Difference between revisions of "Pman CCNP 1"
(→Info:) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
The area virtual-link command includes the router ID of the far-end router. To find the router ID in the far-end router, use the:<br> | The area virtual-link command includes the router ID of the far-end router. To find the router ID in the far-end router, use the:<br> | ||
| − | '''show ip ospf | + | '''show ip ospf '''<br> |
'''show ip ospf interface'''<br> | '''show ip ospf interface'''<br> | ||
Revision as of 11:35, 11 February 2009
Contents
Module 2: EIGRP
2.1 EIGRP Fundamentals and Features
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a Cisco-proprietary routing protocol. It has been described as a hybrid routing protocol, because it combines the best of distance vector routing protocols with link-state algorithms.
2.2 EIGRP Components and Operation
2.3 Implementing and Verifying EIGRP
2.4 Implementing Advanced EIGRP Features
2.5 Configuring EIGRP Authentication
2.6 Using EIGRP in the Enterprise
Module 3: OSPF
3.8 Virtual Links
Enable OSPF & Virtual-link
router ospf 1
router-id 10.0.0.5
area 51 virtual-link 10.0.0.6
network 10.0.0.5 0.0.0.0 area 51
network 172.16.100.12 0.0.0.3 area 51
network 172.16.100.16 0.0.0.3 area 11
Info:
A virtual link is a link that allows discontiguous area 0s to be connected or a disconnected area to be connected to area 0 via a transit area. You should use the OSPF virtual link feature only in very specific cases, such as for temporary connections or backup after a failure. Virtual links should not be used as a primary backbone design feature and should be avoided if possible.
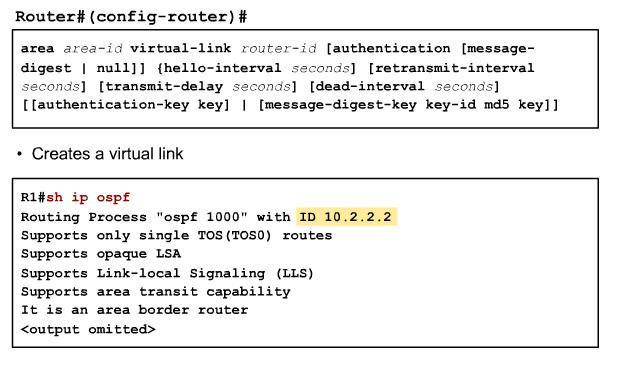
The area virtual-link command includes the router ID of the far-end router. To find the router ID in the far-end router, use the:<br>
show ip ospf
show ip ospf interface
show ip protocol
commands on that remote router, as illustrated in the Figure