Difference between revisions of "Link-Local IPv6 Address"
m |
m |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|Example = FE80::21B:D4FF:FE0F:8CA2 | |Example = FE80::21B:D4FF:FE0F:8CA2 | ||
|CompareIPv4 = 169.254.0.0/16 Link-Local | |CompareIPv4 = 169.254.0.0/16 Link-Local | ||
| + | |Desc1 = [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4291 rfc4291] | ||
|Explanation = These addresses are used on a single link or a non-routed common access network, such as an Ethernet LAN. | |Explanation = These addresses are used on a single link or a non-routed common access network, such as an Ethernet LAN. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 16: | ||
Routers must not forward IPv6 packets if the source or destination contains a link-local address. | Routers must not forward IPv6 packets if the source or destination contains a link-local address. | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | =IPv6 Link-Local Addresses= | + | |
| + | ==IPv6 Link-Local Addresses== | ||
Link-Local Addresses are used by Nodes to communicate to other Nodes on the same Link. Link-Local addresses are ''not'' Routeable. | Link-Local Addresses are used by Nodes to communicate to other Nodes on the same Link. Link-Local addresses are ''not'' Routeable. | ||
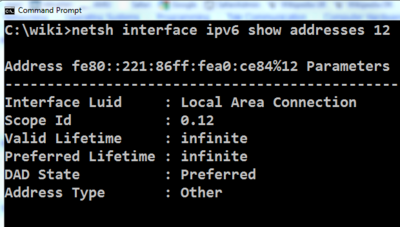
| + | [[Image:Link-Local Address Windows 7.PNG|left|400px|thumb|Windows 7 Link-Local Address Example]] | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | [[Image:Link-Local IPv6 address.png|500px|float|thumb|Format of Link-Local address]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | <source lang=cli> | ||
| + | IPv6#<input>sh ipv6 int fa0/0</input> | ||
| + | FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up | ||
| + | IPv6 is enabled, <notice>link-local address is FE80::21B:D4FF:FE0F:8CA2</notice> | ||
| + | No Virtual link-local address(es): | ||
| + | Description: Outside: Internet connection to ISP | ||
| + | Global unicast address(es): | ||
| + | 2001:16D8:DD85:146::2, subnet is 2001:16D8:DD85:146::/64 | ||
| + | Joined group address(es): | ||
| + | FF02::1 | ||
| + | FF02::2 | ||
| + | FF02::D | ||
| + | FF02::16 | ||
| + | FF02::1:FF00:2 | ||
| + | FF02::1:FF0F:8CA2 | ||
| + | MTU is 1500 bytes | ||
| + | ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds | ||
| + | ICMP redirects are enabled | ||
| + | ICMP unreachables are sent | ||
| + | ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1 | ||
| + | ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds | ||
| + | Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses. | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {{Source cli}} | ||
| + | ==Example why originating interface is important== | ||
| + | Notice in the example below, we telnet to the Heimdal Router - the very same we're on - even I know that the Link-Local address FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 is on a neighboring Router called Campus1. | ||
| + | <source lang=cli> | ||
| + | <notice>Heimdal</notice>#<input>telnet FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440</input> | ||
| + | Trying FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 ... Open | ||
| + | !!!Netadmin Please upgrade the network security!!! | ||
| + | banner motd | ||
| + | |||
| + | User Access Verification | ||
| + | |||
| + | Password: | ||
| + | <notice>Heimdal</notice>><input>exit</input> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [Connection to FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 closed by foreign host] | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | Link-Local addresses are local on a link. We need to tell on which interface the Link-Address are on. First we need to find the interface on which the address resides. | ||
| + | <source lang=cli> | ||
| + | Heimdal#<input>show ipv6 neighbor | inc B440</input> | ||
| + | FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 0 0018.187c.b440 STALE <notice>Vl1</notice> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | In the output in previous command, it's seen that the Link-Local address lives in Vlan1. Now we telnet from that source-interface - and Voila everything works as expected. | ||
| + | <source lang=cli> | ||
| + | <notice>Heimdal</notice>#<input>telnet FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 /source-interface vlan1</input> | ||
| + | Trying FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 ... Open | ||
| + | !!!Netadmin please upgrade Network Security!!! | ||
| + | banner motd | ||
| + | |||
| + | User Access Verification | ||
| + | |||
| + | Password: | ||
| + | <notice>Campus1</notice>> | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | [[Category:CiscoIPv6]] | ||
Latest revision as of 15:28, 15 June 2011
| IPv6 Address Type: | Link-Local |
| Prefix: | fe80::/10 |
| Local Routeable: | No |
| Global Routeable: | No |
| Global Unique: | No |
| Example: | FE80::21B:D4FF:FE0F:8CA2 |
| IPv4 Equivalent: | 169.254.0.0/16 Link-Local |
| Described in: | rfc4291 |
These addresses are used on a single link or a non-routed common access network, such as an Ethernet LAN.
They do not need to be unique outside of that link.
Link-local addresses may appear as the source or destination of an IPv6 packet.
Routers must not forward IPv6 packets if the source or destination contains a link-local address.
IPv6 Link-Local Addresses
Link-Local Addresses are used by Nodes to communicate to other Nodes on the same Link. Link-Local addresses are not Routeable.
IPv6#<input>sh ipv6 int fa0/0</input>
FastEthernet0/0 is up, line protocol is up
IPv6 is enabled, <notice>link-local address is FE80::21B:D4FF:FE0F:8CA2</notice>
No Virtual link-local address(es):
Description: Outside: Internet connection to ISP
Global unicast address(es):
2001:16D8:DD85:146::2, subnet is 2001:16D8:DD85:146::/64
Joined group address(es):
FF02::1
FF02::2
FF02::D
FF02::16
FF02::1:FF00:2
FF02::1:FF0F:8CA2
MTU is 1500 bytes
ICMP error messages limited to one every 100 milliseconds
ICMP redirects are enabled
ICMP unreachables are sent
ND DAD is enabled, number of DAD attempts: 1
ND reachable time is 30000 milliseconds
Hosts use stateless autoconfig for addresses. |
Example why originating interface is important
Notice in the example below, we telnet to the Heimdal Router - the very same we're on - even I know that the Link-Local address FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 is on a neighboring Router called Campus1.
<notice>Heimdal</notice>#<input>telnet FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440</input>
Trying FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 ... Open
!!!Netadmin Please upgrade the network security!!!
banner motd
User Access Verification
Password:
<notice>Heimdal</notice>><input>exit</input>
[Connection to FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 closed by foreign host]Link-Local addresses are local on a link. We need to tell on which interface the Link-Address are on. First we need to find the interface on which the address resides.
Heimdal#<input>show ipv6 neighbor | inc B440</input>
FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 0 0018.187c.b440 STALE <notice>Vl1</notice>In the output in previous command, it's seen that the Link-Local address lives in Vlan1. Now we telnet from that source-interface - and Voila everything works as expected.
<notice>Heimdal</notice>#<input>telnet FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 /source-interface vlan1</input>
Trying FE80::218:18FF:FE7C:B440 ... Open
!!!Netadmin please upgrade Network Security!!!
banner motd
User Access Verification
Password:
<notice>Campus1</notice>>