Difference between revisions of "Mutex"
From Teknologisk videncenter
m (Created page with "A Mutex ('''Mut'''ual '''Ex'''clusion) is a method used to gain exclusive rights to use a shared resource in programming. Often used when designing software in [[embedded system]...") |
m |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Under construction}} | ||
A Mutex ('''Mut'''ual '''Ex'''clusion) is a method used to gain exclusive rights to use a shared resource in programming. Often used when designing software in [[embedded system]]s using [[interrupt]]s and/or [[RTOS]]. | A Mutex ('''Mut'''ual '''Ex'''clusion) is a method used to gain exclusive rights to use a shared resource in programming. Often used when designing software in [[embedded system]]s using [[interrupt]]s and/or [[RTOS]]. | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ==ARM Thumb== | ||
| + | LDREX and STREX<ref name=M3177>The definitive guide to the CORTEX-M3, Second edition - section 10.6 page 177 (ISBN978-1-85617-963-8)</ref><ref name=THUMB>[http://infocenter.arm.com/help/topic/com.arm.doc.dui0489c/DUI0489C_arm_assembler_reference.pdf ARM Assembler reference] section 3.3.13 page 3.39</ref> | ||
| + | =References= | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
[[Category:Embedded]][[Category:ARM]] | [[Category:Embedded]][[Category:ARM]] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:22, 24 March 2012
A Mutex (Mutual Exclusion) is a method used to gain exclusive rights to use a shared resource in programming. Often used when designing software in embedded systems using interrupts and/or RTOS.
Example
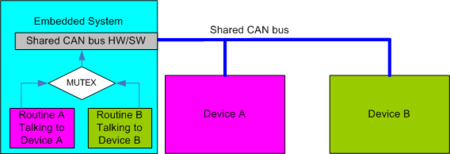
In a interrupt driven embedded system there are two devices connected to a CAN bus. Two independent software routines communicate independent of each other with Device A and Device B through a shared CAN bus. See drawing below.
ARM Thumb
References
- ↑ The definitive guide to the CORTEX-M3, Second edition - section 10.6 page 177 (ISBN978-1-85617-963-8)
- ↑ ARM Assembler reference section 3.3.13 page 3.39
 Under Construction
Under Construction