Understanding Switch Security Issues
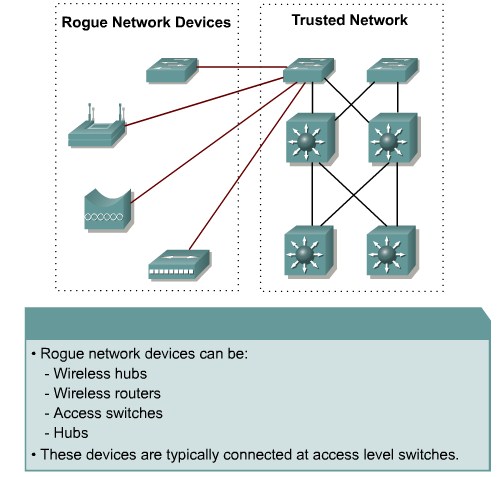
Describing Unauthorized Access by Rogue Devices
Switch Attack Categories
- MAC layer attacks
- VLAN attacks
- Spoof attacks
- Switch device attacks
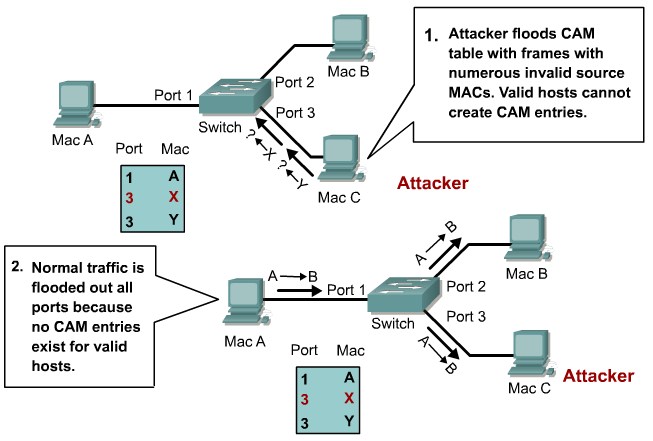
| MAC address Flooding |
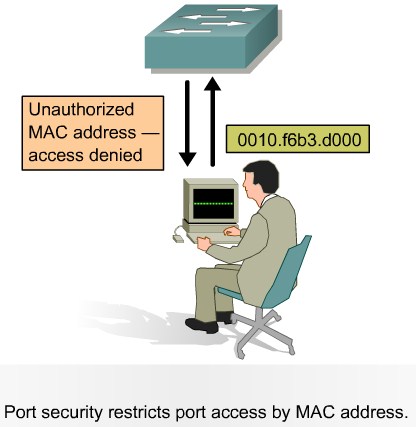
Port Security
|
| VLAN Hooping |
Tighten up trunk configurations and the nogotiation state
|
| Attacks between devices on a common VLAN |
Implement Private VLANS(PVLANs)
|
| DHCP Spoofing |
USe DHCP Snooping
|
| Spanning tree compromises |
Proactively configure the primary and backup root devices, Enable root guard
|
| MAC Spoofing |
Use DHCP Snooping. Port security.
|
| ARP Spoofing |
Use Dynamic ARP Inspection. DHCP Snooping, Port Security
|
| CDP Manipulation |
Diable CDP on al ports where it is not intentionally used.
|
| SSH & Telnet attacks |
Use SSHv2. Use Telnet with VTY ACLs
|
Describing a MAC Flooding Attack
Describing Port Security
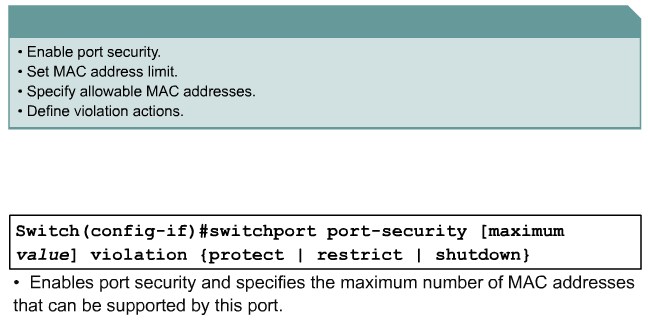
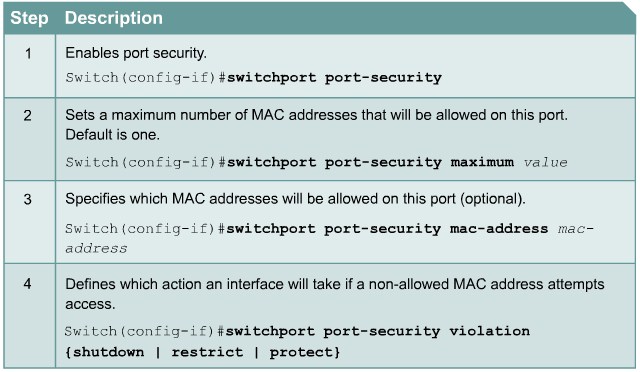
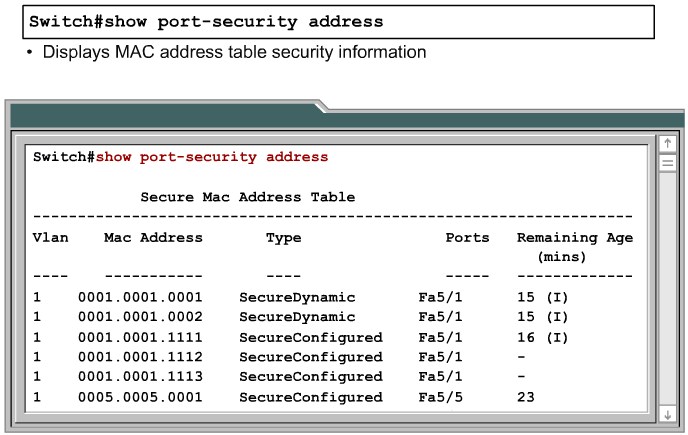
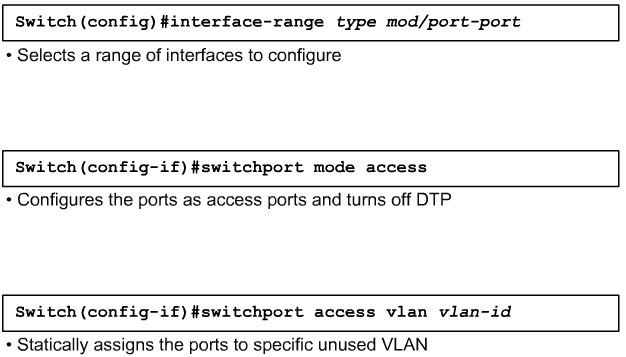
Configuring Port Security on a Switch
|
|
|
Protect: Frames from the non-allowed address are dropped, but there is no log of the violation.
Restrict: Frames from the non-allowed address are dropped, a log message is created, and a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) trap is sent.
Shut down: If any frames are seen from a non-allowed address, the interface is errdisabled, a log entry is made, an SNMP trap is sent, and manual intervention or errdisable recovery must be used to make the interface usable.
|
|
|
|
|
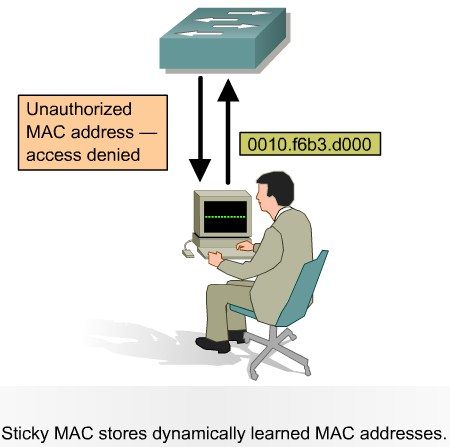
Port Security with Sticky MAC Addresses
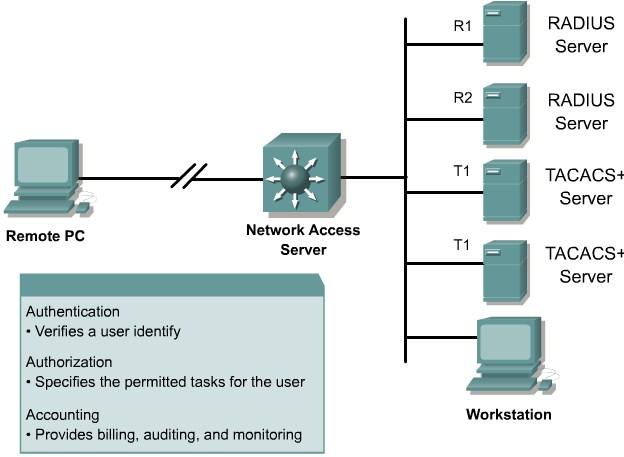
Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting
Authentication Methods
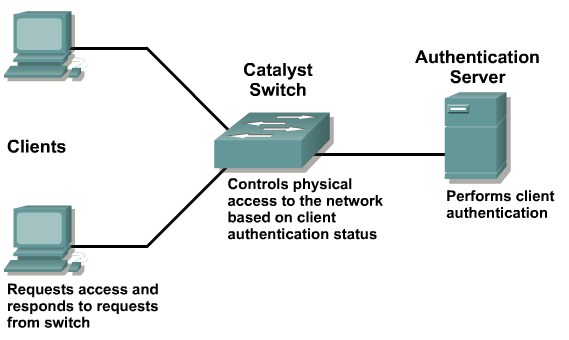
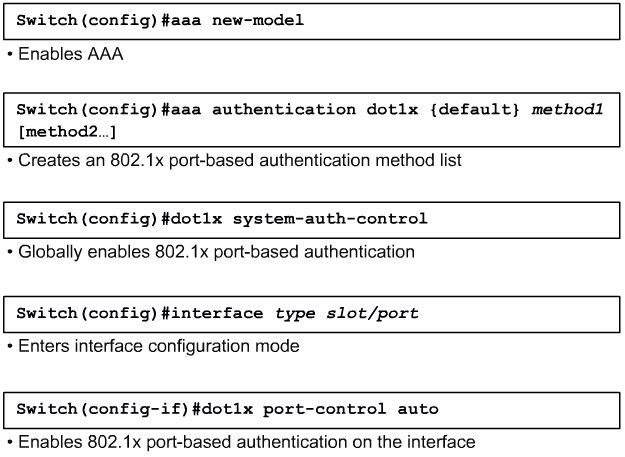
802.1x Port-Based Authentication
|
|
|
|
|
force-authorized: Disables 802.1x port-based authentication and causes the port to transition to the authorized state without any authentication exchange required. The port transmits and receives normal traffic without 802.1x-based authentication of the client. This is the default setting.
force-unauthorized: Causes the port to remain in the unauthorized state, ignoring all attempts by the client to authenticate. The switch cannot provide authentication services to the client through the interface.
auto: Enables 802.1x port-based authentication and causes the port to begin in the unauthorized state, allowing only EAPOL frames to be sent and received through the port. The authentication process begins when the link state of the port transitions from down to up (authenticator initiation) or when an EAPOL-start frame is received (supplicant initiation). The switch requests the identity of the client and begins relaying authentication messages between the client and the authentication server. The switch uniquely identifies each client attempting to access the network with the client MAC address.
|
Protecting Against VLAN Attacks
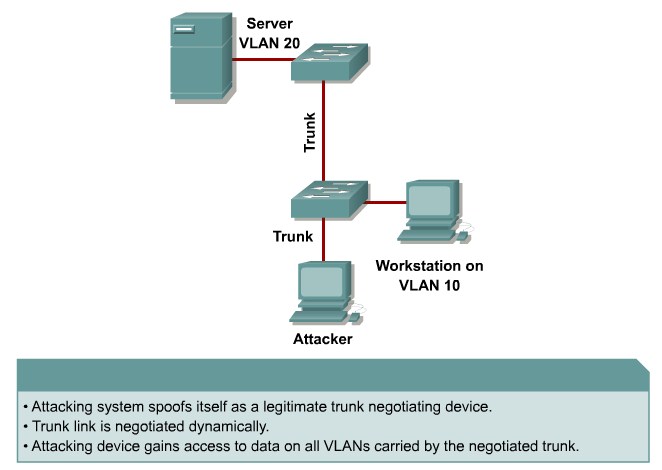
Explaining VLAN Hopping
 VLAN Hopping with Double Tagging |
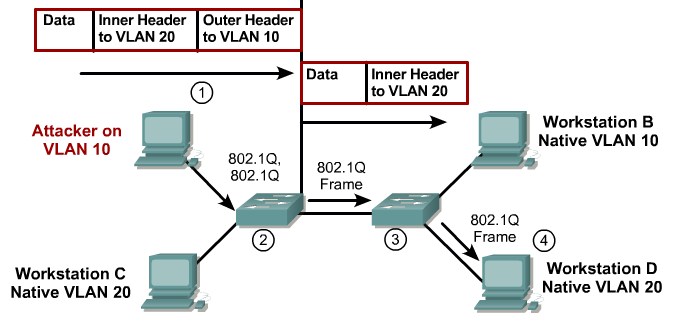 VLAN Hopping with Double Tagging |
Mitigating VLAN Hopping
VLAN Access Control Lists
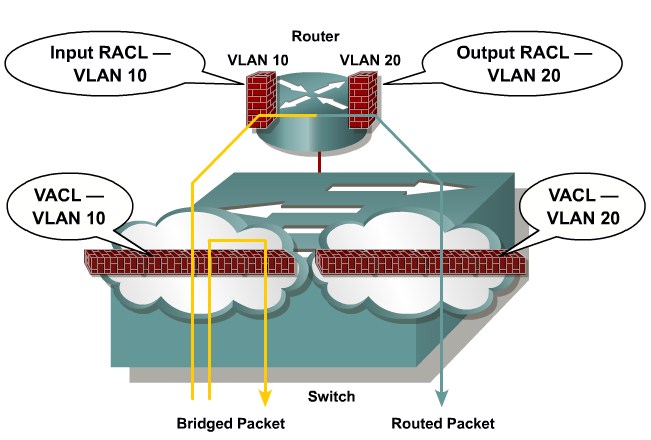 VLAN Access Control Lists |
Configuring VACLs
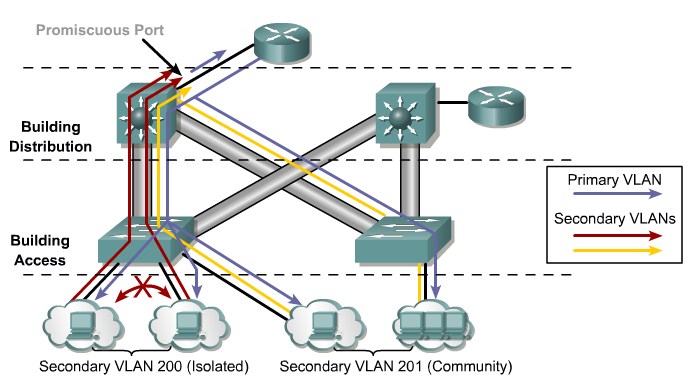
Private VLANs and Protected Ports
Protecting Against Spoof Attacks
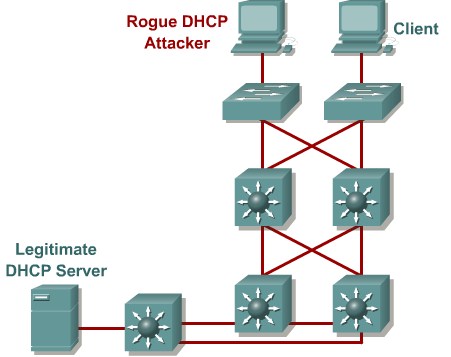
Describing a DHCP Spoof Attack
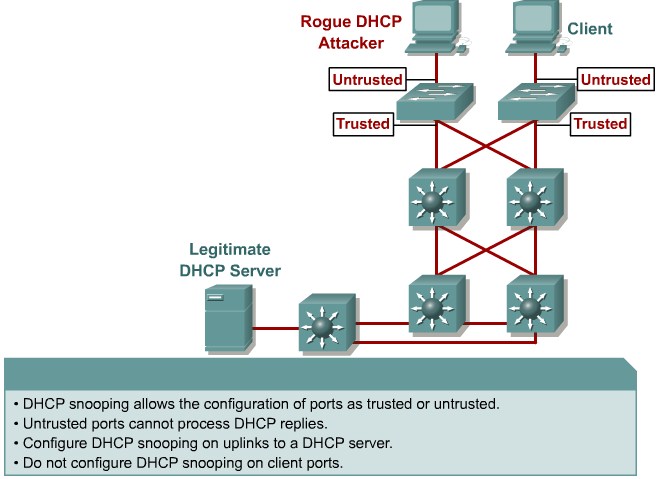
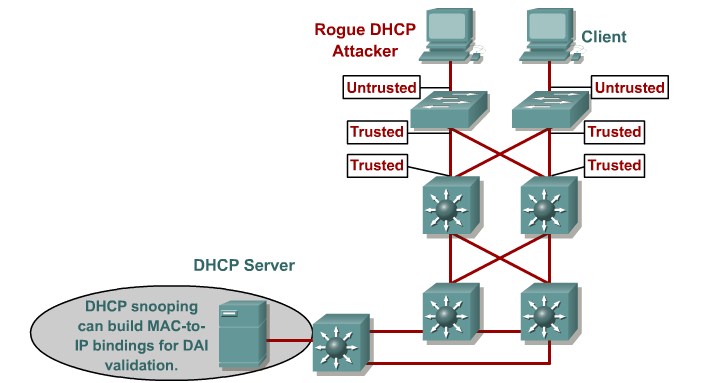
Describing DHCP Snooping
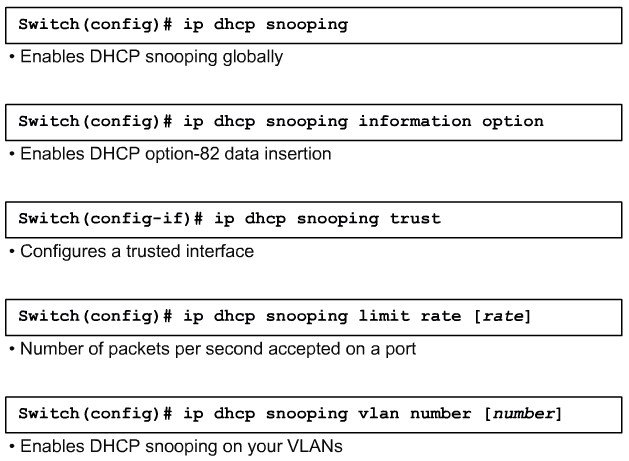
Configuring DHCP Snooping
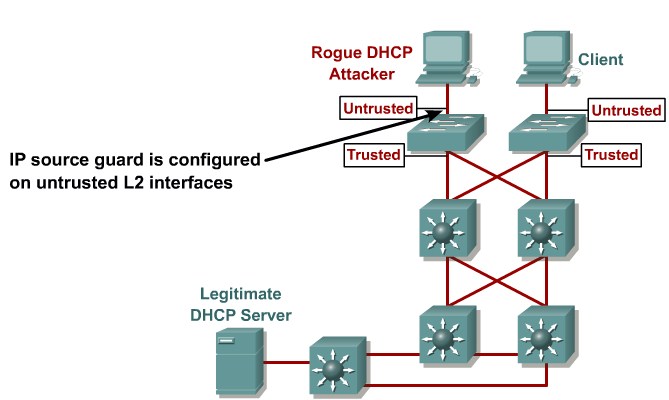
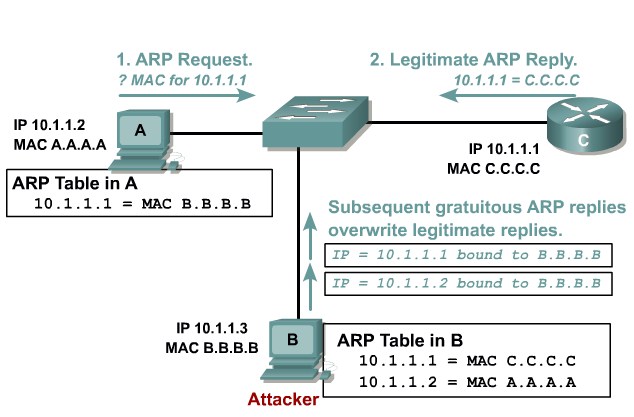
Describing ARP Spoofing
Dynamic ARP Inspection
STP Security Mechanisms
Protecting the Operation of STP
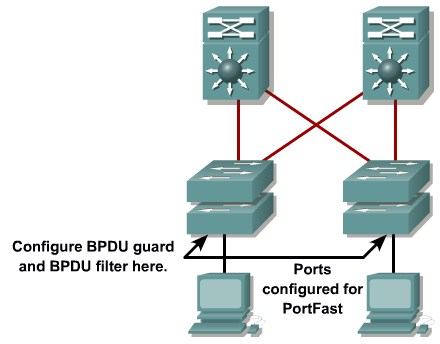
Configuring BPDU Guard
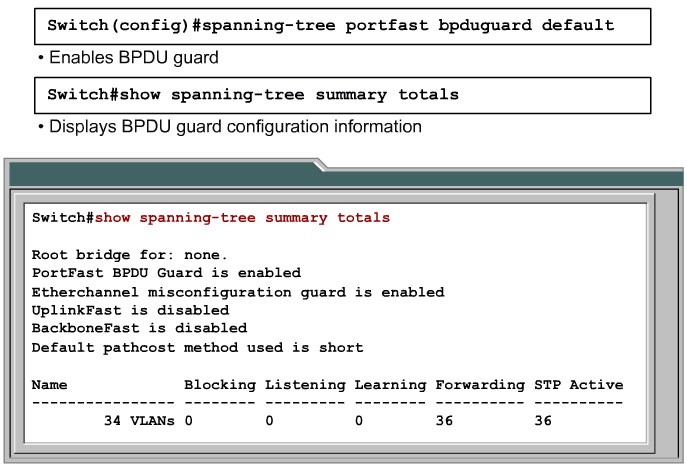 Enabling and Verifying BPDY Guard |
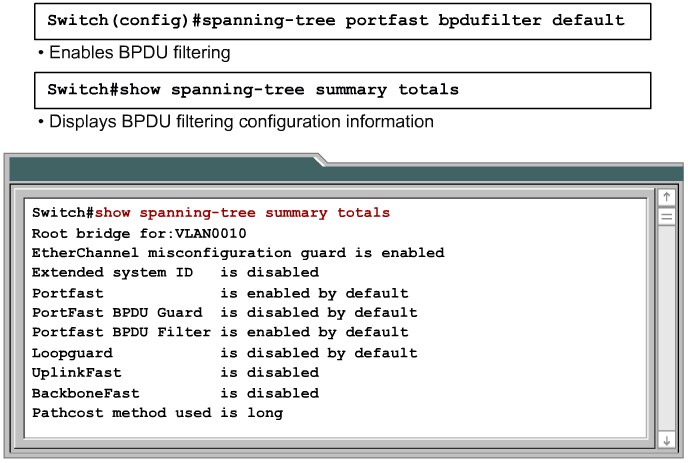
Configuring BPDU Filtering
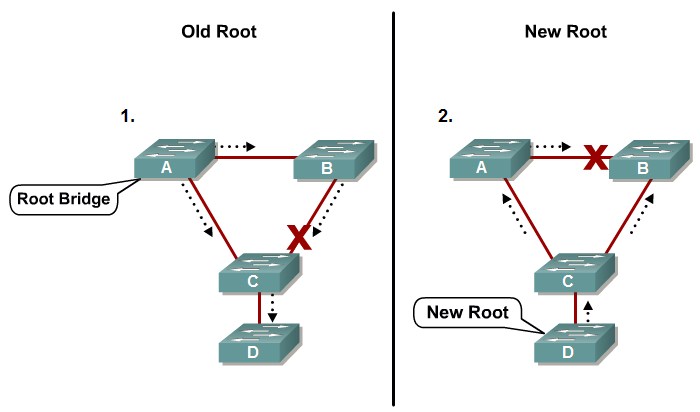
STP Root Guard
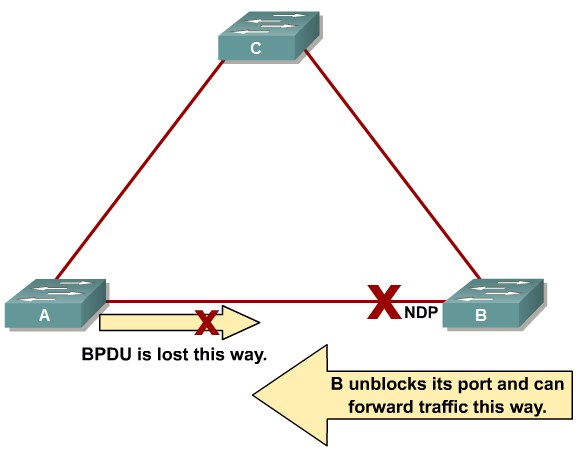
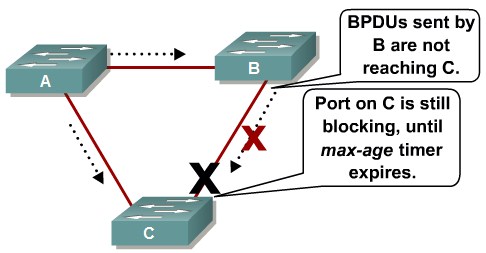
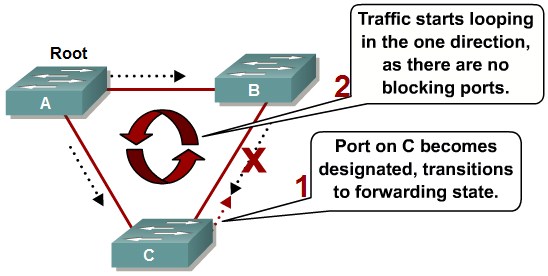
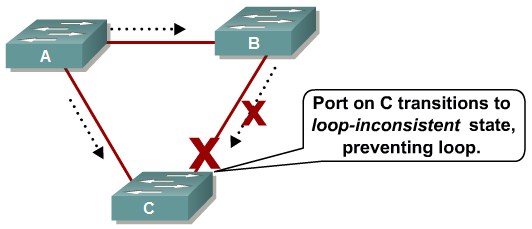
Preventing STP Forwarding Loops
Unidirectional Link Detection
Loop Guard
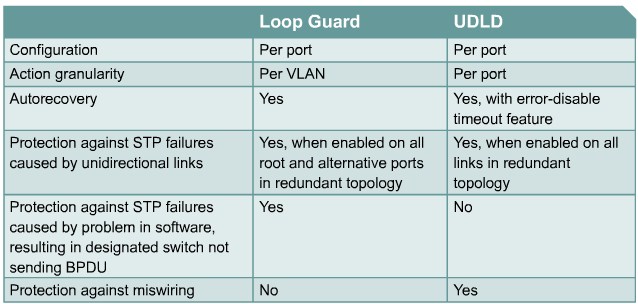
Comparing Loop Guard and UDLD
Securing Network Switches
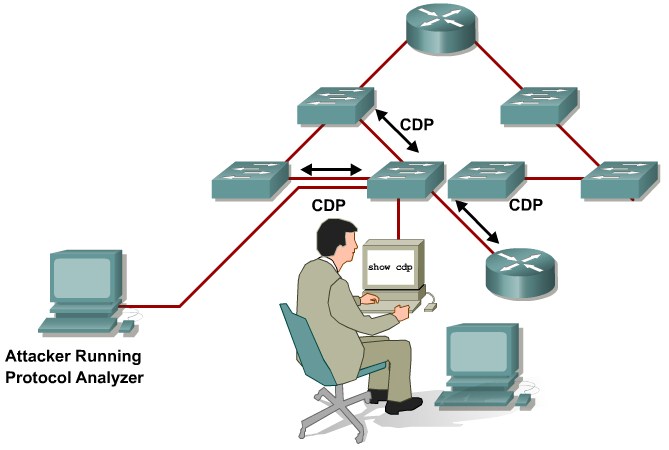
Describing Vulnerabilities in CDP
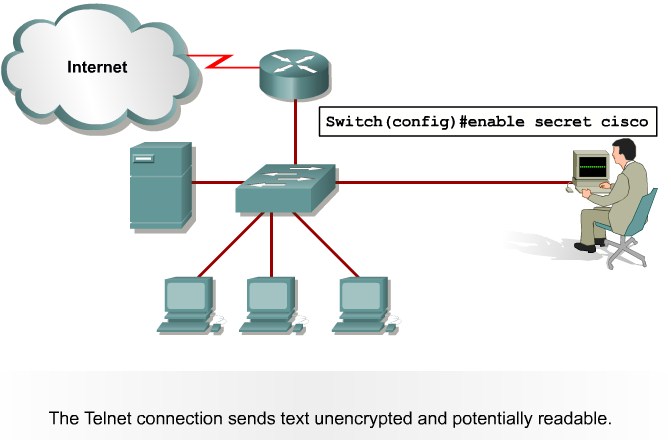
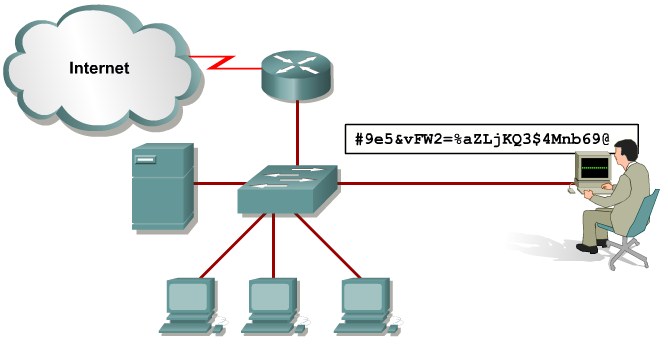
Telnet Protocol Vulnerabilities
Configuring the Secure Shell Protocol
Switch(config)# aaa new-model
Switch(config)# aaa authentication login default local
Switch(config)# username Joe password User
Switch(config)# ip domain-name sshtest.lab
Switch(config)# crypto key generate key
Switch(config)# line vty 0 15
Switch(config-line)# login local
Switch(config-line)# transport input ssh
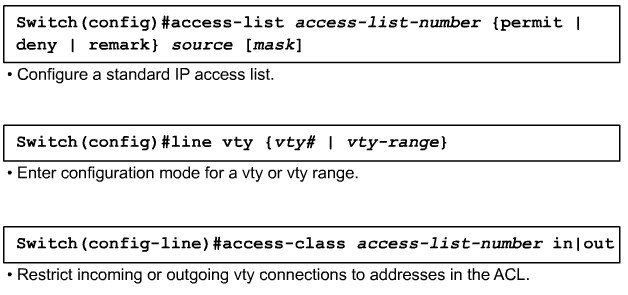
Applying ACLs to vty Lines
Best Practices for Switch Security