Difference between revisions of "CCNP TSHOOT Learning Guide/Chapter 5"
m (→Redistributiuon) |
m (→prefix lists) |
||
| Line 111: | Line 111: | ||
==Route-maps== | ==Route-maps== | ||
==prefix lists== | ==prefix lists== | ||
| + | {{:Route_optimization#PBR:_Policy_Based_Routing}} | ||
{{Source cli}} | {{Source cli}} | ||
| + | |||
=Troubleshooting EIGRP= | =Troubleshooting EIGRP= | ||
EIGRP uses three tables | EIGRP uses three tables | ||
Revision as of 16:09, 18 June 2010
Maintaining and Troubleshooting Routing Solutions
Contents
Redistributiuon
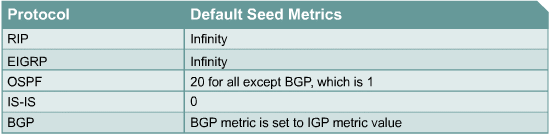
| Protocol | Default Seed Metric |
|---|---|
| RIP | Infinity |
| IGRP/EIGRP | Infinity |
| OSPF | 20 except from BGP then 1 |
| ISIS | 0 |
| BGP | IGP |
Redistribute from OSPF to EIGRP
Example
router eigrp 1
redistribute ospf 100 metric 64 10000 255 1 1500IOS Commands to verify Routing Functions
Verifying and Troubleshooting Route Propagation
Debug ip routing
R1#<input>debug ip routing</input>
IP routing debugging is on
R1#<input>clear ip eigrp 1 neighbors</input>
R1#
Jun 18 12:45:44: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: IP-EIGRP(0) 1: <notice>Nei 10.1.2.1 (Fa0/1) is down: manually cleared</notice>
Jun 18 12:45:44: RT: delete route to 10.1.10.0 via 10.1.2.1, eigrp metric [90/28416]
Jun 18 12:45:44: RT: no routes to 10.1.10.0
Jun 18 12:45:44: RT: NET-RED 10.1.10.0/24
<notice>...OUTPUT OMITTED...</notice>
Jun 18 12:45:44: RT: NET-RED 10.1.200.0/24
Jun 18 12:45:46: RT: NET-RED 0.0.0.0/0
Jun 18 12:45:47: %DUAL-5-NBRCHANGE: IP-EIGRP(0) 1: <notice>Nei 10.1.2.1 (Fa0/1) is up: new adjacency</notice>
Jun 18 12:45:47: RT: network 10.0.0.0 is now variably masked
Jun 18 12:45:47: RT: add 10.1.10.0/24 via 10.1.2.1, eigrp metric [90/28416]
Jun 18 12:45:47: RT: NET-RED 10.1.10.0/24
Jun 18 12:45:47: RT: add 10.1.20.0/24 via 10.1.2.1, eigrp metric [90/28416]
<notice>...OUTPUT OMITTED...</notice>
Jun 18 12:45:47: RT: add 10.1.203.1/32 via 10.1.2.1, eigrp metric [90/158976]
Jun 18 12:45:47: RT: NET-RED 10.1.203.1/32
R1#<input>no debug ip routing</input>
IP routing debugging is offRoute Profiling
R1(config)#<input>ip route profile</input>
R1(config)#<input>^Z</input>
Jun 18 12:46:41.803: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
R1#<input>sh ip route profile</input>
IP routing table change statistics:
Frequency of changes in a 5 second sampling interval
-------------------------------------------------------------
Change/ Fwd-path Prefix Nexthop Pathcount Prefix
interval change add change change refresh
-------------------------------------------------------------
0 2 2 2 2 1
1 0 0 0 0 1
2 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 0 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 0 0
5 0 0 0 0 0
10 0 0 0 0 0
15 0 0 0 0 0
20 0 0 0 0 0
25 0 0 0 0 0
30 0 0 0 0 0
55 0 0 0 0 0
80 0 0 0 0 0
105 0 0 0 0 0
130 0 0 0 0 0
155 0 0 0 0 0
280 0 0 0 0 0
405 0 0 0 0 0
-------------------------------------------------------------
Change/ Fwd-path Prefix Nexthop Pathcount Prefix
interval change add change change refresh
-------------------------------------------------------------
530 0 0 0 0 0
655 0 0 0 0 0
780 0 0 0 0 0
1405 0 0 0 0 0
2030 0 0 0 0 0
2655 0 0 0 0 0
3280 0 0 0 0 0
3905 0 0 0 0 0
7030 0 0 0 0 0
10155 0 0 0 0 0
13280 0 0 0 0 0
Overflow 0 0 0 0 0
R1#<input>conf t</input>
R1(config)#<input>no ip route profile</input>show ip cef
SW1#show ip cef exact-route 172.16.4.16 192.168.22.73
172.16.4.16 -> 192.168.22.73 => IP adj out of Vlan1, addr 172.16.4.16show ip prot
remember
Route-maps
prefix lists
redistribution cavets
Routing loops
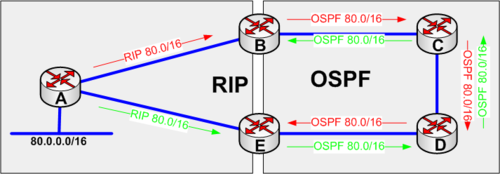
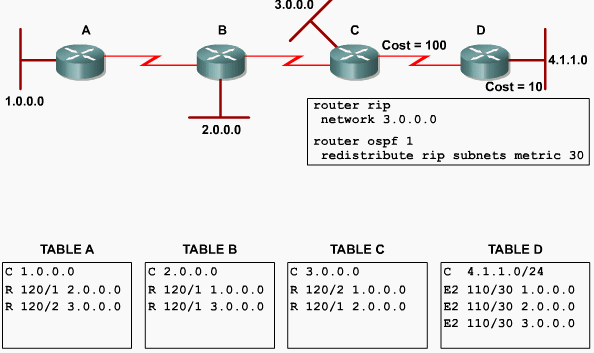
redistribute RIP into OSPF example
Consider the network below and follow the red update path.
- Router A updates router B with RIP. Router B now learne the network 80.0.0.0/16.
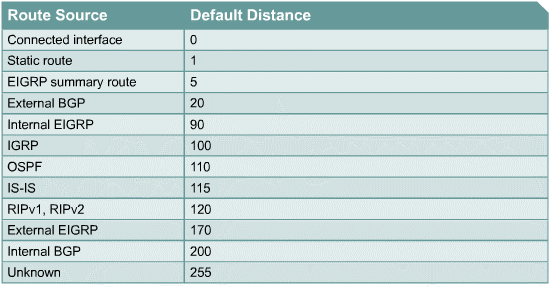
- Please note that the administrative distance for RIP is 120.
- Router B now redistributes 80.0.0.0/16 into OSPF.
- Note that OSPF has an administrative distance of 110.
- Router B updates router C as an external OSPF route administrative distance 110
- Router C updates router D as an external OSPF route administrative distance 110
- Router D updates router E as an external OSPF route administrative distance 110
- Router E now has two router to 80.0.0.0/16
- Via RIP directly to Router A (Preferred route)
- Via OSPF to router D - Path D->C->B->A.
- Router E sends traffic to 80.0.0.0/16 to router D because OSPF(110) administrative distance is better than RIP's(120).
Avoiding Routing loop
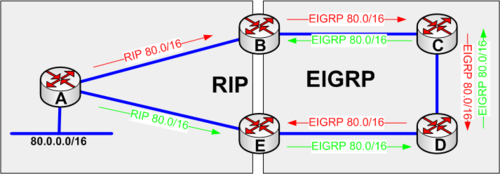
redistribute RIP into EIGRP example
With EIGRP we avoid the routing loop seen from OSPF above. EIGRP has two different administrative distances.
One for internal routes 90 and one for externally learned routes 170.
Consider the network below and follow the red update path.
- Router A updates router B with RIP. Router B now learne the network 80.0.0.0/16.
- Please note that the administrative distance for RIP is 120.
- Router B now redistributes 80.0.0.0/16 into EIGRP.
- EIGRP has an internal route administrative distance of 90. and
- EIGRP has an external route administrative distance of 170.
- Router B updates router C as an external EIGRP route administrative distance 170
- Router C updates router D as an external EIGRP route administrative distance 170
- Router D updates router E as an external EIGRP route administrative distance 170
- Router E now has two router to 80.0.0.0/16
- Via RIP directly to Router A (Preferred route)
- Via EIGRP to router D - Path D->C->B->A.
- Router E sends traffic to 80.0.0.0/16 to router A because RIP(120) administrative distance is better than EIGRP external(170).
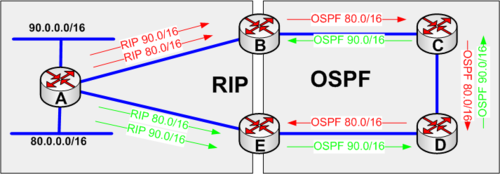
Distribute lists
You can filter updates with distribute lists. The exampe below shows filtering of incoming updates. You can also filter outgoing updates.
hostname B
!
router rip
version 2
distribute-list 23 in
!
access-list 23 deny 90.0.0.0 0.0.255.255
access-list 23 permit anyRouter B Configuration of distribute list
hostname E
!
router rip
version 2
distribute-list 3 in
!
access-list 3 deny 80.0.0.0 0.0.255.255
access-list 3 permit anyRouter E Configuration of distribute list
prefix lists
Routes in routetable
| Nr. | Network |
|---|---|
| 1 | 10.0.0.0/8 |
| 2 | 10.128.0.0/9 |
| 3 | 10.1.1.0/24 |
| 4 | 10.1.2.0/24 |
| 5 | 10.128.10.4/30 |
| 6 | 10.128.10.8/30 |
| Prefix list | Matches in previos table |
|---|---|
| 10.0.0.0/8 | 1 |
| 10.128.0.0/9 | 2 |
| 10.0.0.0/8 ge 9 | 2,3,4,5,6 |
| 10.0.0.0/8 ge 24 le 24 | 3,4 |
| 10.0.0.0/8 le 24 | 1,2,3,4 |
| 0.0.0.0/0 | None |
| 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 | All |
Example
Prefix-lists are numbered. In this example "secret net" are not announced.
- Note: As with access-lists there are an implicit deny in the end.
ip prefix-list SECRET-NET seq 10 deny 172.16.0.0/16
ip prefix-list SECRET-NET seq 20 deny 192.168.22.0/24
ip prefix-list SECRET-NET seq 30 permit 0.0.0.0/0 le 32 !Permit all other nets
!
router bgp 100
neighbor 10.1.2.3 remote-as 200
neighbor 10.1.2.3 prefix-list SECRET-NET outPBR: Policy Based Routing
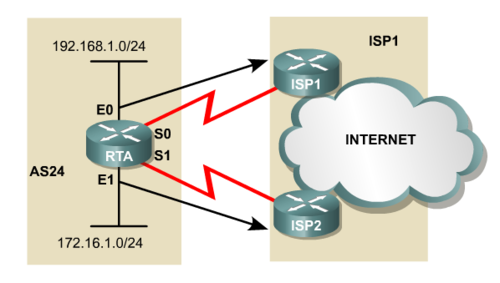
PBR or Policy Based Routing gives more control and more options than distribute lists - see above. PBR introduces the set command which set the interface or next-hop address to which the packet should be sent. To select which packets should go where you can use the match command and match the based on for example source or destination addresses.
In the picture below the traffic from 192.168.1.0/24 on E0 interface must route to ISP1 and traffic from 172.16.1.0/24 on E1 must route to ISP1.
hostname RTA
!
access-list 37 permit 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
access-list 48 permit 172.16.1.0 0.0.0.255
!
route-map ISP1 permit 10
match ip address 37
set interface s0
!
route-map ISP2 permit 20
match ip address 48
set interface s1
!
interface e0
ip policy route-map ISP1
!
interface e1
ip policy route-map ISP2Seed metric
Troubleshooting EIGRP
EIGRP uses three tables
- interface table:
| Table | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface | Contains list of all interfaces that have been enabled for processing of EIGRP packets. Passive interfaces are not listed in this table. |
| Neighbor | Keeps track of all active EIGRP neighbors. Neighbours are added on the reception of hello packet and are removed when the hold-time expires or when the associated interface goes down or removed from the Interface table. This table also keeps track on status on Routing information exchanged. |
| Topology | Holds all Routes received from neighbors, locally injected or redistributed into EIGRP. EIGRP selects the best routes from this table based on the DUAL algorithm. |
Monitoring EIGRP
show commands
- show ip eigrp interface
- show ip eigrp neighbors
- show ip eigrp topology
debug commands
- debug ip routing
- debug eigrp packets - Many options here (terse - except hello packets)
- debug ip eigrp neighbor as-number network mask
- debug ip eigrp as-number network mask - limit info. from debug eigrp packets
Examples
R1#<input>sh ip protocols</input>
Routing Protocol is "eigrp 1"
Outgoing update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Incoming update filter list for all interfaces is not set
Default networks flagged in outgoing updates
Default networks accepted from incoming updates
EIGRP metric weight K1=1, K2=0, K3=1, K4=0, K5=0
EIGRP maximum hopcount 100
EIGRP maximum metric variance 1
Redistributing: static, eigrp 1
EIGRP NSF-aware route hold timer is 240s
Automatic network summarization is not in effect
Maximum path: 4
Routing for Networks:
10.1.2.0/30
192.168.1.1/32
Passive Interface(s):
FastEthernet0/0
Service-Engine0/1
Serial0/0/0
Serial0/0/1
ATM0/3/0
NVI0
Loopback0
Passive Interface(s):
VoIP-Null0
Routing Information Sources:
Gateway Distance Last Update
10.1.2.1 90 00:07:33
Distance: internal 90 external 170Many options debugging eigrp
R1#<input>debug eigrp packets ?</input>
SIAquery EIGRP SIA-Query packets
SIAreply EIGRP SIA-Reply packets
ack EIGRP ack packets
hello EIGRP hello packets
ipxsap EIGRP ipxsap packets
probe EIGRP probe packets
query EIGRP query packets
reply EIGRP reply packets
request EIGRP request packets
retry EIGRP retransmissions
stub EIGRP stub packets
terse Display all EIGRP packets except Hellos
update EIGRP update packets
verbose Display all EIGRP packets
<cr>Troubleshooting OSPF
| Table | Description |
|---|---|
| Interface table | List all interfaces enabled for OSPF. The directly connected subnets are included in the TYPE-1 Router LSA the Router injects into the OSPF link-state database. Passive-interfaces is listed in the tables |
| Neighbor table | Used to keep track of all OSPF neighbors. Neighbors are added on the reception of a hello packet and removed when the dead-time expires or when the associated interface goes down. |
| Link State database | Main data structure containing all network topology information for the OSPF process. |
| Routing Information Base | Contains results from the SPF algorithm. OSPF offers the contents of the RIB to the Routing Table. |
INSERT TABLE 5.2 and FIGURE 5.3 from page 168
Cisco IOS OSPF commands
Show commands
- show ip ospf interface
- show ip ospf neighbor
- show ip ospf datatbase
- show ip ospf statistics
debug commands
- debug ip routing
- debug ip ospf packet
- debug ip ospf adj
- debug ip ospf monitor