Difference between revisions of "CCNA Explorer 4 Network Security"
From Teknologisk videncenter
m |
m (→Hacket Checklist) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{TOCright}} | + | {{TOCright}} |
| + | =Sikkerhed= | ||
| + | ==Security Terms== | ||
| + | ;White hat:An individual who looks for vulnerabilities in systems or networks and then reports these vulnerabilities to the owners of the system so that they can be fixed. | ||
| + | ;Black hat: Another term for individuals who use their knowledge of computer systems to break into systems or networks that they are not authorized to use. | ||
| + | ;Hacker:A general term that has historically been used to describe a computer programming expert. More recently, this term is often used in a negative way to describe an individual that attempts to gain unauthorized access to network resources with malicious intent. | ||
| + | ;Cracker:A more accurate term to describe someone who tries to gain unauthorized access to network resources. | ||
| + | ;Phreaker:An individual who manipulates the phone network to cause it to perform a function that is not allowed. | ||
| + | ;Spammer:An individual who sends large quantities of unsolicited e-mail messages. | ||
| + | ;Phisher:Uses e-mail or other means to trick others into providing sensitive information. | ||
| + | ==Hacker Checklist== | ||
| + | #Performe footprint analysis also called reconnaissance | ||
| + | ##Find responsive IP addresses | ||
| + | #Enumerate information | ||
| + | ##Collect more information about servers/network and version numbers | ||
| + | #Manipulate users to gain access | ||
| + | ##Test common known usernames and passwords | ||
| + | ##Find out how the company chooses usernames and default passwords | ||
| + | #Escalete privileges | ||
| + | #Gather additional usernames, password and secrets | ||
| + | #Install backdoors | ||
| + | #Levage the compomised system | ||
| + | ##Attack other systems | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Network Security Policies== | ||
| + | ISO 27002 define some guidelines for developing organizational security standards through the following 12 sections: | ||
| + | *Risk assessment | ||
| + | *Security policy | ||
| + | *Organization of information security | ||
| + | *Asset management | ||
| + | *Human resources security | ||
| + | *Physical and environmental security | ||
| + | *Communications and operations management | ||
| + | *Access control | ||
| + | *Information systems acquisition, development, and maintenance | ||
| + | *Information security incident management | ||
| + | *Business continuity management | ||
| + | *Compliance | ||
| + | See RFC 2196, Site Security Handbook | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Security Weaknesses== | ||
| + | There are three primary vulnerabilities or weaknesses: | ||
| + | *Technological weaknesses | ||
| + | **TCP/IP protocol weakness | ||
| + | ***Syn flood | ||
| + | ***Unsecure protocols | ||
| + | **OS Weakness | ||
| + | ***All operating systems have weaknesses | ||
| + | ***Is documented in CERT archives at [http://www.cert.org/ www.cert.org] | ||
| + | **Network Equipment weakness | ||
| + | ***Routing protocols | ||
| + | ***Firewall holes | ||
| + | ***Lack of authentication | ||
| + | *Configuration weaknesses | ||
| + | **Unsecure user accounts | ||
| + | **Weak password | ||
| + | **Misconfigures internet services | ||
| + | **Default configuration | ||
| + | *Security policy weaknesses | ||
| + | **Lack of written security policy | ||
| + | **Lack of authentication continuity | ||
| + | **Missing change management | ||
| + | **Missing disaster recovery plan | ||
| + | *Physical security | ||
| + | **Access Threats | ||
| + | ***Unlocked doors to equipment | ||
| + | **Temperature Control | ||
| + | **Electrical | ||
| + | ***No surge protection | ||
| + | ***Missing UPS | ||
| + | **Maintenance threats | ||
| + | ***Poor maintenance of critical components | ||
| + | ***Lack of spare parts | ||
| + | ***Poor cabling | ||
| + | ***Poor labeling | ||
| + | ==Security Threats== | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |[[Image:ScreenShot1220.jpg|800px|left|thumb|Threats to network]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *Social engineering | ||
| + | **Phishing | ||
| + | **Niagara letters | ||
| + | **Fake Helpdesk calls to users | ||
| + | *Reconnaissance | ||
| + | **Internet Queries | ||
| + | **Ping sweeps | ||
| + | **PortScans | ||
| + | **Packet sniffers | ||
| + | *Access | ||
| + | **Password Attacks | ||
| + | ***Easy passwords | ||
| + | ***Dictionary | ||
| + | ***Brute-force | ||
| + | **Trust Exploitation | ||
| + | ***JumpHosts | ||
| + | **Port redirection | ||
| + | **MITM | ||
| + | *Denial of Service | ||
| + | **DoS | ||
| + | **Ping of Death | ||
| + | **SYN Flood | ||
| + | **DDoS | ||
| + | ***Smurf Attack | ||
| + | ***Tribe flood network(TFN) | ||
| + | ***Stacheldraht | ||
| + | ***MyDoom | ||
| + | *Worms, Viruses, and Trojan Horses | ||
| + | **Worms | ||
| + | ***The enabling vulnerability | ||
| + | ***Propagation mechanism | ||
| + | ***Payload | ||
| + | **Virus | ||
| + | **Trojan Horses | ||
| + | ==Mittegation Techniques== | ||
| + | *Host mittegation | ||
| + | **Update OS | ||
| + | **Install firewall | ||
| + | **Install antivirus | ||
| + | **Shutdown unnecessary services | ||
| + | *Network Mittegation | ||
| + | **IPS | ||
| + | **IDS | ||
| + | **NAC | ||
| + | **ASA Firewalls | ||
| + | **IOS Firewalls | ||
| + | |||
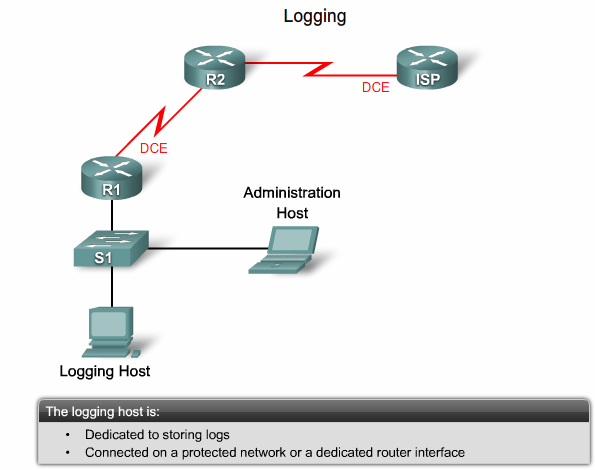
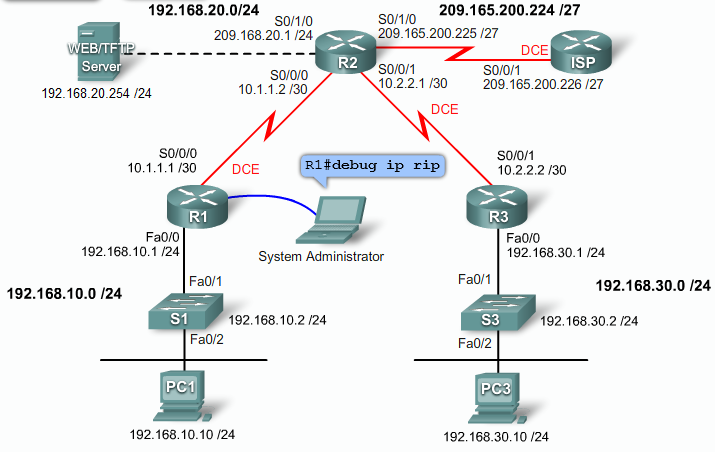
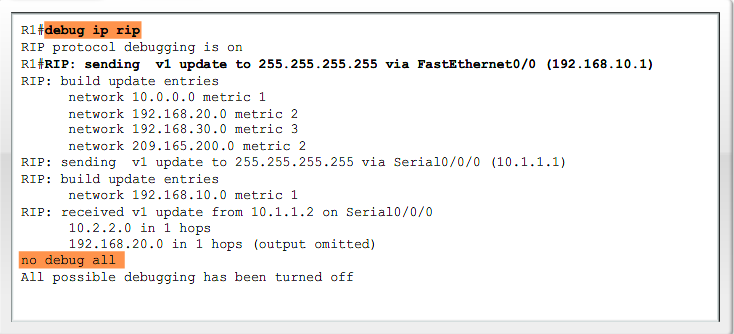
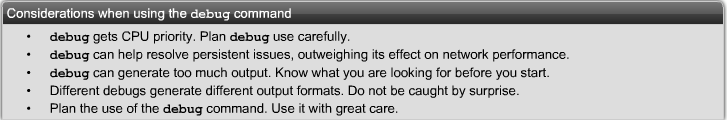
== Logging == | == Logging == | ||
{| | {| | ||
|[[Image:Exp4sec1.png|800px|left|thumb|]] | |[[Image:Exp4sec1.png|800px|left|thumb|]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
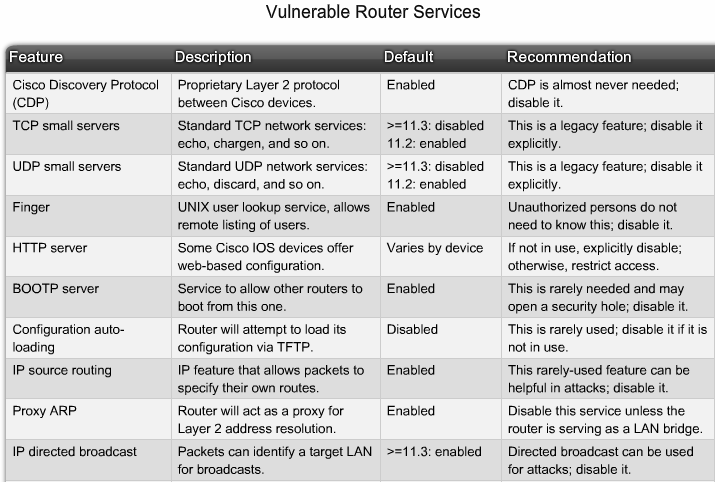
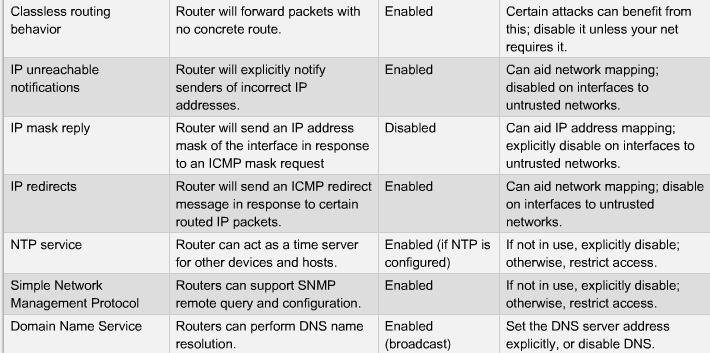
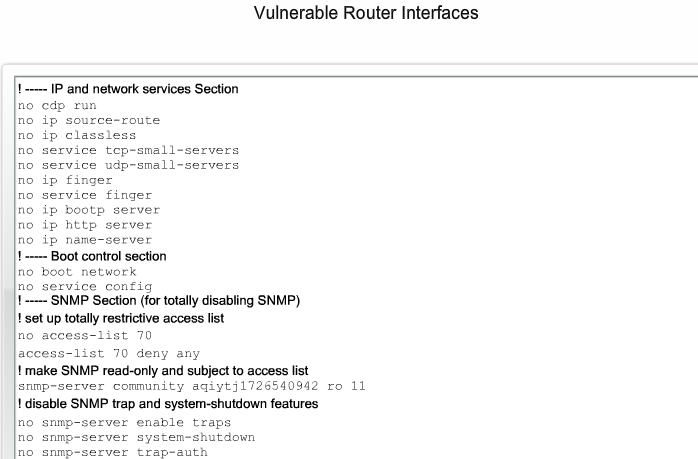
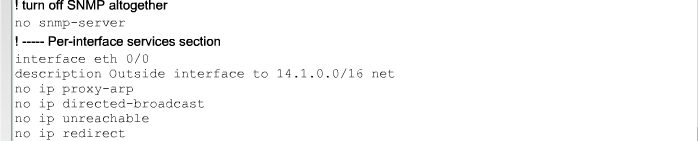
== Sårbare Router Services == | == Sårbare Router Services == | ||
{| | {| | ||
Latest revision as of 13:59, 25 January 2012
Contents
- 1 Sikkerhed
- 1.1 Security Terms
- 1.2 Hacker Checklist
- 1.3 Network Security Policies
- 1.4 Security Weaknesses
- 1.5 Security Threats
- 1.6 Mittegation Techniques
- 1.7 Logging
- 1.8 Sårbare Router Services
- 1.9 Sårbare Router interfaces
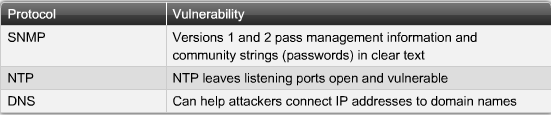
- 1.10 SNMP, NTP og DNS sårbarheder
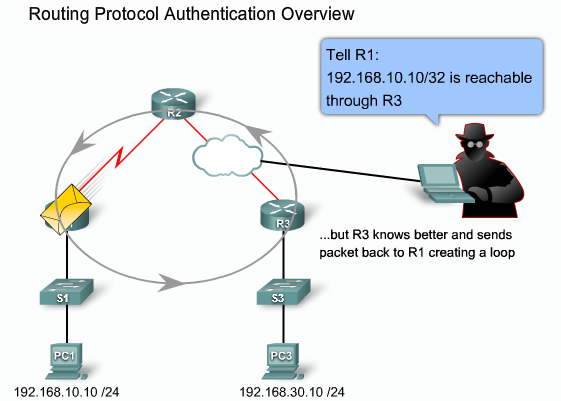
- 1.11 Routenings protokoller sårbarheder
- 1.12 Cisco Auto secure
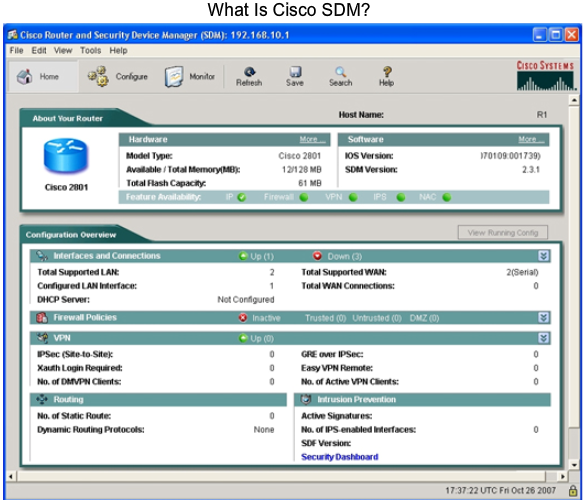
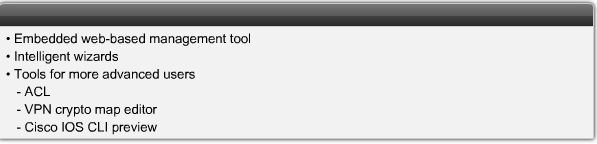
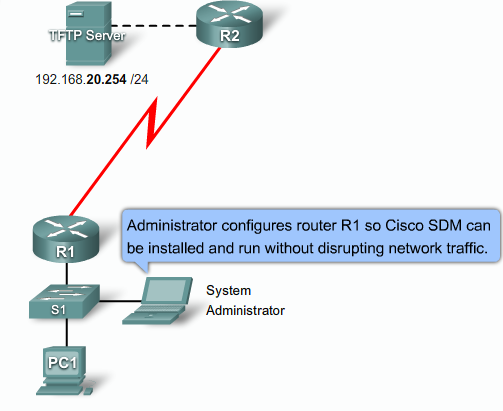
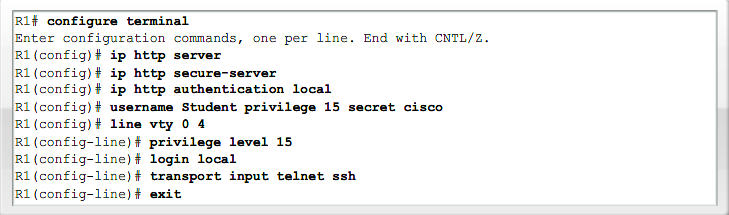
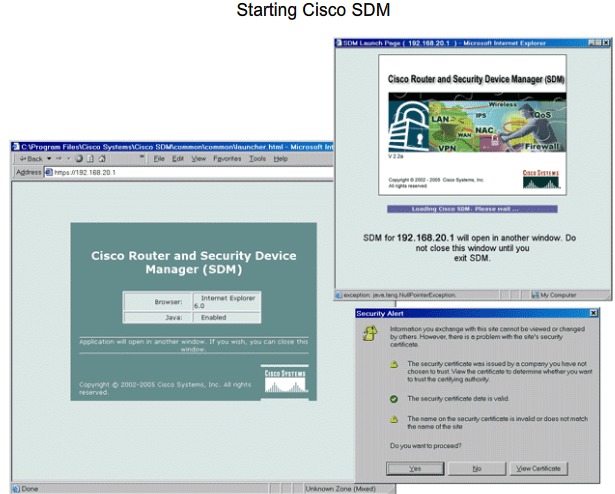
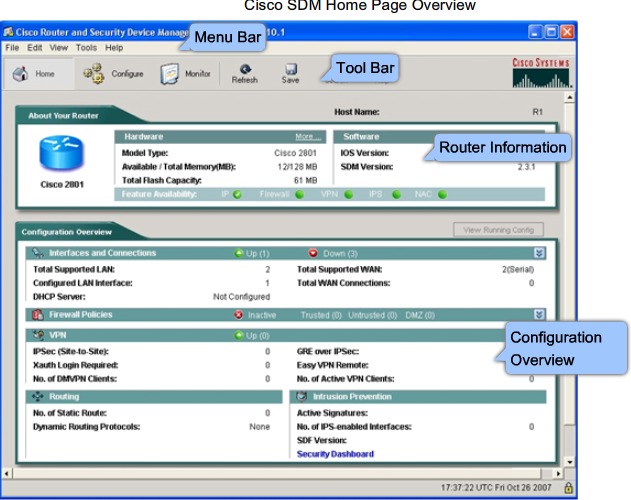
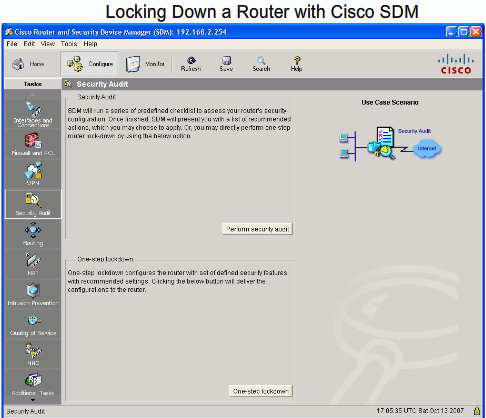
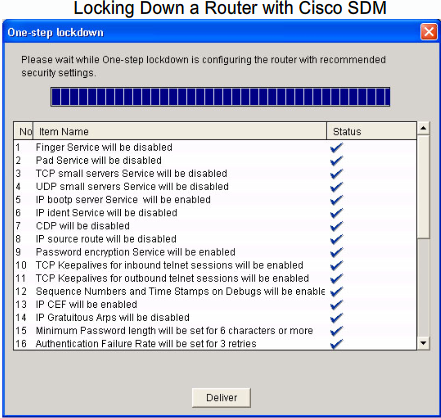
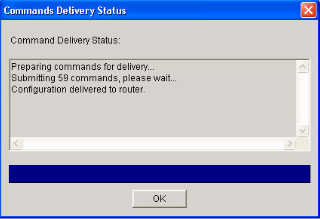
- 1.13 Cisco SDM (Secure Device Manager)
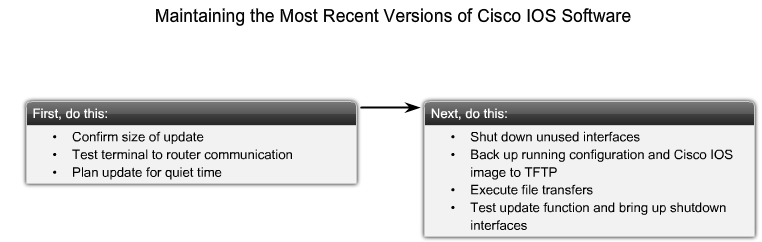
- 1.14 Installer nyeste version af IOS
- 1.15 IOS Filsystemer
- 1.16 Cisco IOS Trouble shooting commands
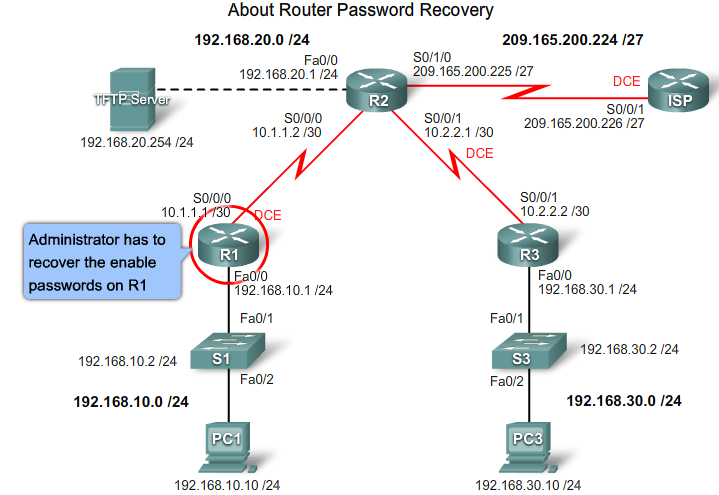
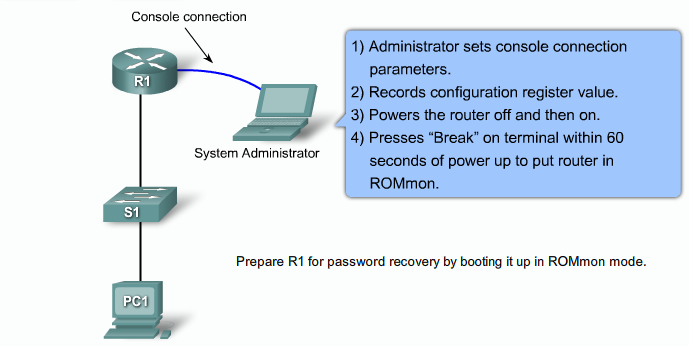
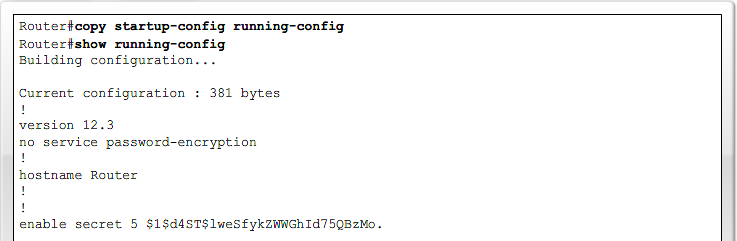
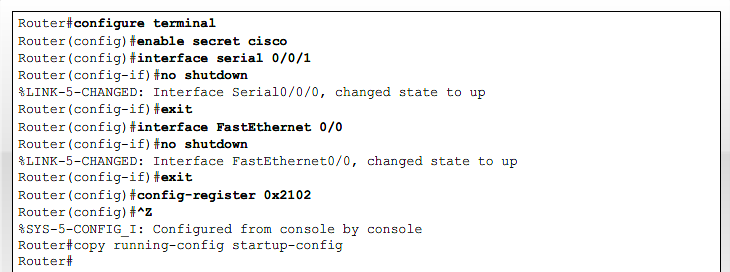
- 1.17 Recovering lost Router password
- 1.18 Opsummering
Sikkerhed
Security Terms
- White hat
- An individual who looks for vulnerabilities in systems or networks and then reports these vulnerabilities to the owners of the system so that they can be fixed.
- Black hat
- Another term for individuals who use their knowledge of computer systems to break into systems or networks that they are not authorized to use.
- Hacker
- A general term that has historically been used to describe a computer programming expert. More recently, this term is often used in a negative way to describe an individual that attempts to gain unauthorized access to network resources with malicious intent.
- Cracker
- A more accurate term to describe someone who tries to gain unauthorized access to network resources.
- Phreaker
- An individual who manipulates the phone network to cause it to perform a function that is not allowed.
- Spammer
- An individual who sends large quantities of unsolicited e-mail messages.
- Phisher
- Uses e-mail or other means to trick others into providing sensitive information.
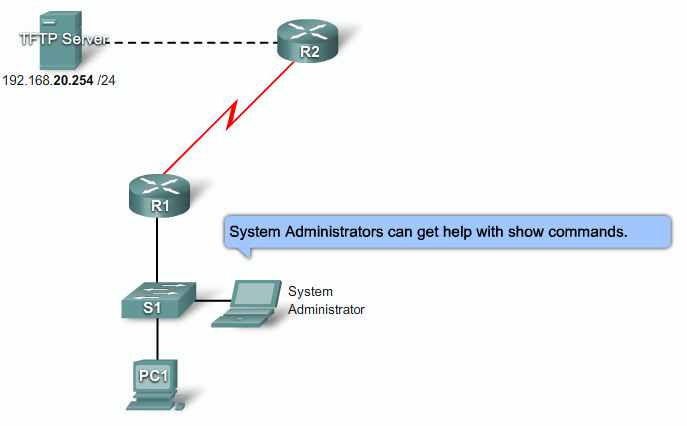
Hacker Checklist
- Performe footprint analysis also called reconnaissance
- Find responsive IP addresses
- Enumerate information
- Collect more information about servers/network and version numbers
- Manipulate users to gain access
- Test common known usernames and passwords
- Find out how the company chooses usernames and default passwords
- Escalete privileges
- Gather additional usernames, password and secrets
- Install backdoors
- Levage the compomised system
- Attack other systems
Network Security Policies
ISO 27002 define some guidelines for developing organizational security standards through the following 12 sections:
- Risk assessment
- Security policy
- Organization of information security
- Asset management
- Human resources security
- Physical and environmental security
- Communications and operations management
- Access control
- Information systems acquisition, development, and maintenance
- Information security incident management
- Business continuity management
- Compliance
See RFC 2196, Site Security Handbook
Security Weaknesses
There are three primary vulnerabilities or weaknesses:
- Technological weaknesses
- TCP/IP protocol weakness
- Syn flood
- Unsecure protocols
- OS Weakness
- All operating systems have weaknesses
- Is documented in CERT archives at www.cert.org
- Network Equipment weakness
- Routing protocols
- Firewall holes
- Lack of authentication
- TCP/IP protocol weakness
- Configuration weaknesses
- Unsecure user accounts
- Weak password
- Misconfigures internet services
- Default configuration
- Security policy weaknesses
- Lack of written security policy
- Lack of authentication continuity
- Missing change management
- Missing disaster recovery plan
- Physical security
- Access Threats
- Unlocked doors to equipment
- Temperature Control
- Electrical
- No surge protection
- Missing UPS
- Maintenance threats
- Poor maintenance of critical components
- Lack of spare parts
- Poor cabling
- Poor labeling
- Access Threats
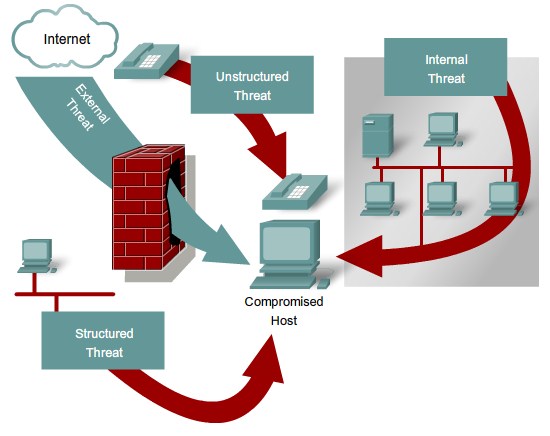
Security Threats
- Social engineering
- Phishing
- Niagara letters
- Fake Helpdesk calls to users
- Reconnaissance
- Internet Queries
- Ping sweeps
- PortScans
- Packet sniffers
- Access
- Password Attacks
- Easy passwords
- Dictionary
- Brute-force
- Trust Exploitation
- JumpHosts
- Port redirection
- MITM
- Password Attacks
- Denial of Service
- DoS
- Ping of Death
- SYN Flood
- DDoS
- Smurf Attack
- Tribe flood network(TFN)
- Stacheldraht
- MyDoom
- Worms, Viruses, and Trojan Horses
- Worms
- The enabling vulnerability
- Propagation mechanism
- Payload
- Virus
- Trojan Horses
- Worms
Mittegation Techniques
- Host mittegation
- Update OS
- Install firewall
- Install antivirus
- Shutdown unnecessary services
- Network Mittegation
- IPS
- IDS
- NAC
- ASA Firewalls
- IOS Firewalls