Difference between revisions of "CCNP 3 Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing"
From Teknologisk videncenter
m (→Explaining Multilayer Switching) |
m (→Describing Routed Ports on a Multilayer Switch) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
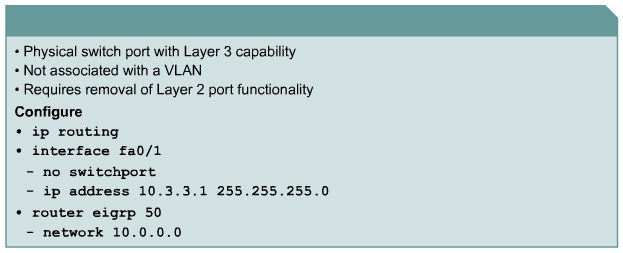
|[[Image:ScreenShot391.jpg|800px|left|thumb|Routed switchport configuration]] | |[[Image:ScreenShot391.jpg|800px|left|thumb|Routed switchport configuration]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | =Deploying CEF-Based Multilayer Switching= | ||
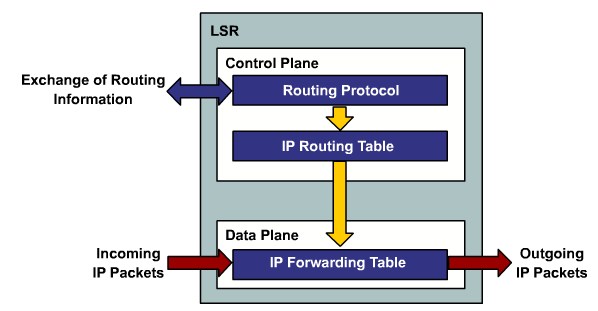
| + | ==Explaining Layer 3 Switch Processing== | ||
| + | {| | ||
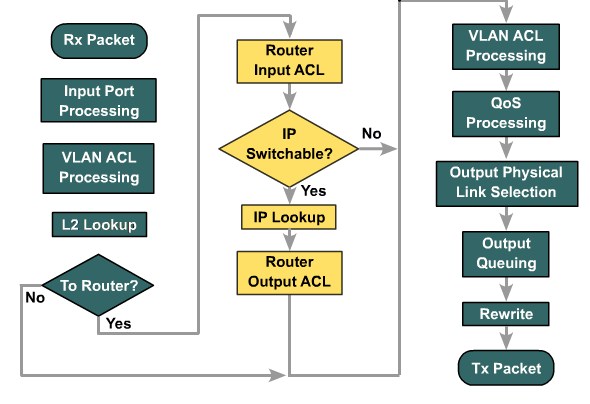
| + | |[[Image:ScreenShot392.jpg|800px|left|thumb|Switch Processing]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | There is a wide range of CEF-based Cisco multilayer switches: | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Catalyst 2970 | ||
| + | *Catalyst 3550 | ||
| + | *Catalyst 3560 | ||
| + | *Catalyst 3750 | ||
| + | *Catalyst 4500 | ||
| + | *Catalyst 4948 | ||
| + | *Catalyst 6500 | ||
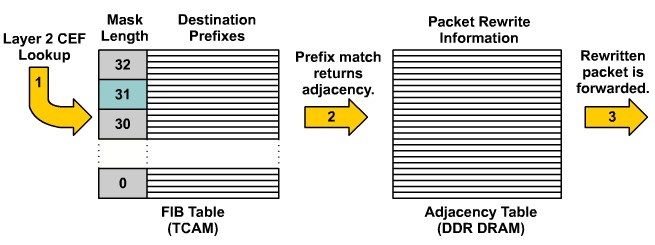
| + | ==Identifying the Multilayer Switch Packet Forwarding Process== | ||
| + | {| | ||
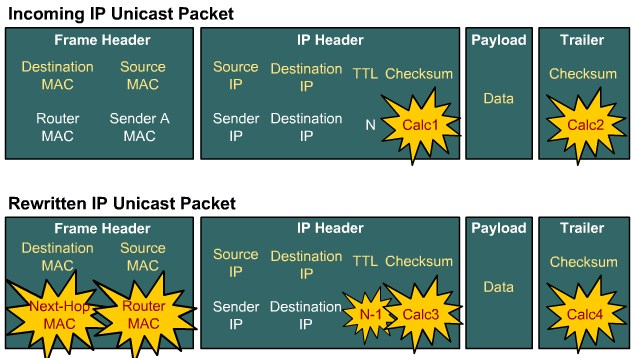
| + | |[[Image:ScreenShot394.jpg|800px|left|thumb|MLS lookup]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
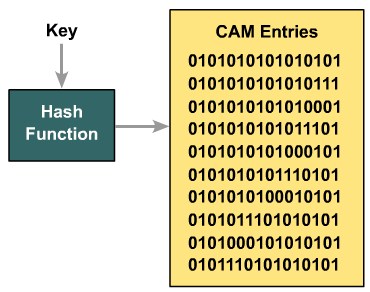
| + | |[[Image:ScreenShot395.jpg|800px|left|thumb|ARP Throttling]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
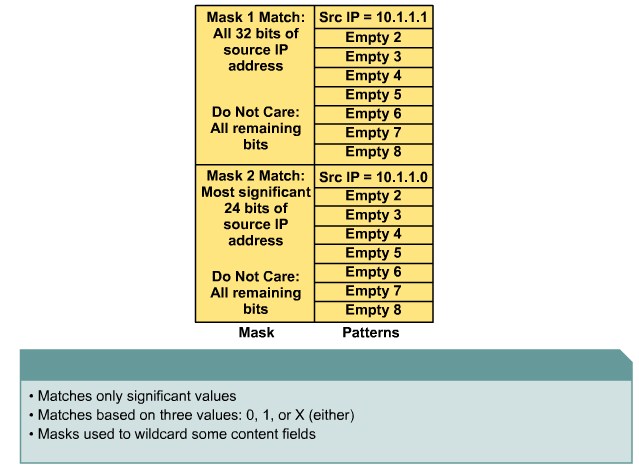
| + | |[[Image:ScreenShot396.jpg|800px|left|thumb|MPLS operation]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *'''Null adjacency:''' Packets destined for a null0 interface are dropped. This can be used as an effective form of access filtering. | ||
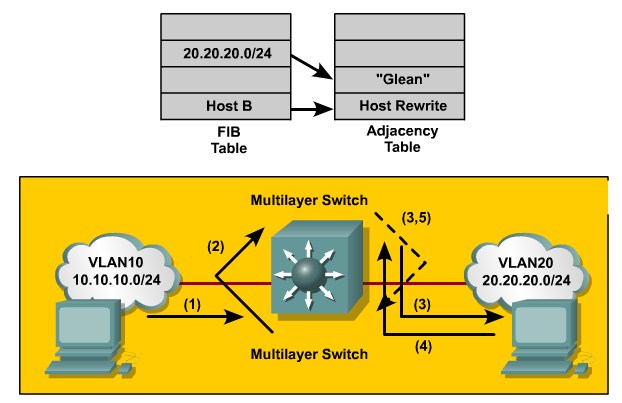
| + | *'''Glean adjacency:''' When a router is connected directly to several hosts, the FIB table on the router maintains a prefix for the subnet rather than for the individual host prefixes. The subnet prefix points to a glean adjacency. When packets need to be forwarded to a specific host, the adjacency database is gleaned for the specific prefix. | ||
| + | *'''Punt adjacency:''' Features that require special handling, or features that are not yet supported in conjunction with CEF switching paths, are forwarded to the next switching layer for handling. For example, the packet may require CPU processing. Features that are not supported are forwarded to the next-higher switching level. | ||
| + | *'''Discard adjacency:''' Packets are discarded. | ||
| + | *'''Drop adjacency:''' Packets are dropped, but the prefix is checked. | ||
Revision as of 14:51, 7 September 2010
Contents
- 1 Describing Routing Between VLANs
- 1.1 Inter-VLAN Routing Using an External Router
- 1.2 Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing Using an External Router
- 1.3 Explaining Multilayer Switching
- 1.4 Frame Rewrite
- 1.5 Describing Configuration Commands for Inter-VLAN Communication on a Multilayer Switch
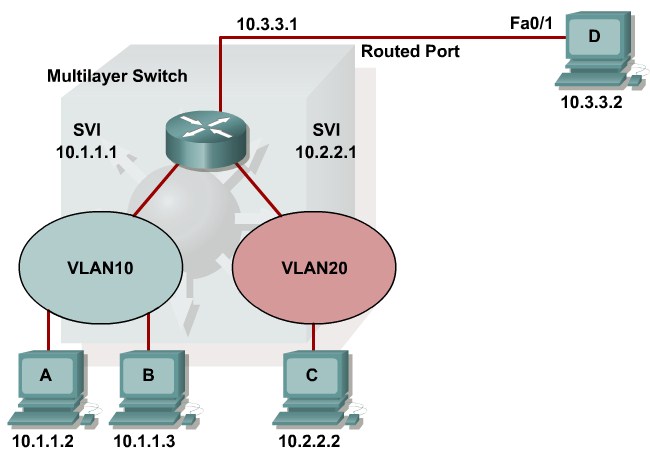
- 1.6 Describing Routed Ports on a Multilayer Switch
- 2 Deploying CEF-Based Multilayer Switching
Describing Routing Between VLANs
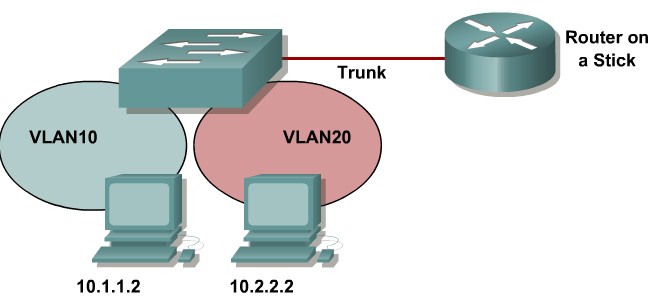
Inter-VLAN Routing Using an External Router
Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing Using an External Router
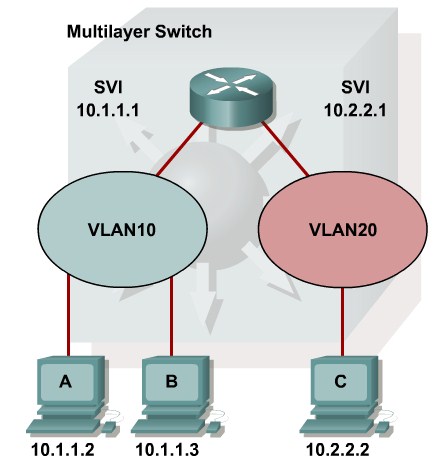
Explaining Multilayer Switching
Frame Rewrite
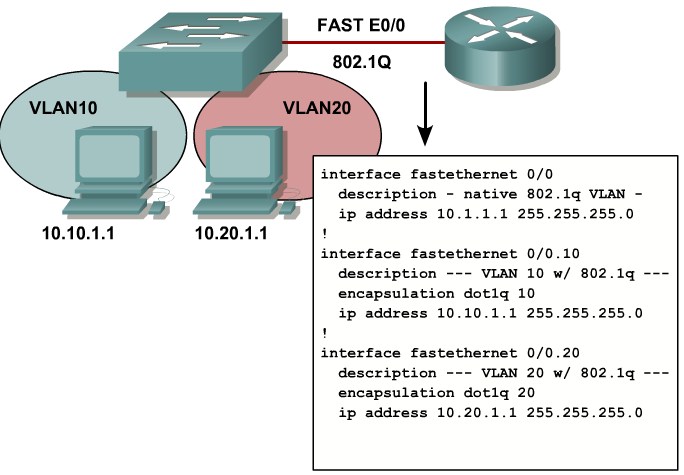
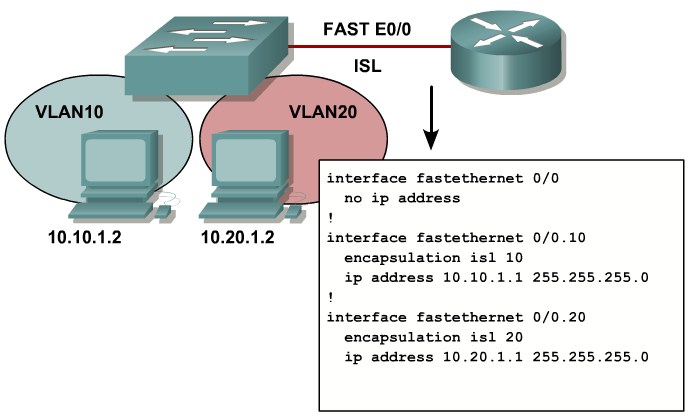
Describing Configuration Commands for Inter-VLAN Communication on a Multilayer Switch
Describing Routed Ports on a Multilayer Switch
Deploying CEF-Based Multilayer Switching
Explaining Layer 3 Switch Processing
There is a wide range of CEF-based Cisco multilayer switches:
- Catalyst 2970
- Catalyst 3550
- Catalyst 3560
- Catalyst 3750
- Catalyst 4500
- Catalyst 4948
- Catalyst 6500
Identifying the Multilayer Switch Packet Forwarding Process
- Null adjacency: Packets destined for a null0 interface are dropped. This can be used as an effective form of access filtering.
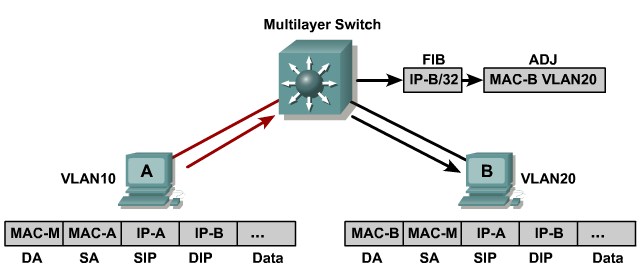
- Glean adjacency: When a router is connected directly to several hosts, the FIB table on the router maintains a prefix for the subnet rather than for the individual host prefixes. The subnet prefix points to a glean adjacency. When packets need to be forwarded to a specific host, the adjacency database is gleaned for the specific prefix.
- Punt adjacency: Features that require special handling, or features that are not yet supported in conjunction with CEF switching paths, are forwarded to the next switching layer for handling. For example, the packet may require CPU processing. Features that are not supported are forwarded to the next-higher switching level.
- Discard adjacency: Packets are discarded.
- Drop adjacency: Packets are dropped, but the prefix is checked.