Difference between revisions of "Cisco SONA and the Cisco Enterprise Architecture"
m |
m (→Plan) |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
This layer contains switching and routing elements to enhance performance and capabilities, including reliability and security. The network infrastructure is built with redundancy to provide increased reliability. Security configurations are applied to the infrastructure to enforce security policies. | This layer contains switching and routing elements to enhance performance and capabilities, including reliability and security. The network infrastructure is built with redundancy to provide increased reliability. Security configurations are applied to the infrastructure to enforce security policies. | ||
| + | *'''Network management''': Includes LAN management for advanced management of multilayer switches | ||
| + | *'''High availability''':Ensures end-to-end availability for services, clients, and sessions. | ||
| + | *'''QoS''':Manages the delay, delay variation (jitter), bandwidth availability, and packetloss parameters on a network | ||
| + | *'''IP multicasting''':Multicasting enables distribution of videoconferencing, corporate communications, distance learning, distribution of software, and other applications. | ||
| + | |||
== Interactive Service Layer == | == Interactive Service Layer == | ||
This layer supports essential applications and the Network Infrastructure layer. Standardized network foundation and virtualization are used to allow security and voice services to scale better. | This layer supports essential applications and the Network Infrastructure layer. Standardized network foundation and virtualization are used to allow security and voice services to scale better. | ||
| Line 38: | Line 43: | ||
*Video delivery | *Video delivery | ||
= Cisco Enterprise Architecture = | = Cisco Enterprise Architecture = | ||
| + | [[Image:ScreenShot301.jpg]] | ||
== Cisco Enterprise Campus Architecture == | == Cisco Enterprise Campus Architecture == | ||
== Cisco Enterprise Edge Architecture == | == Cisco Enterprise Edge Architecture == | ||
| Line 44: | Line 50: | ||
== Cisco Enterprise Branch Architecture == | == Cisco Enterprise Branch Architecture == | ||
== Cisco Enterprise Teleworker Architecture == | == Cisco Enterprise Teleworker Architecture == | ||
| + | |||
= PPDIOO netværk livscyklus = | = PPDIOO netværk livscyklus = | ||
[[Image:PPDIOO.png|right|thumb|300px|PPDIOO netværk livscyklus]] | [[Image:PPDIOO.png|right|thumb|300px|PPDIOO netværk livscyklus]] | ||
| Line 49: | Line 56: | ||
*Koordineret planlægning og strategi | *Koordineret planlægning og strategi | ||
*Økonomi | *Økonomi | ||
| + | *højt level konceptuel design defineres | ||
| + | |||
==Plan== | ==Plan== | ||
*Planlægningsfasen | *Planlægningsfasen | ||
| Line 54: | Line 63: | ||
***faceliteter | ***faceliteter | ||
***Hvilke funktioner og krav har brugerne. | ***Hvilke funktioner og krav har brugerne. | ||
| + | **Lav en GAP analyse | ||
| + | **Analyser netværket efter problemer der skal rettes. | ||
| + | |||
==Design== | ==Design== | ||
*Hvilke krav har organisationen til netværket | *Hvilke krav har organisationen til netværket | ||
| Line 73: | Line 85: | ||
**Nye applikationer skal bruges. | **Nye applikationer skal bruges. | ||
**Nye krav til netværket | **Nye krav til netværket | ||
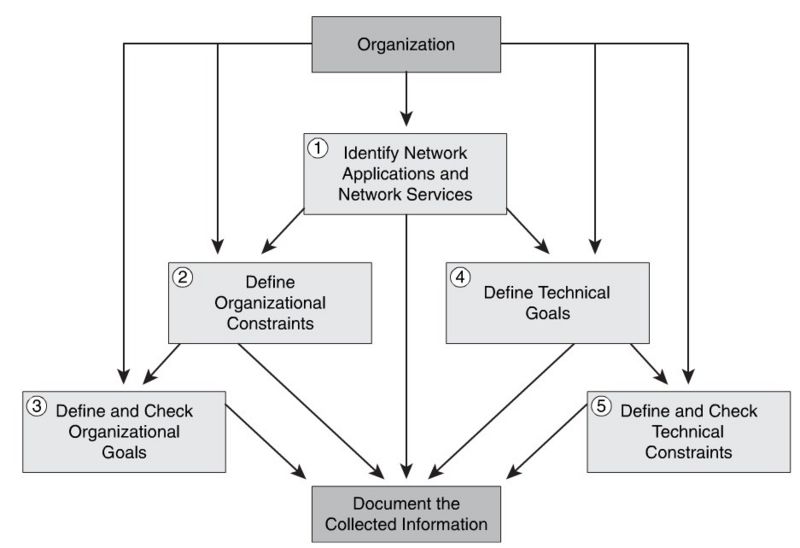
| + | ==Idenetify Customer Requirements== | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |[[Image:ScreenShot349.jpg|800px|left|thumb|Idenetify Customer Requirements]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
[[Category:CCDP]] | [[Category:CCDP]] | ||
Latest revision as of 20:59, 4 September 2011
Kapitel 1 fra CCDP ARCH bogen.
Contents
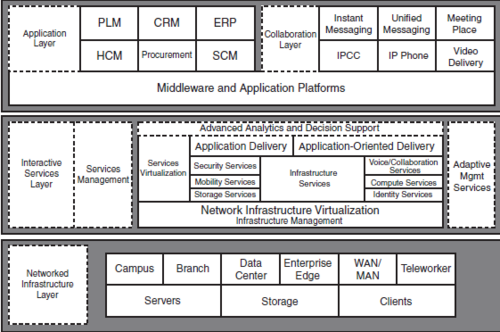
SONA: Service Oriented Network Architecture
Network Infrastructure Layer
The Network Infrastructure layer contains the Enterprise Network Architecture, which includes the Enterprise Campus, Enterprise Branch, data center, Enterprise Edge, WAN and LAN, and teleworkers.
The Cisco Enterprise Architecture is covered in Chapter 2, Network Structure Models. Servers, storage networks, and end-user clients reside at this layer.
This layer contains switching and routing elements to enhance performance and capabilities, including reliability and security. The network infrastructure is built with redundancy to provide increased reliability. Security configurations are applied to the infrastructure to enforce security policies.
- Network management: Includes LAN management for advanced management of multilayer switches
- High availability:Ensures end-to-end availability for services, clients, and sessions.
- QoS:Manages the delay, delay variation (jitter), bandwidth availability, and packetloss parameters on a network
- IP multicasting:Multicasting enables distribution of videoconferencing, corporate communications, distance learning, distribution of software, and other applications.
Interactive Service Layer
This layer supports essential applications and the Network Infrastructure layer. Standardized network foundation and virtualization are used to allow security and voice services to scale better.
A standardized network architecture can be duplicated and further copied to scale a network.
Services provided at this layer fall into two categories: Infrastructure Services and Application Networking Services.
Infrastructure Services
The six infrastructure services are essential in the operation and optimization of network services and applications:
- Identity services include authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA); Network Admission Control (NAC); and Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR).
- Mobility services allow network access regardless of the location. An example is VPN.
- Storage services improve storage of critical data. Critical data must be backed up and stored offsite to allow for business continuity and disaster recovery.
- Compute services improve computing resources enterprise-wide. High-end servers can be used for virtual machines to scale the amount of servers on the network.
- Security services deliver security for all network devices, servers, and users. These services include intrusion detection and prevention devices.
- Voice and collaboration services allow user collaboration through all network resources. Cisco’s MeetingPlace is an example of a collaboration application.
Aplication Layer
- PLM: Product Lifecycle Management
- CRM: Customer relation Management Applications
- ERP: Enterprise Resource Planning Applications
- HCM: Human Capital Mangement
- Procurement Applications
- SCM: Supplu Chain Management
Collaboration applications include
- IM: Instant messaging
- UM: Unified Messaging
- IPCC: IP Contact Center
- Meeting Place
- Video delivery
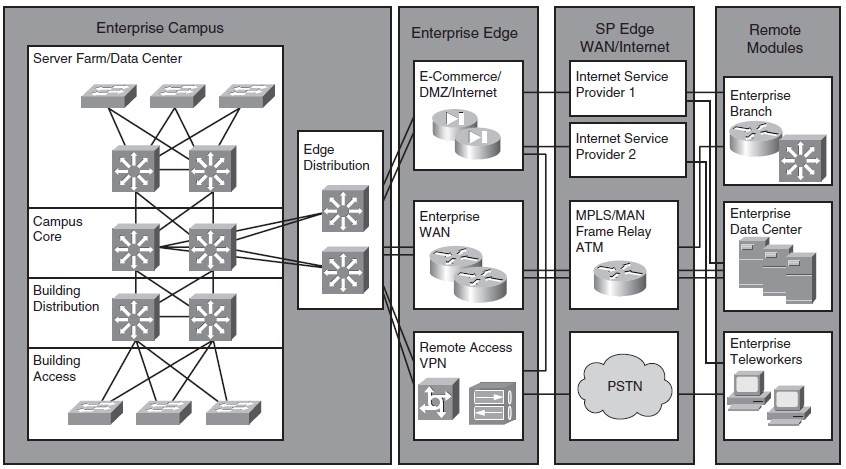
Cisco Enterprise Architecture
Cisco Enterprise Campus Architecture
Cisco Enterprise Edge Architecture
Cisco Enterprise WAN and MAN Architecture
Cisco Enterprise Data Center Architecture
Cisco Enterprise Branch Architecture
Cisco Enterprise Teleworker Architecture
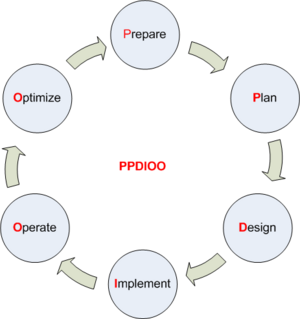
PPDIOO netværk livscyklus
Prepare
- Koordineret planlægning og strategi
- Økonomi
- højt level konceptuel design defineres
Plan
- Planlægningsfasen
- Hvilke krav til netværket er der ud fra
- faceliteter
- Hvilke funktioner og krav har brugerne.
- Lav en GAP analyse
- Analyser netværket efter problemer der skal rettes.
- Hvilke krav til netværket er der ud fra
Design
- Hvilke krav har organisationen til netværket
- Oppetid
- Sikkerhed
- Skalerbarhed
- Performance
- Tekniske krav. for eksempel en eller flere leverandører.
- Hvilket udstyr skal genbruges
Implement
- Installation og konfiguration som planlagt under design fasen
- Kontinuerlig drift under implementering?
Operate
- Drift af netværk
- Overvågning
- Fejlfinding
Optimize
- Opgradering af netværket nødvendig gå til Prepare fasen
- Nye applikationer skal bruges.
- Nye krav til netværket