CCNP SWITCH/Implementing VLANs in Campus Networks
Contents
- 1 This article is under development....
- 2 VLANs
- 3 Implementing Trunking in Cisco Campus Network
 This article is under development....
This article is under development....
VLANs
VLAN definition
Trunking:
- ISL(Is not a part of this exam)
- 802.1Q(The Industry standard)
End-To-End VLANs
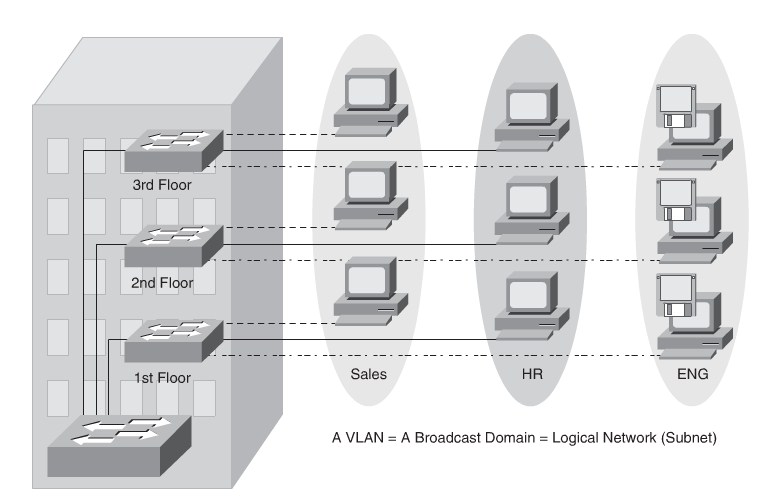
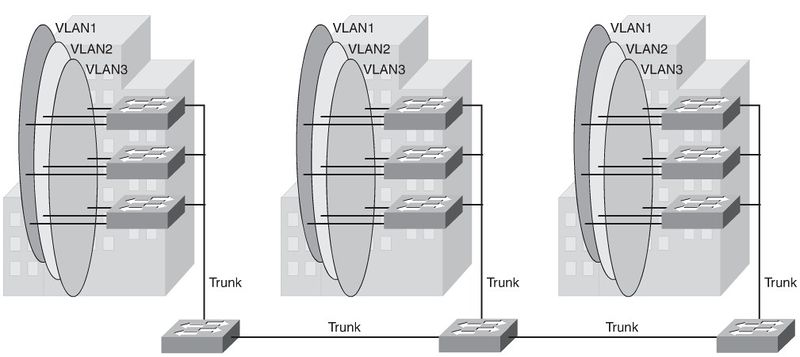
- Each VLAN is dispersed geographically throughout the network.
- Users are grouped into each VLAN regardless of the physical location.
- As a user moves throughout a campus, the VLAN membership of that user remains
the same, regardless of the physical switch to which this user attaches.
- Users are typically associated with a given VLAN for network management reasons.
This is why they are kept in the same VLAN, therefore the same group, as they move through the campus.
- All devices on a given VLAN typically have addresses on the same IP subnet
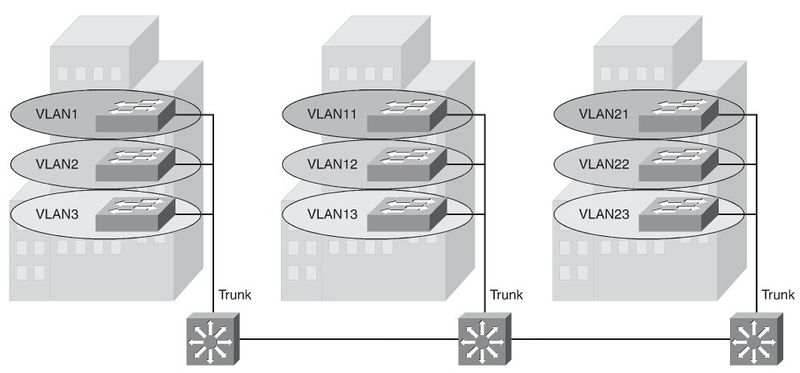
Local VLANs
- The network administrator should create local VLANs with physical boundaries in
mind rather than the job functions of the users on the end devices.
- Generally, local VLANs exist between the access and distribution levels.
- Traffic from a local VLAN is routed at the distribution and core levels to reach desti-
nations on other networks.
- Configure the VTP mode in transparent mode because VLANs on a given access
switch should not be advertised to all other switches in the network, nor do they need to be manually created in any other switch’s VLAN database.
- A network that consists entirely of local VLANs can benefit from increased conver-
gence times offered via routing protocols, instead of a spanning tree for Layer 2 net- works. It is usually recommended to have one to three VLANs per access layer switches.
Comparison of End-to-End VLANs and Local VLANs
Reasons for using End-To-End VLANs
- Grouping users:Users can be grouped on a common IP segment, even though they are geographically dispersed. Recently the trend has been moving toward virtualiza-
tion. Solutions such as VMWARE need end-to-end VLANs to be spread across segments of the campus.
- Applying quality of service (QoS):Traffic can be a higher or lower access priority to network resources from a given VLAN.
- Routing avoidance:If much of the VLAN user traffic is destined for devices on that same VLAN, and routing to those devices is not desirable, users can access resources on their VLAN without their traffic being routed off the VLAN, even though the traffic might traverse multiple switches.
- Special purpose VLAN:Sometimes a VLAN is provisioned to carry a single type of traffic that must be dispersed throughout the campus (for example, multicast, voice, or visitor VLANs).
- Poor design:For no clear purpose, users are placed in VLANs that span the campus or even span WANs. Sometimes when a network is already configured and running, organizations are hesitant to improvethe design because of downtime or other political reasons.
- Finally, troubleshooting devices on a campus with end-to-end VLANs can be challenging because the traffic for a single VLAN can traverse multiple switches in a large area of the campus, and that can easily cause potential spanning-tree problems.
Mapping VLANs to a Hierarchical Network
In the past, network designers have attempted to implement the 80/20 rule when design-
ing networks. Today it is reversed to 20/80 because most traffic will end in the Data Center.
End-To-End VLANs was attractive when IP addresses were manually administered. Today most networks use DHCP.
In addition, because STP is configured for redun-
dancy, the switch limits the STP to only the access and distribution switches that help to
reduce the network complexity in times of failure.
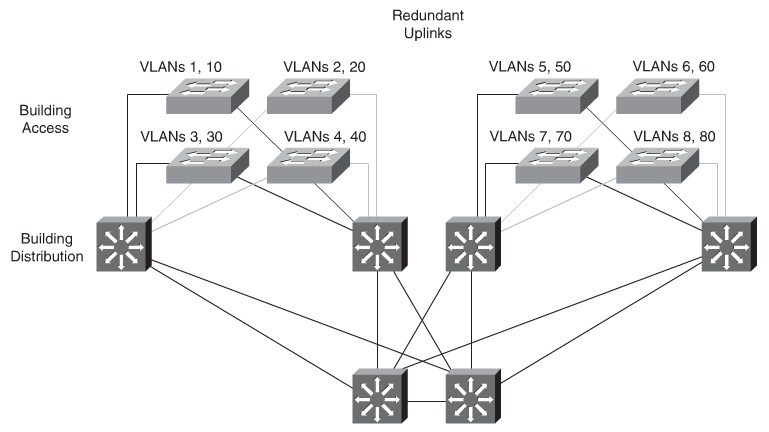
Implementing the enterprise campus architecture design using local VLANs provides the
following benefits:
- Deterministic traffic flow:The simple layout provides a predictable Layer 2 and Layer 3 traffic path.
- Active redundant paths:When implementing Per VLAN Spanning Tree (PVST) or Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) because there is no loop, all links can be used to make use of the redundant paths.
- Finite failure domain:If VLANs are local to a switch block, and the number of devices on each VLAN is kept small, failures at Layer 2 are confined to a small subset of users.
- Scalable design:Following the enterprise campus architecture design, new access switches can be easily incorporated, and new submodules can be added when necessary.
Best Practices for VLAN Design
- For the Local VLANs model, it is usually recommended to have only one to three VLANs per access module
- Avoid using VLAN 1 as the “blackhole” for all unused ports.*
- Try to always have separate voice VLANs, data VLANs, management VLANs, native VLANs, blackhole VLANs, and default VLANs (VLAN 1).
- In the local VLANs model, avoid VTP.
- For trunk ports, turn off DTP and configure it manually. Use IEEE 802.1Q rather than ISL
- Manually configure access ports.
- Prevent all data traffic from VLAN 1; only permit control protocols to run on VLAN1 (DTP, VTP, STP BPDUs, PAgP, LACP, CDP, and such.)
- Avoid using Telnet because of security risks; enable SSH support on management VLANs.
Configuring VLANs
Cisco Catalyst switches support up to 4096 VLANs depending on the platform and soft-
ware version. See Cisco Catalyst Switch Guide
| VLAN Range | Range | Usage | Propagated via VTP |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0, 4095 | Reserved | For system use only. You cannot see or use these VLANs. | - |
| 1 | Normal | Cisco default. You can use this VLAN, but you cannot delete | Yes |
| 2-1001 | Normal | For Ethernet VLANs. You can create, use, and delete these VLANs. | Yes |
| 1002–1005 | Normal | Cisco defaults for FDDI and Token Ring. You cannot delete VLANs 1002–1005. | Yes |
| 1006–1024 | Reserved | For system use only. You cannot see or use these VLANS. | - |
| 1025–4094 | Extended | For Ethernet VLANs only. | Not supported in VTP versions 1 and 2. The switch must be in VTP transparent mode to configure extended- range VLANS. Only supported in version 3. |
Switch#<input>show vlan brief</input>
VLAN Name Status Ports
---- -------------------------------- --------- -------------------------------
1 default active Fa0/1
100 VLAN0100 active Fa0/2, Fa0/3, Fa0/4, Fa0/5, Fa0/6, Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9, Fa0/10
Fa0/11, Fa0/12, Fa0/13, Fa0/14, Fa0/15, Fa0/16, Fa0/17, Fa0/18
Fa0/19, Fa0/20, Fa0/21, Fa0/22, Fa0/23, Fa0/24
200 VLAN0200 active
300 VLAN0300 active
1002 fddi-default act/unsup
1003 trcrf-default act/unsup
1004 fddinet-default act/unsup
1005 trbrf-default act/unsupConfigure VLANs
Switch# <input>configure terminal</input>
Switch(config)# <input>vlan 5</input>
Switch(config-vlan)# <input>name Engineering</input>
Switch(config-vlan)# <input>exit</input>
Switch(config)#<input> no vlan 3</input>
Switch(config)# <input>end</input>Assign an Access Port to a VLAN
Switch# <input>configure terminal</input>
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# <input>interface FastEthernet 0/1</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>description PC A</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>switchport</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>switchport host</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>switchport mode access</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>switchport access vlan 200</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>no shutdown</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>end</input>The switchport host command effectively configures a port for a host device, such as a workstation or server. This feature is a macro for enabling SpanningTree PortFast and dis abling EtherChanneling on a per-port basis. These features are discussed in later chapters. The switchport mode access command is needed so that the interface doesn’t attempt to negotiate trunking.
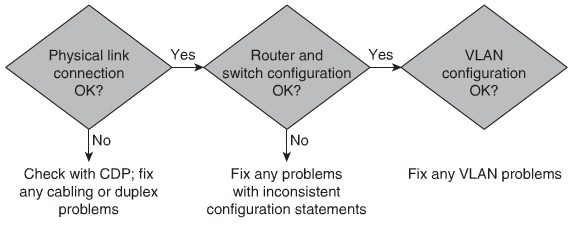
Troubleshooting VLANs
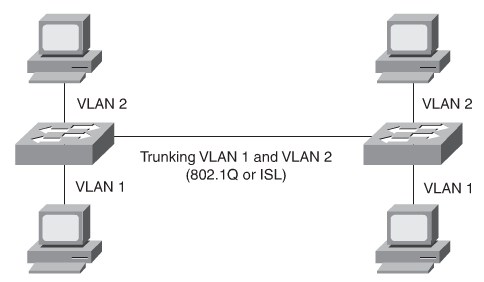
Implementing Trunking in Cisco Campus Network
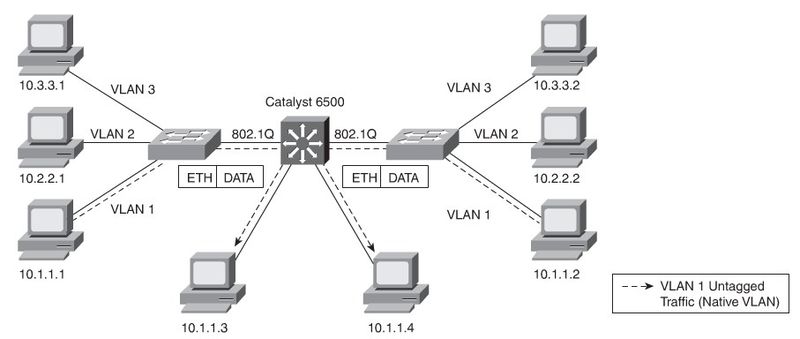
Allows different VLANs to traverse a singe link. 802.1Q Needs a matching nativ VLAN on all trunks.
Trunking Protocols
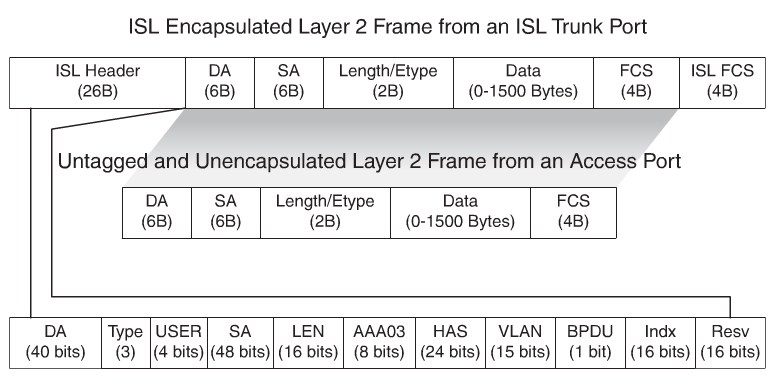
- ISL: A Cisco proprietary trunking encapsulation(not used anymore)
- IEEE 802.1Q:An industry-standard trunking method
ISL Frames
IEEE801.1Q
The IEEE 802.1Q/802.1p standard provides thefollowing inherent architectural advan- tages over ISL:
- Smaller frame overhead than ISL.
- 802.1Q is a widely supported industry-standard protocol.
- 802.1Q has the support for 802.1p fields for QoS.
| [[Image:ScreenShot1081.jpg|800px|left|thumb|IEEE 802.1Q] |
802.1Q tag fields:
- EtherType(TPID):Set to 0x8100 to specify that the 802.1Q tag follows.
- PRI:3-bit 802.1p priority field
- CFI:Canonical Format Identifier; is always set to 0 for Ethernet switches and to 1 for Token Ring-type networks.
- VLAN ID:12-bit VLAN field. Of the 4096 possible VLAN IDs, the maximum number of possible VLAN configurations is 4094. A VLAN ID of 0 indicates priority frames, and value 4095 (FFF) is reserved. CFI, PRI, and VLAN ID are represented as Tag Control information (TCI) fields.
IEEE802.1Q recalculates the CRC value for the entire frame with the tag, and inserts the new CRC value in a new FCS. ISL,in comparison, wraps the original frame and adds a second FCS to the frame.
Nativ VLANs
Be aware of native VLAN mismatch could cause STP Loops. CDP issues a Native VLAN Mismatch error.
Dynamic Trunking Protocol (DTP)
Cisco proprietary point-to-point protocol that negotiates the operational mode of directly connected switch ports to a trunk port and selects an appropriate trunking protocol.