From Teknologisk videncenter
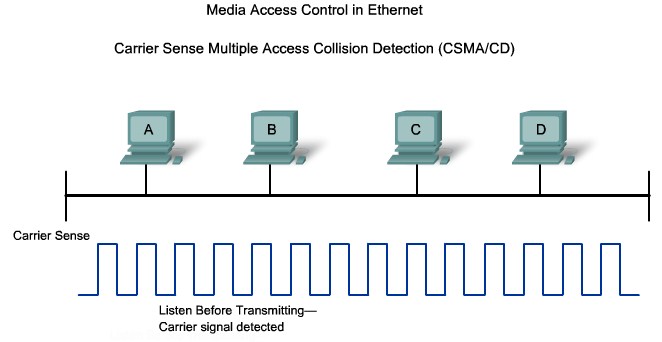 CSMA/CD on a multi-access half-Dublex network |
- 1. Carrier Sense
- 2. Collision Detection
- 3. Jam Signal
- 4. Random Backoff
|
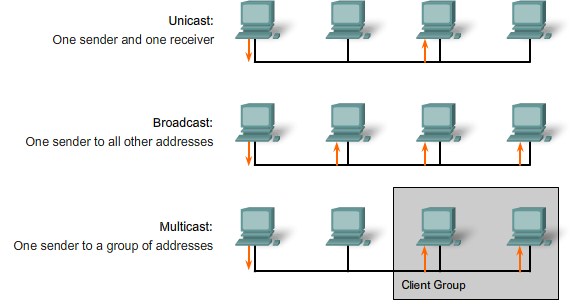 Difference between Unicast, Multicast and Broadcast |
 IEEE 802.3 Ethernet frame |
|
|
|
|
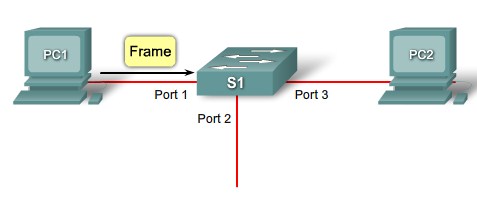 MAC table population step 1 |
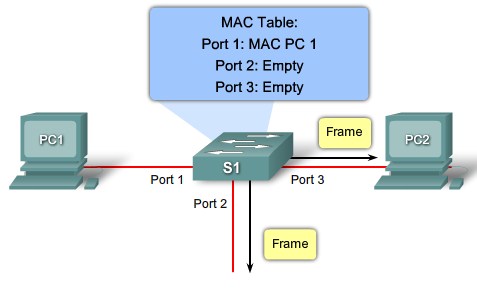 MAC table population step 2 |
 MAC table population step 3 |
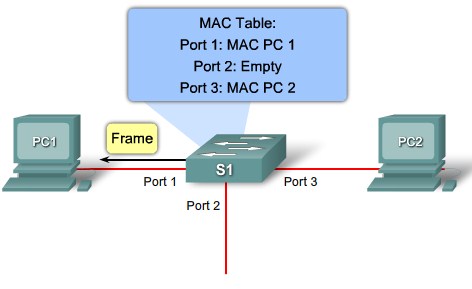 MAC table population step 4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
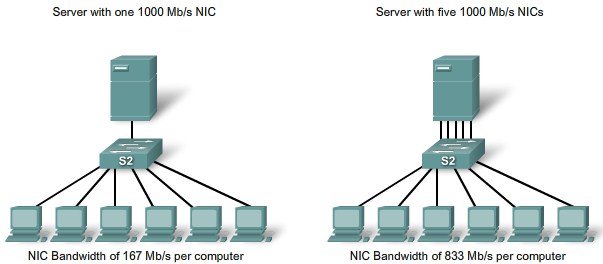 Removing Server Bottlenecks |
 Switch Packet Forwarding Methods |
- Store-and-Forward - Gemmer pakken og tjekker for crc fejl
- Cut-Through Switching - Switcher pakken når den har læst destinationen
- Fast-forward - Switcher pakken med det samme den har læst destinationen
- Fragment-free - Læser de første 64 byte og sender videre.
|
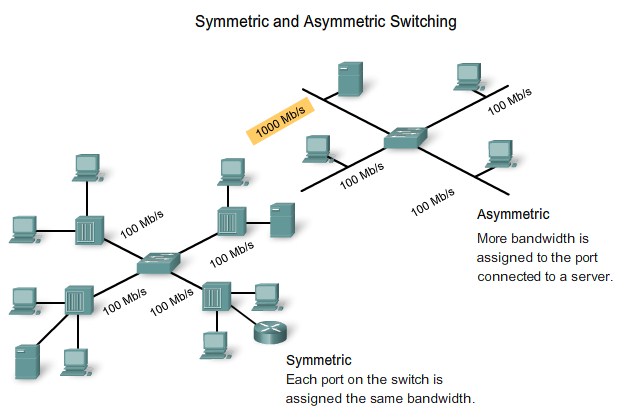 Symmetric vs. Asymmetric Switching |
|
|
 L3 Switch and Router comparison |
Navigating Command-Line Interfaces Modes
|
|
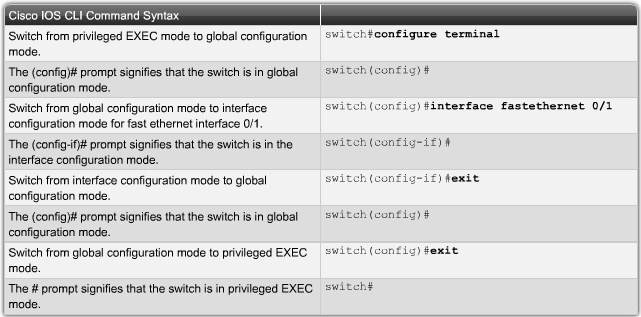 Navigation configuration modes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Configure the Command History Buffer |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
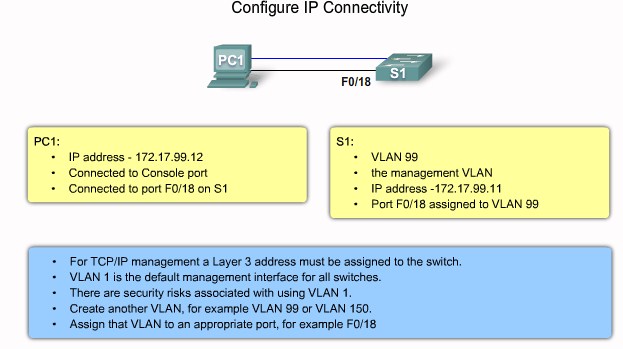 Configure IP connectivity Step 1 |
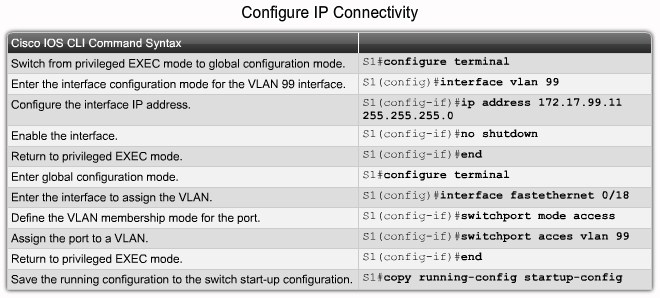 Configure IP connectivity Step 2 |
|
|
 Configuring Duplex and Speed |
|
|
|
|
| Create static MAC entry: mac-address-table static <MAC address> vlan {1-4096, ALL} interface interface-id
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Filsystem prefixer
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
 Configure encypted passwords |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hvad med aaa new-model & username cisco password cisco
Common Security Attacks
MAC Address Flooding
 MAC flooding attack step 1 |
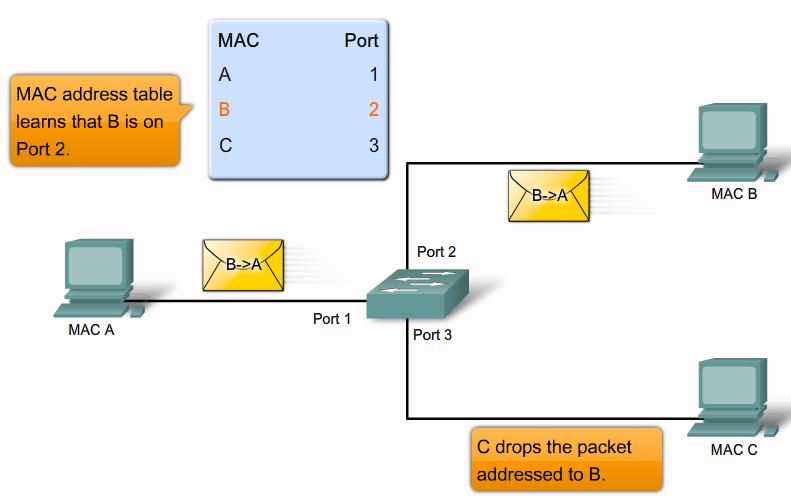 MAC flooding attack step 2 |
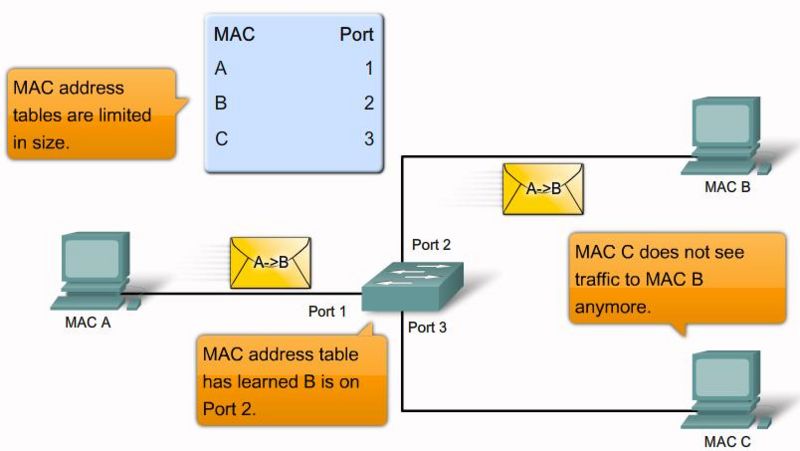 MAC flooding attack step 3 |
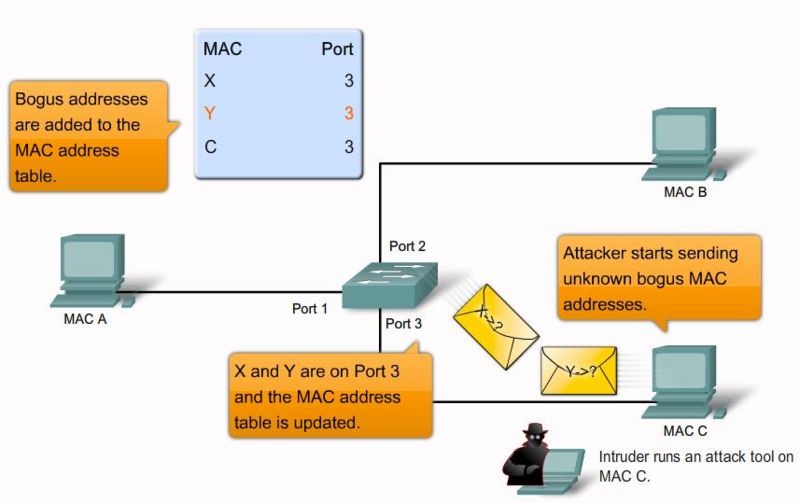 MAC flooding attack step 4 |
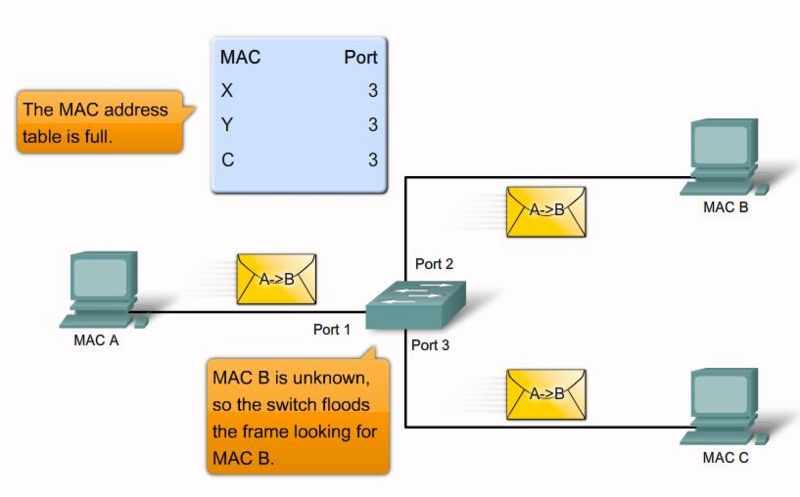 MAC flooding attack step 5 |
SDM Templates
DHCP Spoofing
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
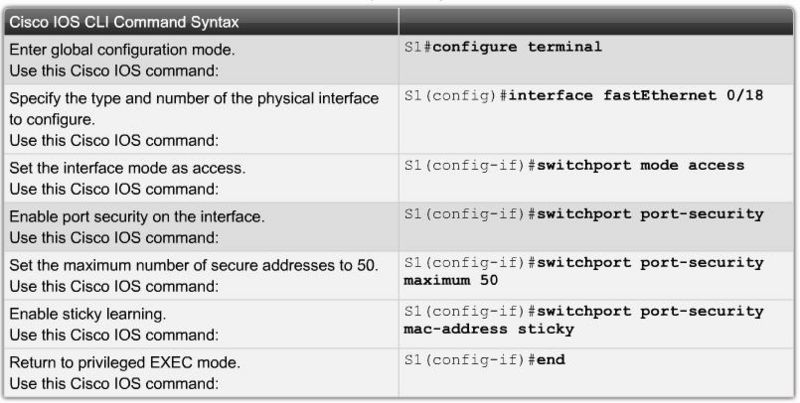 Switchport Security configuration |
|
|
|
|
Security Violation Modes
- Protect: When the number of secure MAC addresses reaches the limit allowed on the port, packets with unknown source addresses are dropped.
- Restrict: When the number of secure MAC addresses reaches the limit allowed on the port, packets with unknown source addresses are dropped. A SNMP trap is sent, a syslog message is logged, and the violation counter increments.
- Shutdown(Default[1]): In this mode, a port security violation causes the interface to immediately become error-disabled and turns off the port LED. It also sends an SNMP trap, logs a syslog message.
References
|
|