Difference between revisions of "NAT Cisco IOS"
m (→Network Address Translantion) |
m (→Overloading example 3: Cisco Router as a SOHO Router) |
||
| Line 107: | Line 107: | ||
The configration with an example of a fire-wall. Remember this config is at '''own''' risc!! | The configration with an example of a fire-wall. Remember this config is at '''own''' risc!! | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168. | + | ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.99 |
| − | ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.200 192.168. | + | ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.200 192.168.1.255 |
! | ! | ||
ip dhcp pool INTERNAL-NET | ip dhcp pool INTERNAL-NET | ||
| Line 151: | Line 151: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| + | ==== Having a WEB-server on the inside network ==== | ||
| + | If you want a WEB server on the internal network 192.168.1.88 to be accessed from the outside, you could issue the following nat rule. | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | ip nat inside source static tcp 192.168.1.88 80 interface FastEthernet0/1 80 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
--> | --> | ||
Revision as of 12:45, 7 March 2009
| |
The information in this article is targeted to Cisco CCNA and CCNP curriculum, and not meant as in-depth information on all IOS |
Contents
Network Address Translantion
For an explanation of NAT see Wikipedias Network address translation
Cisco NAT
Static NAT
In static NAT The Internal IP address is always translated to the same External IP address, on a one-to-one basis.
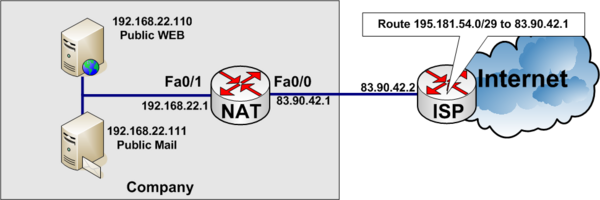
Example of static NAT
In the example below, a company has acquired an Internet connection with four additional addresses 195.181.54.0/29.
- Connection Link address to internet 83.90.42.0/30
- ISP uses 83.90.42.2/30
- Company Router 83.90.42.1/30
- The network 195.181.54.0/29 is routed to 83.90.42.1 by the ISP
- 195.181.54.1/29 is a real IP address the company wants to use to their WEB-server
- The companys WEB-server is located on the internal private network on local IP Address 192.168.22.110
- 195.181.54.2/29 is a real IP address the company wants to use to their MAIL-server
- The companys MAIL-server is located on the internal private network on local IP Address 192.168.22.111
ip nat inside source static 192.168.22.110 195.181.54.1 ip nat inside source static 192.168.22.111 195.181.54.2 ! interface fastethernet 0/0 description Connected to ISP (Outside) ip address 83.90.42.1 255.255.255.252 ip nat outside ! interface fastethernet 0/1 description Local private LAN (Inside) ip address 192.168.22.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside
Dynamic NAT
Overloading
Overloading is often used, when you have a private internal LAN for example 192.168.1.0/24 and connect to the Internet through as ISP that lend you a Pulic IP address, through DHCP like a small SOHO router.
Overloading example 1: Connection with fixed WAN IP Address
- Internal private network: 192.168.1.0/24
- Fixed WAN IP address: 83.90.1.30/30
interface FastEthernet0/0 description Inside. Internal LAN ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! interface FastEthernet0/1 description Outside: Internet connection to ISP ip address 83.90.1.30 255.255.255.252 ip nat outside ! ip nat inside source list 38 interface FastEthernet0/1 overload ! access-list 38 permit 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
Overloading example 2: Connection with floating WAN IP Address (DHCP)
- Internal private network: 192.168.1.0/24
- WAN Address: DHCP
interface FastEthernet0/0 description Inside. Internal LAN ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! interface FastEthernet0/1 description Outside: Internet connection to ISP ip address dhcp ip nat outside ! ip nat inside source list 38 interface FastEthernet0/1 overload ! access-list 38 permit 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.255
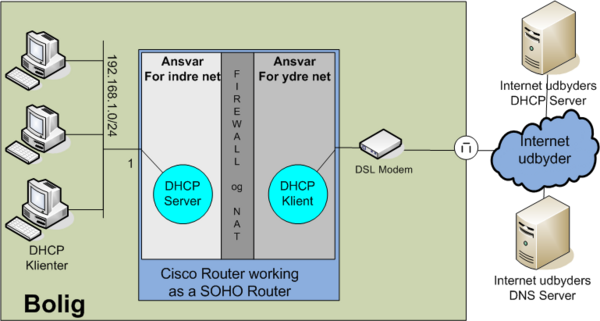
Overloading example 3: Cisco Router as a SOHO Router
- Internal private network: 192.168.1.0/24 connected to fastethernet 0/0
- WAN Address: DHCP client connected to fastethernet 0/1
NAT, PAT (overloading) and DHCP configuration
ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.1 192.168.100.99 ip dhcp excluded-address 192.168.1.200 192.168.100.255 ! ip dhcp pool INTERNAL-NET network 192.168.1.0 255.255.255.0 domain-name jenshansen.dk default-router 192.168.1.1 import all ! interface FastEthernet0/0 description Inside. Internal LAN ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! interface FastEthernet0/1 description Outside: Internet connection to ISP ip address dhcp ip nat outside ! ip nat inside source list 1 interface FastEthernet0/1 overload ! access-list 1 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
Overlapping
Server load distribution - Load balancing between servers
You can load use nat pools to load balance between multiple IP addresses. Just remember a nat pool must be contiguous IP addresses.
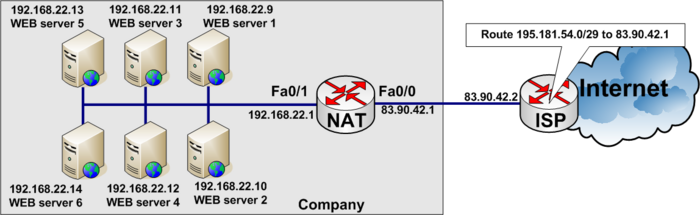
Load balancing example
Load balancing between six WEB-servers to distribute the load among them.
In the real World www.tekkom.dk would for example resolve to IP Address 195.181.54.1 to which all users would connect.
In the figure below you see the company has six equal WEB-servers with the same content.
To load balance between several servers, you need to define a virtual IP address to which the users connect.
access-list 37 permit 195.181.54.1
See the full configuration below
ip nat pool WEB-SERVERS 192.168.22.9 192.168.22.14 netmask 255.255.255.0 type rotary ip nat inside destination list 37 pool WEB-SERVERS ! interface fastethernet 0/0 description Connected to ISP (Outside) ip address 83.90.42.1 255.255.255.252 ip nat outside ! interface fastethernet 0/1 description Local private LAN (Inside) ip address 192.168.22.1 255.255.255.0 ip nat inside ! access-list 37 permit 195.181.54.1