Difference between revisions of "Storage Area Network"
m |
m (→Additional reading) |
||
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
*[[image:PDF-logo.png|25px]][http://www.snia.org/education/storage_networking_primer/education/storage_networking_primer/stor_virt/sniavirt.pdf Storage virtualization by SNIA] | *[[image:PDF-logo.png|25px]][http://www.snia.org/education/storage_networking_primer/education/storage_networking_primer/stor_virt/sniavirt.pdf Storage virtualization by SNIA] | ||
* [http://www.snia.org/education/ SNIA education WEB. Lots of god stuff] | * [http://www.snia.org/education/ SNIA education WEB. Lots of god stuff] | ||
| − | + | *[[SAN Design Considerations|Cisco CCDP Storage Area Network]] | |
| − | + | =Links= | |
| − | + | *[http://whiptail.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/05/ACCELA-Product-Brief.pdf Whiptail SAN with 250.000 IOPS (Write)] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 10:21, 11 May 2012
Definition
1. A network whose primary purpose is the transfer of data between computer systems and storage elements and among storage elements.
A SAN consists of a communication infrastructure, which provides physical connections, and a management layer, which organizes the connections, storage elements, and computer systems so that data transfer is secure and robust. The term SAN is usually (but not necessarily) identified with block I/O services rather than file access services.
2. A storage system consisting of storage elements, storage devices, computer systems, and/or appliances, plus all control software, communicating over a network.
The SNIA definition specifically does not identify the term SAN with Fibre Channel technology. When the term SAN is used in connection with Fibre Channel technology, use of a qualified phrase such as "Fibre Channel SAN" is encouraged. According to this definition, an Ethernet-based network whose primary purpose is to provide access to storage elements would be considered a SAN. SANs are sometimes also used for system interconnection in clusters.
- definition source Storage Networking Industry Association (SNIA) definition
- SNIA's] full definition of a SAN
See also
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
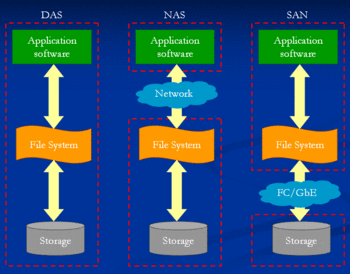
Differences between a SAN and a NAS
- A NAS is defined by SNIA as
- systems that provide file services to host computers using file access protocols
- A SAN is is defined by SNIA as
- The term SAN is usually (but not necessarily) identified with block I/O services rather than file access services.
Conclusion
- A NAS can always be called a SAN
- A SAN can not necessarily be called a NAS unless it offers File Services via a network.
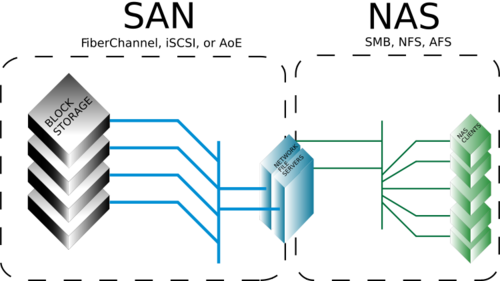
A NAS using a SAN backend
It is possible for a NAS to use a SAN backend as displayed in picture 2.
Additional reading
 IP Storage White Paper by SNIA
IP Storage White Paper by SNIA Storage Network Security by SNIA
Storage Network Security by SNIA Storage virtualization by SNIA
Storage virtualization by SNIA- SNIA education WEB. Lots of god stuff
- Cisco CCDP Storage Area Network