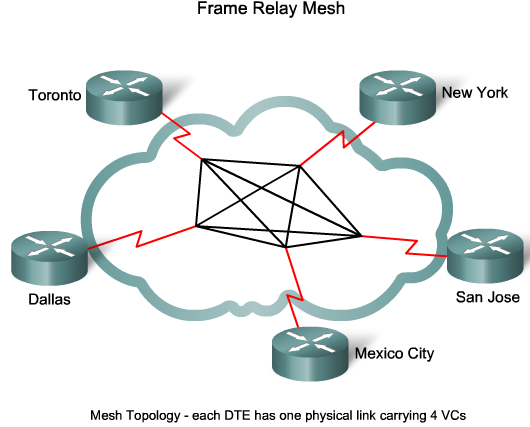
Virtual Circuits
|
|
There are two ways to establish VCs:
- SVCs, switched virtual circuits, are established dynamically by sending signaling messages to the network (CALL SETUP, DATA TRANSFER, IDLE, CALL TERMINATION).
- PVCs, permanent virtual circuits, are preconfigured by the carrier, and after they are set up, only operate in DATA TRANSFER and IDLE modes. Note that some publications refer to PVCs as private VCs.
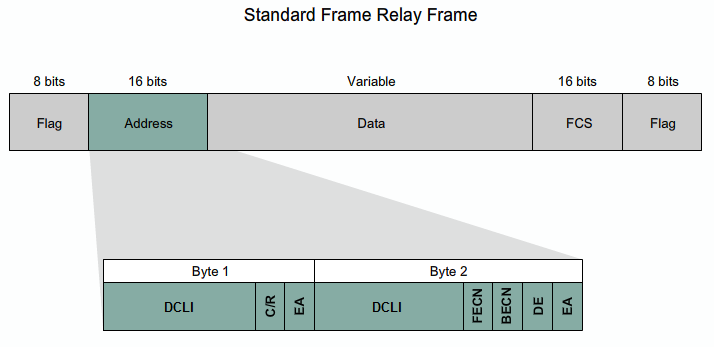
- EN VC er kendt lokalt via sin DLCI - Data Link Connection Identifier. Har kun lokal betydning.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
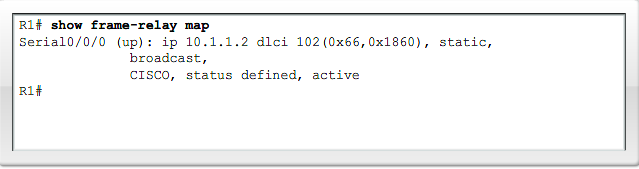
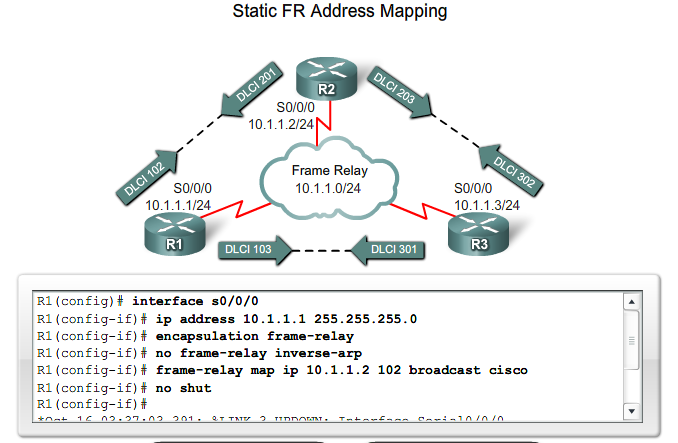
(IP) adresse til DLCI mapping
|
Statisk Adresse til DLCI mapping
|
|
|
|
|
Dynamisk Adresse til DLCI mapping
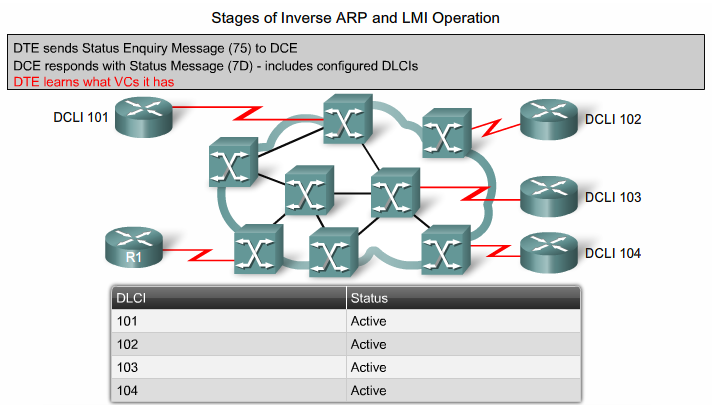
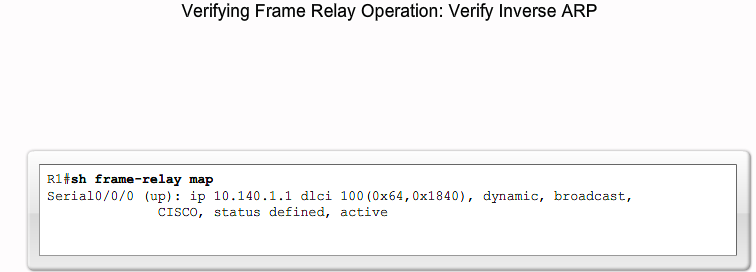
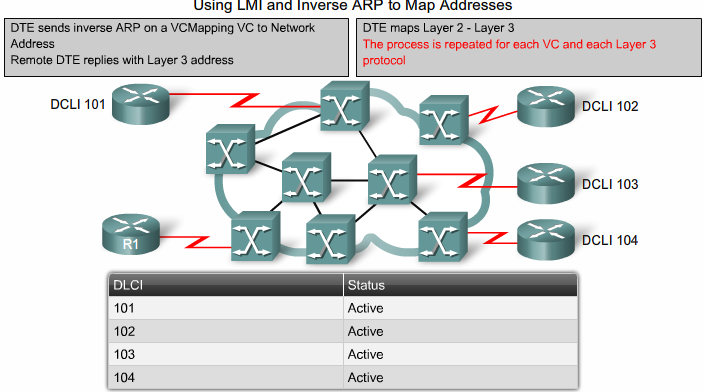
Interfacet udsender Inverse ARP request på alle kendte DLCI'er og modtager addresse retur. (IP)
- Dynamisk Mapping er default aktiveret på alle Cisco Routere. (Inverse ARP)
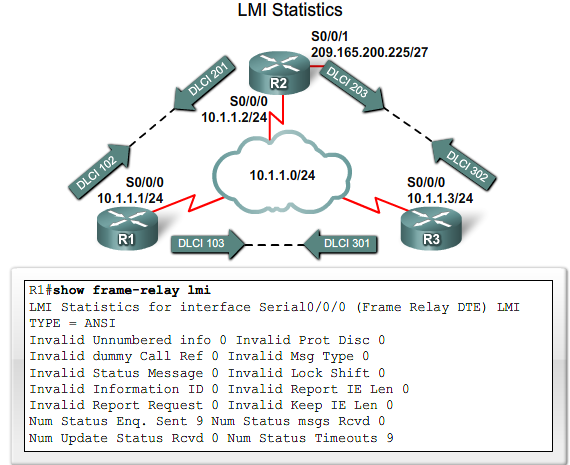
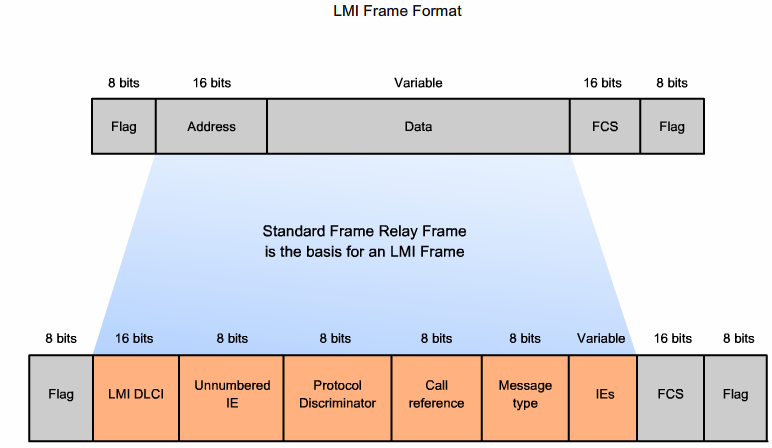
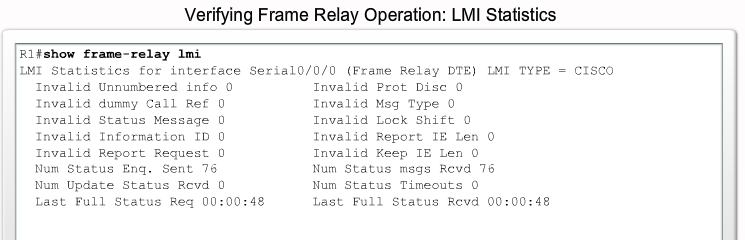
LMI - Local Management Interface
Ca. hvert 10. sekund sender DTE'en en LMI en request (Dumb eller FULL) til Frame Relay Switchen (ISP) som returner status. Switchen returnerer svar. (Hvis FULL også en liste med aktive DLCI'er)
LMI Extensions
In addition to the Frame Relay protocol functions for transferring data, the Frame Relay specification includes optional LMI extensions that are extremely useful in an internetworking environment. Some of the extensions include:
- VC status messages - Provide information about PVC integrity by communicating and synchronizing between devices, periodically reporting the existence of new PVCs and the deletion of already existing PVCs. VC status messages prevent data from being sent into black holes (PVCs that no longer exist).
- Multicasting - Allows a sender to transmit a single frame that is delivered to multiple recipients. Multicasting supports the efficient delivery of routing protocol messages and address resolution procedures that are typically sent to many destinations simultaneously.
- Global addressing - Gives connection identifiers global rather than local significance, allowing them to be used to identify a specific interface to the Frame Relay network. Global addressing makes the Frame Relay network resemble a LAN in terms of addressing, and ARPs perform exactly as they do over a LAN.
- Simple flow control - Provides for an XON/XOFF flow control mechanism that applies to the entire Frame Relay interface. It is intended for those devices whose higher layers cannot use the congestion notification bits and need some level of flow control.
|
|
|
|
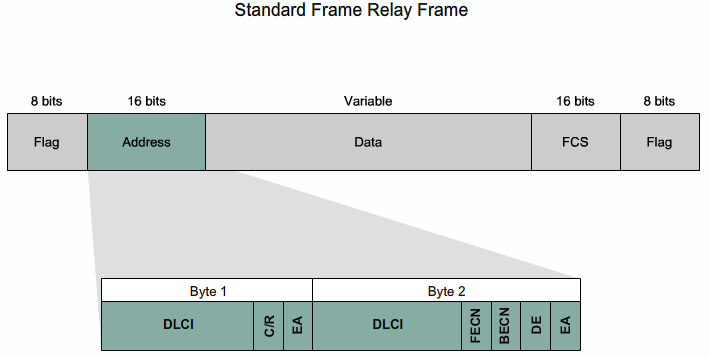
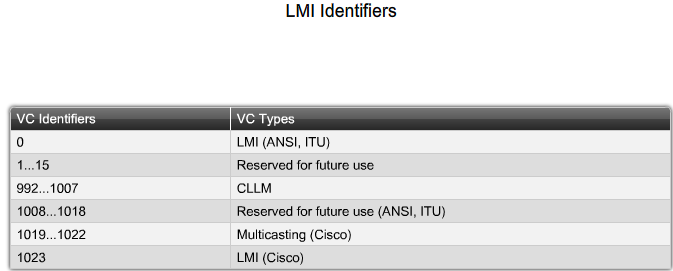
The 10-bit DLCI field supports 1,024 VC identifiers: 0 through 1023. The LMI extensions reserve some of these identifiers, thereby reducing the number of permitted VCs. LMI messages are exchanged between the DTE and DCE using these reserved DLCIs.
There are several LMI types, each of which is incompatible with the others. The LMI type configured on the router must match the type used by the service provider. Three types of LMIs are supported by Cisco routers:
- Cisco - Original LMI extension
- Ansi - Corresponding to the ANSI standard T1.617 Annex D
- q933a - Corresponding to the ITU standard Q933 Annex A
Starting with Cisco IOS software release 11.2, the default LMI autosense feature detects the LMI type supported by the directly connected Frame Relay switch. Based on the LMI status messages it receives from the Frame Relay switch, the router automatically configures its interface with the supported LMI type acknowledged by the Frame Relay switch.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
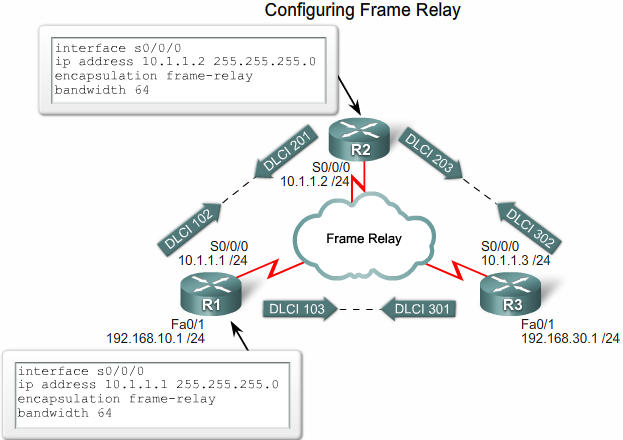
Configuring Frame Relay
|
 Configuring Frame Relay tasks |
Eksempel 1
|
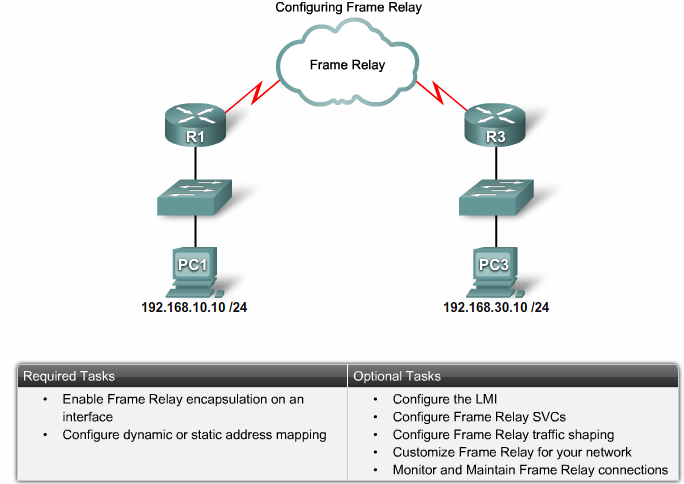 Configuring Frame Relay tasks |
|
|
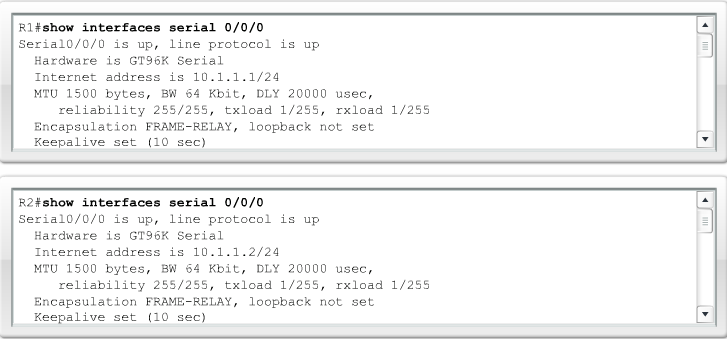 Checking Frame Relay Status |
Eksempel 2
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
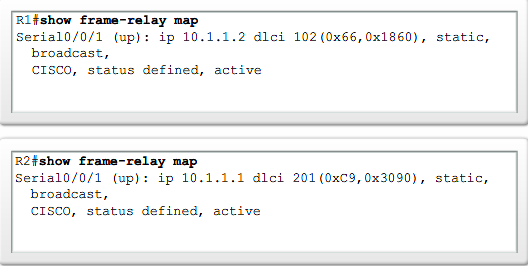 Checking Frame Relay Status |
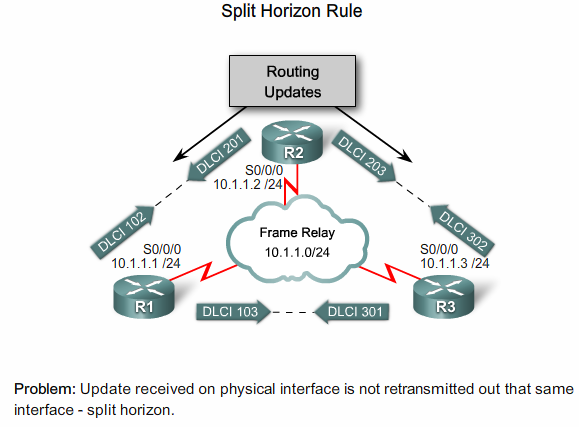
Split Horizon
Bemærk: Der er en fejl i de to tegninger nedenunder. Der står at R2 er en Spoke og R1 er en Hub. Der er vist et Full Mesh. Der skal ikke være en PVC mellem R2 og R3.
|
|
|
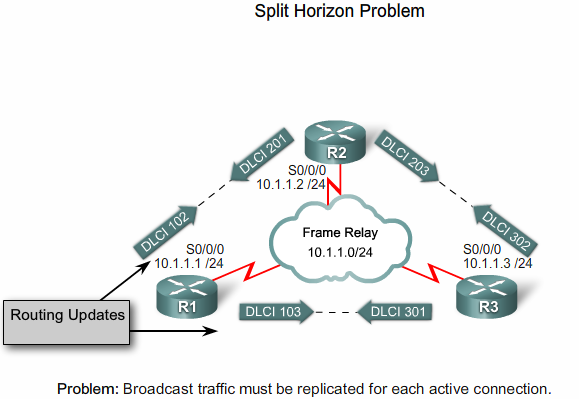 R1 må ikke sende opdatering fra R2 til R3 grundet Split Horizon reglen |
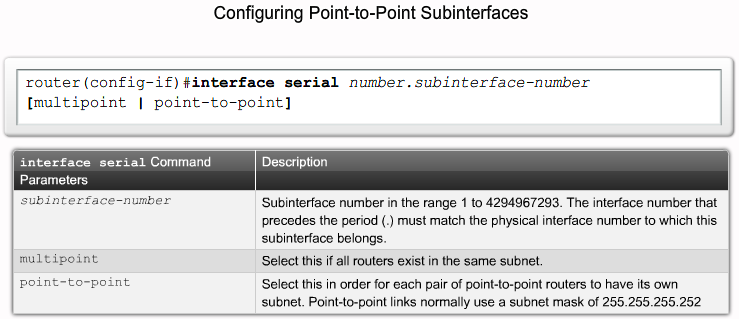
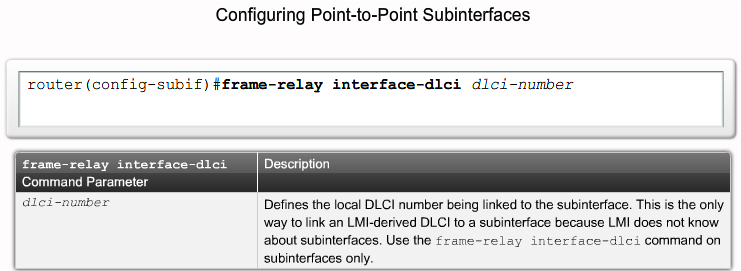
Frame Relay Subinterfaces
|
|
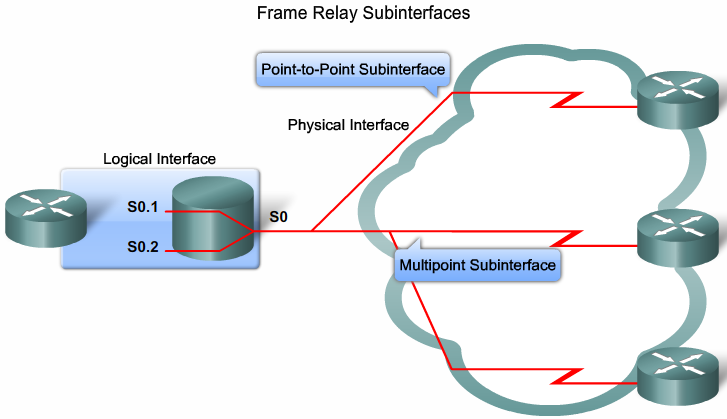 Frame Relay Subinterfaces |
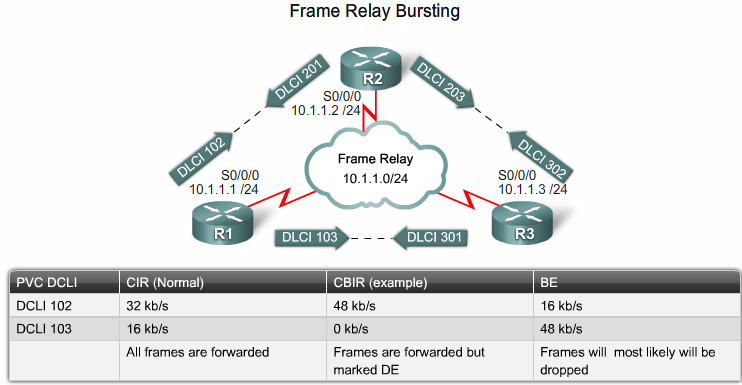
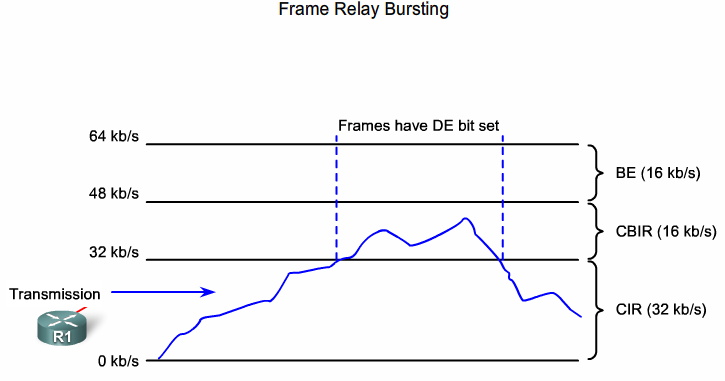
Frame Relay Bursting
- Committed Information Rate
- Committed Burst Information Rate
- Excess Burst
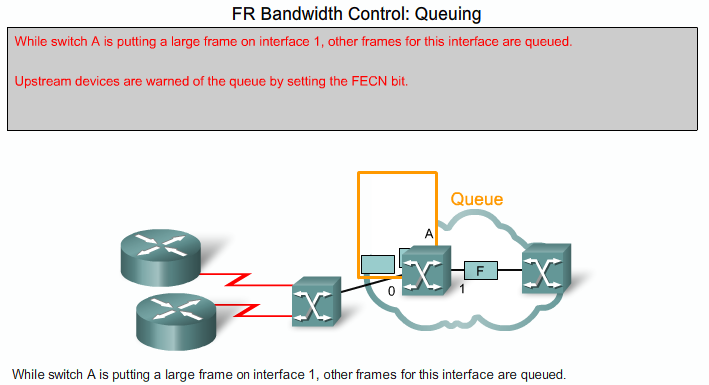
Frame Relay Flow Control
- FECN: Forward Explicit Congestion Notification
- BECN: Backward Explicit Congestion Notification
- DE: Discard Eligibility
|
|
|
|
|
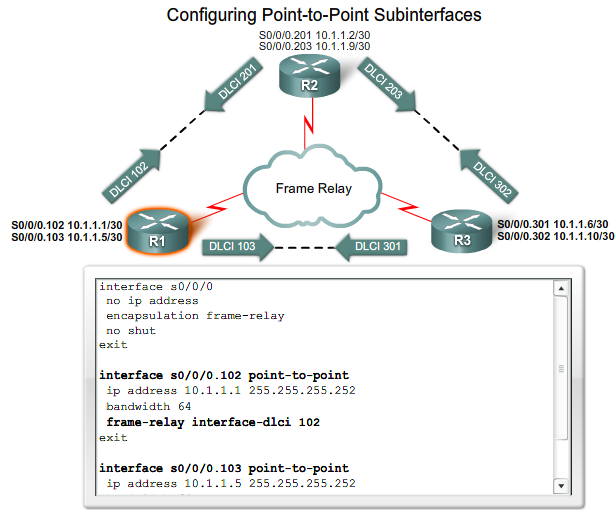
configuring Subinterfaces
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
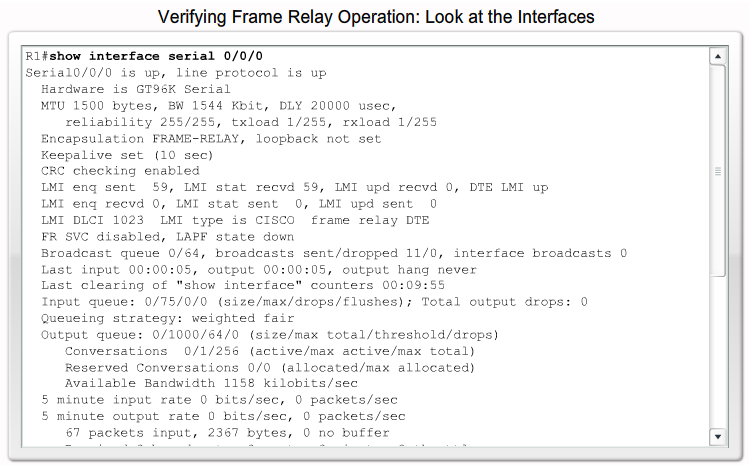
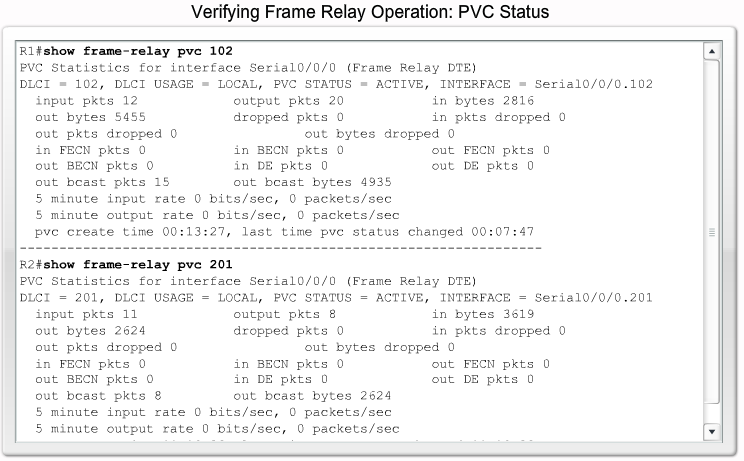
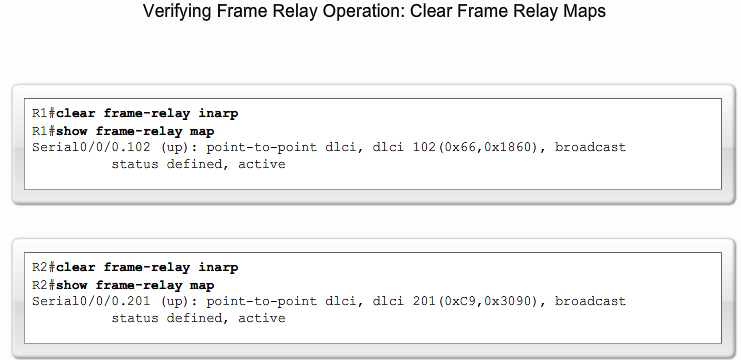
Verifying Frame Relay Operation
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
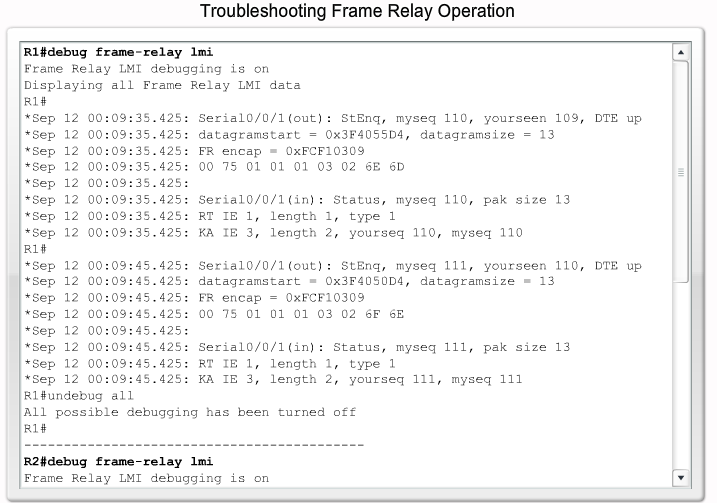
Debugging Frame relay operation
|
|
|
Overview
|
|
|