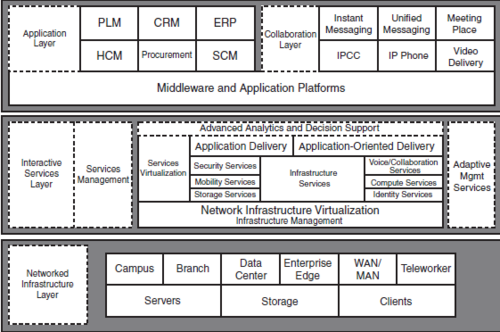
Cisco SONA and the Cisco Enterprise Architecture
Contents
Network Infrastructure Layer
The Network Infrastructure layer contains the Enterprise Network Architecture, which includes the Enterprise Campus, Enterprise Branch, data center, Enterprise Edge, WAN and LAN, and teleworkers.
The Cisco Enterprise Architecture is covered in Chapter 2, Network Structure Models. Servers, storage networks, and end-user clients reside at this layer.
This layer contains switching and routing elements to enhance performance and capabilities, including reliability and security. The network infrastructure is built with redundancy to provide increased reliability. Security configurations are applied to the infrastructure to enforce security policies.
Interactive Service Layer
This layer supports essential applications and the Network Infrastructure layer. Standardized network foundation and virtualization are used to allow security and voice services to scale better.
A standardized network architecture can be duplicated and further copied to scale a network.
Services provided at this layer fall into two categories: Infrastructure Services and Application Networking Services.
Infrastructure Services
The six infrastructure services are essential in the operation and optimization of network services and applications:
- Identity services include authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA); Network Admission Control (NAC); and Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR).
- Mobility services allow network access regardless of the location. An example is VPN.
- Storage services improve storage of critical data. Critical data must be backed up and stored offsite to allow for business continuity and disaster recovery.
- Compute services improve computing resources enterprise-wide. High-end servers can be used for virtual machines to scale the amount of servers on the network.
- Security services deliver security for all network devices, servers, and users. These services include intrusion detection and prevention devices.
- Voice and collaboration services allow user collaboration through all network resources. Cisco’s MeetingPlace is an example of a collaboration application.
Aplication Layer
- PLM: Product Lifecycle Management
- CRM: Customer relation Management Applications
- ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning Applications
- HCM: Human Capital Mangement
- Procurement Applications
- SCM: Supplu Chain Management
Collaboration applications include
- IM: Instant messaging
- UM: Unified Messaging
- IPCC: IP Contact Center
- Meeting Place
- Video delivery