Difference between revisions of "Hot Standby Router Protocol"
From Teknologisk videncenter
m |
m |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
HSRP or Hot Standby Router Protocol is a protocol defined by Cisco and now described in [http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2281.txt rfc2281]. | HSRP or Hot Standby Router Protocol is a protocol defined by Cisco and now described in [http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2281.txt rfc2281]. | ||
| − | = Other high availability Router protocols | + | = Purpose of HSRP = |
| + | The purpose of HSRP is to ensure network connectivity in case of Router or access circuit failure, by having one or more ''standby'' Router(s) waiting to take over from the failing ''active'' Router. | ||
| + | |||
| + | = Other high availability Router protocols = | ||
*GLBP [[Gateway Load Balancing Protocol]] | *GLBP [[Gateway Load Balancing Protocol]] | ||
*VRRP [[Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol]] | *VRRP [[Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | = How does HSRP work = | ||
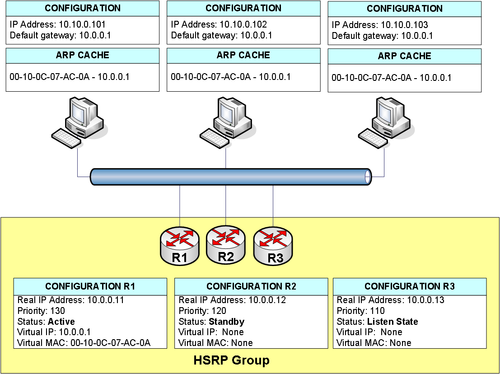
| + | HSRP works by two or more Routers agreeing upon which Router serves the ''virtual Router''. | ||
| + | == The Virtual Router == | ||
| + | The Virtual Router is a MAC-address and a IP Address the ''active'' Router serves beside its configured IP address. If the ''active'' Router fails one of the ''standby'' Routers becomes the Virtual Router by serving the virtual MAC-address and IP Address. | ||
| + | [[Image:HSRP1.png|thumb|500px|float|HSRP group with Router R1 active and Router R2 and R3 as standby Routers]] | ||
[[Category:Cisco]][[Category:CCNP]][[Category:IOS]][[Category:Network]][[Category:CCNP3]] | [[Category:Cisco]][[Category:CCNP]][[Category:IOS]][[Category:Network]][[Category:CCNP3]] | ||
Revision as of 09:25, 3 May 2009
HSRP or Hot Standby Router Protocol is a protocol defined by Cisco and now described in rfc2281.
Contents
Purpose of HSRP
The purpose of HSRP is to ensure network connectivity in case of Router or access circuit failure, by having one or more standby Router(s) waiting to take over from the failing active Router.
Other high availability Router protocols
How does HSRP work
HSRP works by two or more Routers agreeing upon which Router serves the virtual Router.
The Virtual Router
The Virtual Router is a MAC-address and a IP Address the active Router serves beside its configured IP address. If the active Router fails one of the standby Routers becomes the Virtual Router by serving the virtual MAC-address and IP Address.