Difference between revisions of "Calendar standards"
m (moved Time and date standards to Calendar standards) |
m (added Category:Time using HotCat) |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
=Links= | =Links= | ||
*[http://www.fourmilab.ch/documents/calendar/ Calendar converter] | *[http://www.fourmilab.ch/documents/calendar/ Calendar converter] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category:Time]] | ||
Revision as of 13:12, 6 July 2013
The purpose of this article is to describe the necessary background information to understand time and date issues on the Internet and in computer clocks.
Western time standards
The western time standards dividing the year into 12 months, the day into 24 hours or 12 hours AM and 12 hours PM, the hour into 60 minutes and the hour into 60 seconds derived from the Mesopotamia[1] using the sexagesimal[2] or base 60 numeral system.
- Note:
- The base 60 systems is a highly composite number as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10, 12, 15, 20, 30 and 60 are factors.
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar[3] was introduced by Julius Caesar in 46 BC and was the dominant calendar in the western world, until it was superseded by the Gregorian calendar.
- NOTE: The term Julian day[4] is the day in the year counted from January. 1st and should not be confused with the Julian calendar
Leap year
The Earths rotation of the Sun is not exactly 365 days, but sligtly higher. To avoid drift over centuries between the calendar year[5] and the astronomical year[6] or the seasons, it was necessary to add an extra day at intervals.
The Julian calendar has 12 months, 365 days and a leap day added in February every four years giving an average year of 365,25 days or 365 days and 6 hours.
<math>\text{Average year} = 365 \text{ days/year } + {1 \over 4} = 365,25 \text{ days}</math>
Problem with the Julian calendar
The actual average earth year is a few minutes shorter than 365,25 days meaning that the calendar gained about three days every four centuries.
The historical Julian calendar is currently 13 days advanced of the Gregorian calendar.
Gregorian calendar
I the western world we are following the Gregorian calendar[7] also called the Western or the Christian calendar. The Gregorian calendar is internationally the most widely accepted calendar and are used as civil calendar.
It was discovered that the actual average earth year was nearly 365,2425[8] days instead of the Julian 365,25 days, which lead to the calendar reform in the year 1582 introduced by Pope Gregory XIII[9].
Gregorian leap year
To compensate for the drift in the Julian calendar the rules for the leap year was changed to:
- Rule 1: The year is evenly divisible by 4;
- Rule 2: If the year can be evenly divided by 100 it is NOT a leap year.
- Rule 3: Exception from rule 2 - If the year is evenly divisible by 400 it is a leap year.
Number of leap years in a 400 year period
Given the rule above there will be 97 leap years in a period of 400 years
<math>rule_1 - rule_2 + rule_3 = ( {400 \text{ year} \over 4 \text{ year}} ) - ( {400 \text{ year} \over 100 \text{ yeas}} ) + ( {400 \text{ year} \over 400 \text{ year}} ) = 97</math>
Number of days in a 400 years period
<math>\text{days in 400 year } \eqcirc 400 \text{ year} * 365 \text{ days/year} + 97 \text{ days } \eqcirc 146097 \text{ days}</math>
Average year length in a 400 years period
Given from above that there are 97 leap years in a 400 years period, the average year length will be
<math>\text{Average year} = {\text{ days in 400 year } \over 400 \text{ year}} = {146097 \text{ days} \over 400 \text{ year}} = 365,2425 \text{ days/year}</math>
Adoption of the Gregorian calendar
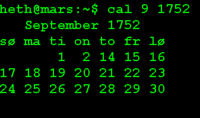
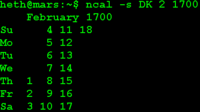
The Gregorian was adopted by various countries in different countries. For example Denmark adopted the Gregorian calender March 1st 1700[10] dropping days in February and the British Empire in September 14th 1752.
When switching from the Julian to the Gregorian calendar it was necessary to adjust the calender by dropping the the days accumulated in the nearly 1800 years since the Julian calender was introduced.
In the western world today we refer to the British adoption of the Gregorian calender September 14th 1752.
Problems with the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is a Solar calendar whose dates indicate the position of the earth on its revolution around the sun. The observed average day of 365.2425 achieved with the above explained leap year is still a approximation missing about 1 day every 3.000 years.