Difference between revisions of "Cisco basic configuration/en"
m (New page: right|500px|thumb|Picture 1: Putty serial communication {{#css: pre { font-weight: bold; font-size: 150%; color: #00FF00; background: black;} }} In this...) |
m (→Erasing existing configuration) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:Puttyserial.png|right|500px|thumb|Picture 1: Putty serial communication]] | [[Image:Puttyserial.png|right|500px|thumb|Picture 1: Putty serial communication]] | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ---- | |
| − | + | *[[Cisco basic configuration | Læs denne artikel på dansk]] | |
| − | |||
In this example we will configure a Cisco 2621XM Router | In this example we will configure a Cisco 2621XM Router | ||
*hostname Viborg1 | *hostname Viborg1 | ||
| Line 15: | Line 14: | ||
= Checking for existing configuration = | = Checking for existing configuration = | ||
If the router after boot start the ''System Configuration Dialog'' as shown in the dialog below, the router has no ''startup-configuration'' and you can proceed to [[Cisco basic configuration#setup step 1| Setup step 1]]. If the router writes some weird messages, you need to erase the configuration. | If the router after boot start the ''System Configuration Dialog'' as shown in the dialog below, the router has no ''startup-configuration'' and you can proceed to [[Cisco basic configuration#setup step 1| Setup step 1]]. If the router writes some weird messages, you need to erase the configuration. | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang=cli> |
--- System Configuration Dialog --- | --- System Configuration Dialog --- | ||
| − | Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: yes | + | Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: <input>yes</input> |
| − | </ | + | </source> |
= Erasing existing configuration = | = Erasing existing configuration = | ||
To erase the existing configuration you need to login on the router as shown below. Note that we only use the passwords ''cisco'' or ''class''. If your router has another password you need to perform the [[Cisco password recovery procedure| password recovery procedure]]. | To erase the existing configuration you need to login on the router as shown below. Note that we only use the passwords ''cisco'' or ''class''. If your router has another password you need to perform the [[Cisco password recovery procedure| password recovery procedure]]. | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang=cli> |
| − | R5>enable | + | R5><input>enable</input> |
Password: | Password: | ||
R5# | R5# | ||
| − | </ | + | </source> |
After a successful login like shown above you need to erase the ''startup-config'' file in nvram: and ''reload'' the router. Show below. | After a successful login like shown above you need to erase the ''startup-config'' file in nvram: and ''reload'' the router. Show below. | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang=cli> |
| − | R5#erase startup-config | + | R5#<input>erase startup-config</input> |
Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files! Continue? [confirm] | Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files! Continue? [confirm] | ||
[OK] | [OK] | ||
Erase of nvram: complete | Erase of nvram: complete | ||
| − | R5#reload | + | R5#<input>reload</input> |
| − | </ | + | </source> |
And the Router reloads with a empty configuration | And the Router reloads with a empty configuration | ||
<span id="setup step 1"></span> | <span id="setup step 1"></span> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 41: | ||
= setup step 1 = | = setup step 1 = | ||
See the example below | See the example below | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang=cli> |
--- System Configuration Dialog --- | --- System Configuration Dialog --- | ||
| − | Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: yes | + | Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: <input>yes</input> |
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help. | At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 55: | ||
to configure each interface on the system | to configure each interface on the system | ||
| − | Would you like to enter basic management setup? [yes/no]: yes | + | Would you like to enter basic management setup? [yes/no]: <input>yes</input> |
Configuring global parameters: | Configuring global parameters: | ||
| − | Enter host name [Router]: Viborg1 | + | Enter host name [Router]: <input>Viborg1</input> |
The enable secret is a password used to protect access to | The enable secret is a password used to protect access to | ||
privileged EXEC and configuration modes. This password, after | privileged EXEC and configuration modes. This password, after | ||
entered, becomes encrypted in the configuration. | entered, becomes encrypted in the configuration. | ||
| − | Enter enable secret: cisco | + | Enter enable secret: <input>cisco</input> |
The enable password is used when you do not specify an | The enable password is used when you do not specify an | ||
enable secret password, with some older software versions, and | enable secret password, with some older software versions, and | ||
some boot images. | some boot images. | ||
| − | Enter enable password: class | + | Enter enable password: <input>class</input> |
The virtual terminal password is used to protect | The virtual terminal password is used to protect | ||
access to the router over a network interface. | access to the router over a network interface. | ||
| − | Enter virtual terminal password: cisco | + | Enter virtual terminal password: <input>cisco</input> |
| − | Configure SNMP Network Management? [yes]: no | + | Configure SNMP Network Management? [yes]: <input>no</input> |
Current interface summary | Current interface summary | ||
| Line 89: | Line 88: | ||
Configuring interface FastEthernet0/0: | Configuring interface FastEthernet0/0: | ||
| − | Use the 100 Base-TX (RJ-45) connector? [yes]: | + | Use the 100 Base-TX (RJ-45) connector? [yes]:<input>yes</input> |
| − | Operate in full-duplex mode? [no]: yes | + | Operate in full-duplex mode? [no]: <input>yes</input> |
| − | Configure IP on this interface? [yes]: | + | Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:<input>yes</input> |
| − | IP address for this interface: 192.168.22.1 | + | IP address for this interface: <input>192.168.22.1</input> |
| − | Subnet mask for this interface [255.255.255.0] : | + | Subnet mask for this interface [255.255.255.0] :<input>255.255.255.0</input> |
Class C network is 192.168.22.0, 24 subnet bits; mask is /24 | Class C network is 192.168.22.0, 24 subnet bits; mask is /24 | ||
| Line 126: | Line 125: | ||
[2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit. | [2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit. | ||
| − | Enter your selection [2]:2 | + | Enter your selection [2]:<input>2</input> |
| − | </ | + | </source> |
=Setup step 2= | =Setup step 2= | ||
== FastEthernet 0/1 == | == FastEthernet 0/1 == | ||
Now we need to configure ''fastethernet0/1'' | Now we need to configure ''fastethernet0/1'' | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang=cli> |
| − | Viborg1#configure terminal | + | Viborg1><input>enable</input> |
| + | Viborg1#<input>configure terminal</input> | ||
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. | Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. | ||
| − | Viborg1(config)#interface FastEthernet0/1 | + | Viborg1(config)#<input>interface FastEthernet0/1</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0 | + | Viborg1(config-if)#<input>ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-if)#no shutdown | + | Viborg1(config-if)#<input>no shutdown</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-if)#CTRL-Z | + | Viborg1(config-if)#<input>CTRL-Z</input> |
| − | </ | + | </source> |
== Loopback 0 == | == Loopback 0 == | ||
And the ''loopback0'' interface | And the ''loopback0'' interface | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang=cli> |
| − | Viborg1#configure terminal | + | Viborg1#<input>configure terminal</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config)#interface loopback 0 | + | Viborg1(config)#<input>interface loopback 0</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-if)#ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.255 | + | Viborg1(config-if)#<input>ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.255</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-if)#no shutdown | + | Viborg1(config-if)#<input>no shutdown</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-if)#CTRL-Z | + | Viborg1(config-if)#<input>CTRL-Z</input> |
| − | </ | + | </source> |
== Enabling RIP == | == Enabling RIP == | ||
Now the ''rip'' routing protocol | Now the ''rip'' routing protocol | ||
| − | < | + | <source lang=cli> |
| − | Viborg1#configure terminal | + | Viborg1#<input>configure terminal</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config)#ip routing | + | Viborg1(config)#<input>ip routing</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config)#router rip | + | Viborg1(config)#<input>router rip</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-router)#version 2 | + | Viborg1(config-router)#<input>version 2</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-router)#network 192.168.22.0 | + | Viborg1(config-router)#<input>network 192.168.22.0</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-router)#network 172.16.0.0 | + | Viborg1(config-router)#<input>network 172.16.0.0</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-router)#network 10.0.0.0 | + | Viborg1(config-router)#<input>network 10.0.0.0</input> |
| − | Viborg1(config-router)#CTRL-Z | + | Viborg1(config-router)#<input>CTRL-Z</input> |
| − | </ | + | </source> |
| + | {{Source cli}} | ||
[[Category:Cisco]][[Category:CCNA]][[Category:IOS]][[Category:Network]] | [[Category:Cisco]][[Category:CCNA]][[Category:IOS]][[Category:Network]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:15, 27 November 2012
In this example we will configure a Cisco 2621XM Router
- hostname Viborg1
- fastethernet 0/0 - 192.168.22.1/24
- fastethernet 0/1 - 172.16.0.1/16
- loopback 0/0 - 10.10.10.1/32
- RIP version 2 on both subnets
Connect a cisco Roolover cable from the Routers Consoleport to a COM port on your PC. Start a terminalemulator. I will recommend the terminalemulator putty
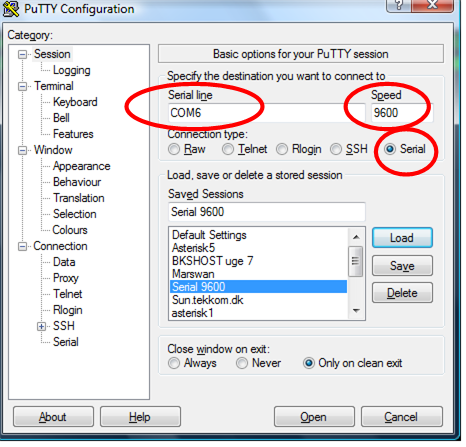
Start putty and fill out the serial data. Marked with red rings in picture 1. (My COM-port is on COM6, you need to find your own COM-port number)
Start the router and you can see on Putty that it is booting. When it has bootet you need to remove the existing configuration if it has one.
Contents
Checking for existing configuration
If the router after boot start the System Configuration Dialog as shown in the dialog below, the router has no startup-configuration and you can proceed to Setup step 1. If the router writes some weird messages, you need to erase the configuration.
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: <input>yes</input>Erasing existing configuration
To erase the existing configuration you need to login on the router as shown below. Note that we only use the passwords cisco or class. If your router has another password you need to perform the password recovery procedure.
R5><input>enable</input>
Password:
R5#After a successful login like shown above you need to erase the startup-config file in nvram: and reload the router. Show below.
R5#<input>erase startup-config</input>
Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all configuration files! Continue? [confirm]
[OK]
Erase of nvram: complete
R5#<input>reload</input>And the Router reloads with a empty configuration
setup step 1
See the example below
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: <input>yes</input>
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
Basic management setup configures only enough connectivity
for management of the system, extended setup will ask you
to configure each interface on the system
Would you like to enter basic management setup? [yes/no]: <input>yes</input>
Configuring global parameters:
Enter host name [Router]: <input>Viborg1</input>
The enable secret is a password used to protect access to
privileged EXEC and configuration modes. This password, after
entered, becomes encrypted in the configuration.
Enter enable secret: <input>cisco</input>
The enable password is used when you do not specify an
enable secret password, with some older software versions, and
some boot images.
Enter enable password: <input>class</input>
The virtual terminal password is used to protect
access to the router over a network interface.
Enter virtual terminal password: <input>cisco</input>
Configure SNMP Network Management? [yes]: <input>no</input>
Current interface summary
Any interface listed with OK? value "NO" does not have a valid configuration
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
FastEthernet0/0 unassigned NO unset up down
FastEthernet0/1 unassigned NO unset up down
Enter interface name used to connect to the
management network from the above interface summary: FastEthernet0/0
Configuring interface FastEthernet0/0:
Use the 100 Base-TX (RJ-45) connector? [yes]:<input>yes</input>
Operate in full-duplex mode? [no]: <input>yes</input>
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]:<input>yes</input>
IP address for this interface: <input>192.168.22.1</input>
Subnet mask for this interface [255.255.255.0] :<input>255.255.255.0</input>
Class C network is 192.168.22.0, 24 subnet bits; mask is /24
The following configuration command script was created:
hostname Viborg1
enable secret 5 $1$Q0eK$BS6PyvYOB0dfDILGrDYLc.
enable password class
line vty 0 4
password cisco
no snmp-server
!
no ip routing
!
interface FastEthernet0/0
no shutdown
media-type 100BaseX
full-duplex
ip address 192.168.22.1 255.255.255.0
no mop enabled
!
interface FastEthernet0/1
shutdown
no ip address
!
end
[0] Go to the IOS command prompt without saving this config.
[1] Return back to the setup without saving this config.
[2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit.
Enter your selection [2]:<input>2</input>Setup step 2
FastEthernet 0/1
Now we need to configure fastethernet0/1
Viborg1><input>enable</input>
Viborg1#<input>configure terminal</input>
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Viborg1(config)#<input>interface FastEthernet0/1</input>
Viborg1(config-if)#<input>ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.0.0</input>
Viborg1(config-if)#<input>no shutdown</input>
Viborg1(config-if)#<input>CTRL-Z</input>Loopback 0
And the loopback0 interface
Viborg1#<input>configure terminal</input>
Viborg1(config)#<input>interface loopback 0</input>
Viborg1(config-if)#<input>ip address 10.10.10.1 255.255.255.255</input>
Viborg1(config-if)#<input>no shutdown</input>
Viborg1(config-if)#<input>CTRL-Z</input>Enabling RIP
Now the rip routing protocol
Viborg1#<input>configure terminal</input>
Viborg1(config)#<input>ip routing</input>
Viborg1(config)#<input>router rip</input>
Viborg1(config-router)#<input>version 2</input>
Viborg1(config-router)#<input>network 192.168.22.0</input>
Viborg1(config-router)#<input>network 172.16.0.0</input>
Viborg1(config-router)#<input>network 10.0.0.0</input>
Viborg1(config-router)#<input>CTRL-Z</input>