Difference between revisions of "Spanning tree"
m (→MST: Multiple Spanning Tree protocol) |
m (→BPDU: Bridge Protocol Data unit) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
*Switches participating in STP receives the packets on the [[multicast]] addresses 01-80-C2-00-00-00 and 01-80-C2-00-00-10 | *Switches participating in STP receives the packets on the [[multicast]] addresses 01-80-C2-00-00-00 and 01-80-C2-00-00-10 | ||
*BPDU packets are send every 2 seconbds. | *BPDU packets are send every 2 seconbds. | ||
| + | {|border=1 ;style="margin: 0 auto; text-align: center;cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" | ||
| + | |+ Bridge Protocol Data Unit | ||
| + | |- bgcolor=lightgrey | ||
| + | ! Bytes !! Field name !! Notes | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2 || '''Protocol ID''' || Always 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1 || '''Version''' || Always 0 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1 || '''Message Type''' || Configuration or TCN BPPU | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 1 || '''Flags''' || | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 8 || '''Root Bridge ID''' || 2 Bytes priority and 6 Bytes MAC address | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 4 || '''Cost of path''' || Cost of all links from the transmitting switch to the root bridge | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 8 || '''Bridge ID''' || 2 Bytes priority and 6 Bytes MAC address | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2 || '''Port ID''' || Transmitting switch port ID | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2 || '''Message age''' || in 256's of a second | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2 || '''Max age''' || in 256's of a second | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2 || '''Hello Time''' || in 256's of a second | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 2 || '''Forward delay''' || in 256's of a second | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
=MST: Multiple Spanning Tree protocol= | =MST: Multiple Spanning Tree protocol= | ||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
Revision as of 13:53, 28 April 2009
The Spanning Tree protocol are used on Ethernet Switches to avoid broadcast storms.
Contents
Problems with Switches without Spanning Tree
Broadcast Storms
A broadcast starts when a Ethernet switch receives a broadcast from a Host and there exist a loop. See example below:
Duplicate Ethernet Frames
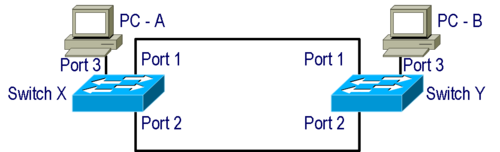
Another problem with Ethernet loops is duplicate Ethernet frames. In the picture below, switch X can see PC-B mac-address on two ports and send the frame out of each port.
Instability in Switch MAC-Address table
Another problem with with Ethernet loops is instability in the Switches MAC-Address table See the picture below and consider:
- The MAC-Address off PC-B is timed out on both Switches.
- PC-A send a unicast packet to PC-B's MAC-Address.
- PC-B's MAC-address is unknown to Switch X which send the Frame out of all ports. (Except the originating port 3)
- Switch Y receives the Frame to PC-B on port 1 and on port 2.
- PC-B's MAC-address is unknown to Switch X which send the Frame out of all ports. (Except originating port)
- Switch X know receives Frames on port 1 and port 2 with source MAC-address o fPC-A
- Switch X now thinks that PC-A is on Port 1, Port 2 and Port 3.
The Spanning Tree protocol principle
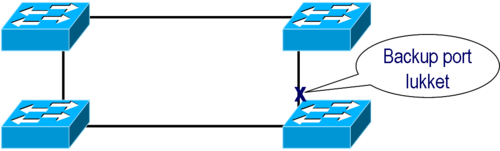
If the Switches has enabled the Spanning Tree Protocol - STP - the Switches discover the loop and close one of the links for traffic. The closed link will be enabled if one of the other links breaks down.
BPDU: Bridge Protocol Data unit
Connected Switches sends BPDU packets to each other, to make a hierarchy among them. The purpose is to build a loop free network.
- BPDU packets are send as 802.1d multicast packets.
- Switches not participating in the STP sends the BPDU packets out all ports. (Broadcast)
- Switches participating in STP receives the packets on the multicast addresses 01-80-C2-00-00-00 and 01-80-C2-00-00-10
- BPDU packets are send every 2 seconbds.
| Bytes | Field name | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Protocol ID | Always 0 |
| 1 | Version | Always 0 |
| 1 | Message Type | Configuration or TCN BPPU |
| 1 | Flags | |
| 8 | Root Bridge ID | 2 Bytes priority and 6 Bytes MAC address |
| 4 | Cost of path | Cost of all links from the transmitting switch to the root bridge |
| 8 | Bridge ID | 2 Bytes priority and 6 Bytes MAC address |
| 2 | Port ID | Transmitting switch port ID |
| 2 | Message age | in 256's of a second |
| 2 | Max age | in 256's of a second |
| 2 | Hello Time | in 256's of a second |
| 2 | Forward delay | in 256's of a second |
MST: Multiple Spanning Tree protocol
hostname Switch-1 spanning-tree mode mst spanning-tree extend system-id ! spanning-tree mst configuration name TEKKOM revision 1 instance 1 vlan 10-50 instance 2 vlan 51-99 ! spanning-tree mst 1 priority 24576 spanning-tree mst 2 priority 32768 ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending
hostname Switch-2 spanning-tree mode mst spanning-tree extend system-id ! spanning-tree mst configuration name TEKKOM revision 1 instance 1 vlan 10-50 instance 2 vlan 51-99 ! spanning-tree mst 1 priority 32768 spanning-tree mst 2 priority 24576 ! vlan internal allocation policy ascending