Difference between revisions of "NAT Cisco IOS"
m (→Referencer) |
m (→Links) |
||
| Line 374: | Line 374: | ||
*[http://articles.techrepublic.com.com/5100-10878_11-6081743.html Learn how to use the NAT Order of Operations] | *[http://articles.techrepublic.com.com/5100-10878_11-6081743.html Learn how to use the NAT Order of Operations] | ||
*[[Media:NAT intro.pdf|NAT intro Power Point]] | *[[Media:NAT intro.pdf|NAT intro Power Point]] | ||
| − | + | =Q&A= | |
| + | Q. How many concurrent NAT sessions are supported in Cisco IOS NAT?<ref>http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/ip/network-address-translation-nat/26704-nat-faq-00.html</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | A. The NAT session limit is bounded by the amount of available DRAM in the router. Each NAT translation consumes about 312 bytes in DRAM. As a result, 10,000 translations (more than would generally be handled on a single router) consume about 3 MB. Therefore, typical routing hardware has more than enough memory to support thousands of NAT translations. | ||
=Referencer= | =Referencer= | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 3 September 2015
NAT Cisco IOS
Network Address Translantion
- For an explanation of NAT see Wikipedias Network address translation
- Cisco IOS explanation from Cisco
Order of operations
To see in which order Cisco IOS performs operations Access-list before NAT see Understand_the_order_of_operations_for_Cisco_IOS
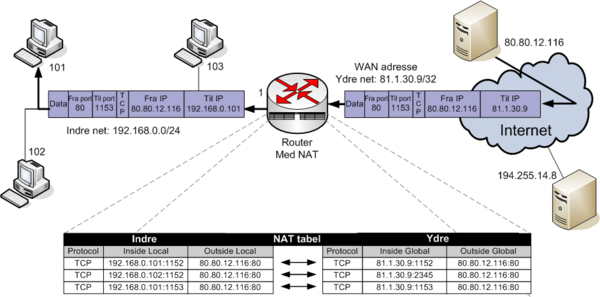
Static NAT
In static NAT The Internal IP address is always translated to the same External IP address, on a one-to-one basis.
Example of static NAT
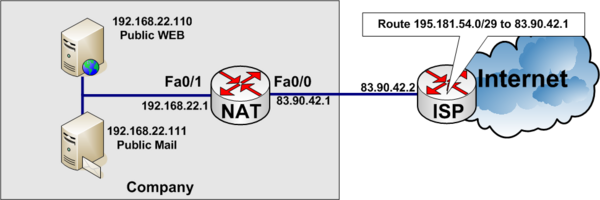
In the example below, a company has acquired an Internet connection with four additional addresses 195.181.54.0/29.
- Connection Link address to internet 83.90.42.0/30
- ISP uses 83.90.42.2/32
- Company Router 83.90.42.1/32
- The network 195.181.54.0/29 is routed to 83.90.42.1 by the ISP
- 195.181.54.1/29 is a real IP address the company wants to use to their WEB-server
- The companys WEB-server is located on the internal private network on local IP Address 192.168.22.110
- 195.181.54.2/29 is a real IP address the company wants to use to their MAIL-server
- The companys MAIL-server is located on the internal private network on local IP Address 192.168.22.111
ip nat inside source static 192.168.22.110 195.181.54.1
ip nat inside source static 192.168.22.111 195.181.54.2
!
interface fastethernet 0/0
description Connected to ISP (Outside)
ip address 83.90.42.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
interface fastethernet 0/1
description Local private LAN (Inside)
ip address 192.168.22.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat insideDynamic NAT
Dynamic NAT translates internal addresses to a random pool of outside addresses.
Dynamic NAT example
Internal addresses 192.168.1.9 to 192.168.1.14 are NAT'ed to outside 195.181.54.1 to 195.181.54.6 dynamically, not knowing which inside address are NAT'ed to which outside address.
ip nat pool DYNAMIC-IP-POOL 195.181.54.1 195.181.54.6 netmask 255.255.255.248
!
access-list 54 permit 192.168.1.8 255.255.255.248
!
ip nat inside source list 54 pool DYNAMIC-IP-POOL
!
interface FastEthernet 0/0
description Inside private network
ip address 192.168.1.1
ip nat inside
!
interface FastEthernet 0/1
description Outside Connection to internet
ip address dhcp
ip nat outsideOverloading or PAT
Overloading or PAT - Port Address Translation - is often used, when you have a private internal LAN for example 192.168.1.0/24 and connect to the Internet through your ISP that lend you a Pulic IP address, through DHCP like a small SOHO router.
Overloading example 1: Connection with fixed WAN IP Address
- Internal private network: 192.168.1.0/24
- Fixed WAN IP address: 83.90.1.30/30
interface FastEthernet0/0
description Inside. Internal LAN
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
description Outside: Internet connection to ISP
ip address 83.90.1.30 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
ip nat inside source list 38 interface FastEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 38 remark Permit traffic from RFC1918 private net
access-list 38 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
access-list 38 permit 172.16.0.0 0.15.255.255
access-list 38 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255Overloading example 2: Connection with floating WAN IP Address (DHCP)
- Internal private network: 192.168.1.0/24
- WAN Address: DHCP
interface FastEthernet0/0
description Inside. Internal LAN
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
description Outside: Internet connection to ISP
ip address dhcp
ip nat outside
!
ip nat inside source list 38 interface FastEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 38 remark Permit traffic from RFC1918 private net
access-list 38 permit 10.0.0.0 0.255.255.255
access-list 38 permit 172.16.0.0 0.15.255.255
access-list 38 permit 192.168.0.0 0.0.255.255Telneting or SSH'ing to the NAT outside interface
If you want to telnet or ssh to a routers outside interface.
interface FastEthernet 0/1
ip address 83.90.47.30 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
ip nat inside source static tcp 83.90.47.30 22 interface FastEthernet0/1 22
ip nat inside source static tcp 83.90.47.30 23 interface FastEthernet0/1 23If you have a floating IP Address on the outside interface, you can use a loopback IP address to connect to
interface loopback 0
ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.255
!
interface FastEthernet 0/1
ip address dhcp
ip nat outside
!
ip nat inside source static tcp 10.10.10.1 22 interface FastEthernet0/1 22
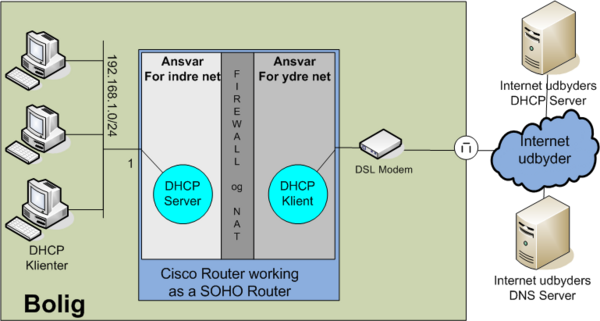
ip nat inside source static tcp 10.10.10.1 23 interface FastEthernet0/1 23Overloading example 3: Cisco Router as a SOHO Router
- Internal private network: 192.168.1.0/24 connected to fastethernet 0/0
- WAN Address: DHCP client connected to fastethernet 0/1
NAT, PAT (overloading) and DHCP configuration. Notice firewall not configured in this example.
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.100.99
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.200 192.168.100.255
!
ip dhcp pool INTERNAL-NET
network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0
domain-name jenshansen.dk
default-router 192.168.1.1
import all
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
description Inside. Internal LAN
ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
description Outside: Internet connection to ISP
ip address dhcp
ip nat outside
!
ip nat inside source list 1 interface FastEthernet0/1 overload
!
access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255Having a WEB-server on the inside network
If you want a WEB server on the internal network 192.168.1.88 to be accessed from the outside, you could issue the following nat rule.
ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.88 80 interface FastEthernet0/1 80NAT Virtual Interface
NAT virtual interface (NVI), which removes the requirement to configure an interface as inside or outside.
R1(config)# <input>interface ethernet 0/0</input>
R1(config-if)# <input>ip nat enable</input>
R1(config-if)# <input>interface ethernet 0/1</input>
R1(config-if)# <input>ip nat enable</input>
R1(config-if)# <input>interface ethernet 0/2</input>
R1(config-if)# <input>ip nat enable</input>
R1(config)# <input>access-list 10 permit 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255</input>
R1(config)# <input>ip nat pool NVI 209.165.201.5 209.165.201.10 prefix-length 27</input>
R1(config)# <input>ip nat source list 10 interface Ethernet0/2 overload</input> ! PAT
R1(config)# <input>ip nat source static 172.16.10.10 209.165.201.2</input>Overlapping
Server load distribution - Load balancing between servers
You can load use nat pools to load balance between multiple IP addresses. Just remember a nat pool must be contiguous IP addresses.
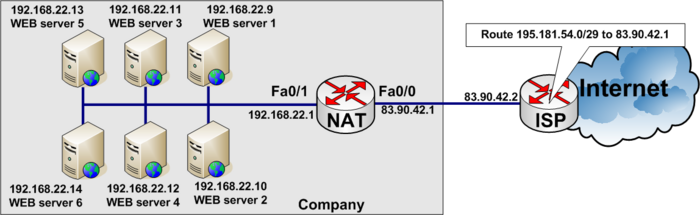
Load balancing example
Load balancing between six WEB-servers to distribute the load among them.
In the real World www.tekkom.dk would for example resolve to IP Address 195.181.54.1 to which all users would connect.
In the figure below you see the company has six equal WEB-servers with the same content.
To load balance between several servers, you need to define a virtual IP address to which the users connect.
access-list 37 permit 195.181.54.1See the full configuration below
ip nat pool WEB-SERVERS 192.168.22.9 192.168.22.14 netmask 255.255.255.0 type rotary
ip nat inside destination list 37 pool WEB-SERVERS
!
interface fastethernet 0/0
description Connected to ISP (Outside)
ip address 83.90.42.1 255.255.255.252
ip nat outside
!
interface fastethernet 0/1
description Local private LAN (Inside)
ip address 192.168.22.1 255.255.255.0
ip nat inside
!
access-list 37 permit 195.181.54.1NAT Sensitive protocols
| Protocol | Behavior |
|---|---|
| IPsec | NAT changes certain IP header fields such as IP Address and the IP header checksum. This can conflict with IPsec integrity. |
| ICMP | Many ICMP packets, such as Destination Unreachable, carry embedded IP header information inside the ICMP message payload, not matching IP packet's translated address. |
| SIP | Protocols such as SIP negotiate address and port numbers at the application layer, which can become invalid through a NAT device. |
Checking and debugging NAT
current NAT translations
To show current NAT translations use show ip nat translations. See example below.
Mercantec#<input>show ip nat translations</input>
Pro Inside global Inside local Outside local Outside global
tcp 192.168.22.178:23 10.0.0.1:23 192.168.22.73:52076 192.168.22.73:52076
tcp 192.168.22.178:23 10.0.0.1:23 --- ---
udp 192.168.22.178:161 80.166.167.96:161 --- ---
udp 192.168.22.178:162 80.166.167.96:162 --- ---
udp 192.168.22.178:68 192.168.22.178:68 192.168.22.73:67 192.168.22.73:67
icmp 192.168.22.178:512 192.168.22.178:512 58.80.117.74:512 58.80.117.74:512debuging NAT
Be aware Debugging NAT on a heavily loaded Router could slow down the Router and overload the connection to the monitor terminal.
NOTE: To stop the debug in flight, enter no debug all and press <ENTER>. This will stop debugging. Even if you cant see the command on the screen, because of to much debugging output. It will stop.
Mercantec#<input>terminal monitor</input>
Mercantec#<input>debug ip nat</input>
IP NAT debugging is on
TDC_SNMP#
Mar 10 05:53:02.302: NAT: s=10.0.0.1->192.168.22.178, d=192.168.22.73 [34292]
Mar 10 05:53:02.302: NAT*: s=192.168.22.73, d=192.168.22.178->10.0.0.1 [55215]
Mar 10 05:53:03.886: NAT: s=10.0.0.1->192.168.22.178, d=192.168.22.73 [34293]
Mar 10 05:53:03.986: NAT*: s=192.168.22.73, d=192.168.22.178->10.0.0.1 [55220]
Mar 10 05:53:05.886: NAT: s=10.0.0.1->192.168.22.178, d=192.168.22.73 [34294]
Mar 10 05:53:05.986: NAT*: s=192.168.22.73, d=192.168.22.178->10.0.0.1 [55224]
Mar 10 05:53:07.886: NAT: s=10.0.0.1->192.168.22.178, d=192.168.22.73 [34295]
Mar 10 05:53:07.986: NAT*: s=192.168.22.73, d=192.168.22.178->10.0.0.1 [55228]
Mar 10 05:53:08.826: NAT: expiring 192.168.22.178 (10.0.0.1) tcp 23 (23)
Mar 10 05:53:08.826: NAT: expiring 192.168.22.178 (192.168.22.178) tcp 17 (23)<input>no de</input>
Mar 10 05:53:09.886: NAT: s=10.0.0.1->192.168.22.178, d=192.168.22.73 [34296]<input>bug all</input>
Mar 10 05:53:09.986: NAT*: s=192.168.22.73, d=192.168.22.178->10.0.0.1 [55233]
Mar 10 05:53:11.094: NAT*: s=192.168.22.73, d=192.168.22.178->10.0.0.1 [55235]
Mar 10 05:53:11.094: NAT: s=10.0.0.1->192.168.22.178, d=192.168.22.73 [34297]
Mar 10 05:53:11.194: NAT*: s=192.168.22.73, d=192.168.22.178->10.0.0.1 [55237]
Mar 10 05:53:11.314: NAT*: s=192.168.22.73, d=192.168.22.178->10.0.0.1 [55238]
Mar 10 05:53:11.318: NAT: s=10.0.0.1->192.168.22.178, d=192.168.22.73 [34298]Is DHCP enabled
Show ip sockets[1]
R1#<input>sh ip sockets</input>
Proto Remote Port Local Port In Out Stat TTY OutputIF
R1#Start DHCP service
R1(config)#<input>service dhcp</input>
R1(config)#<input>^Z</input>
R1#<input>sh ip sockets</input>
Proto Remote Port Local Port In Out Stat TTY OutputIF
17 0.0.0.0 0 10.10.10.1 67 0 0 2211 0
R1#Order of operations in IOS
Sometimes you need to understand the order of operations when setting up complex configurations
Order of operations for the inside-to-outside
- If IPSec, then check input access list
- Decryption—for Cisco Encryption Technology (CET) or IPSec
- Check input access list
- Check input rate limits
- Input accounting
- Policy routing
- Routing
- Redirect to Web cache
- NAT inside to outside (local to global translation)
- Crypto (check map and mark for encryption)
- Check output access list
- Inspect context-based access control (CBAC)
- TCP intercept
- Encryption
Order of operations for the outside-to-inside
- If IPSec, then check input access list
- Decryption—for CET or IPSec
- Check input access list
- Check input rate limits
- Input accounting
- NAT outside to inside (global to local translation)
- Policy routing
- Routing
- Redirect to Web cache
- Crypto (check map and mark for encryption)
- Check output access list
- Inspect CBAC
- TCP intercept
- Encryption
Links
Q&A
Q. How many concurrent NAT sessions are supported in Cisco IOS NAT?[2]
A. The NAT session limit is bounded by the amount of available DRAM in the router. Each NAT translation consumes about 312 bytes in DRAM. As a result, 10,000 translations (more than would generally be handled on a single router) consume about 3 MB. Therefore, typical routing hardware has more than enough memory to support thousands of NAT translations.