Difference between revisions of "Gateway Load Balancing Protocol"
From Teknologisk videncenter
m (→Timers) |
m (→AVF - Active Virtual Forwarder) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
=== AVF - Active Virtual Forwarder === | === AVF - Active Virtual Forwarder === | ||
The AVF Routers Route traffic from the connected clients. Each AVF is assigned its own MAC-Address. The MAC-Address is assigned from the AVG. | The AVF Routers Route traffic from the connected clients. Each AVF is assigned its own MAC-Address. The MAC-Address is assigned from the AVG. | ||
| + | === Load Balancing === | ||
| + | When the clients broadcast [[ARP]] requests to get the MAC Address of the default gateway - 10.0.0.1 - the AVG responds with a MAC-Address of one of the AVF's. load balancing can be either | ||
| + | * Round Robin: The AVG responds to ARP requests in sequence first AVF, second AVF, third AVF, first AVF.... (Default) | ||
| + | * Host dependent: Specifies a load balancing method based on the MAC address of a host where the same forwarder is always used for a particular host while the number of GLBP group members remains unchanged. | ||
| + | * Weighted: Specifies a load balancing method that is dependent on the weighting value advertised by the gateway. | ||
| + | |||
=== Timers === | === Timers === | ||
Default the hello time for GLBP is 3 seconds and holdtime is 10 seconds. In the example hello time is set to 0.25 second and holdtime is 0.7 second. | Default the hello time for GLBP is 3 seconds and holdtime is 10 seconds. In the example hello time is set to 0.25 second and holdtime is 0.7 second. | ||
Revision as of 14:30, 3 May 2009
Contents
Purpose of GLBP
- The purpose of GLBP is to ensure network connectivity in case of Router or access circuit failure. GLBP automatically Load balances the load from the IP traffic sources.
- Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that attempts to overcome the limitations of existing redundant router protocols by adding basic load balancing functionality.
Other high availability protocols
GLBP functions
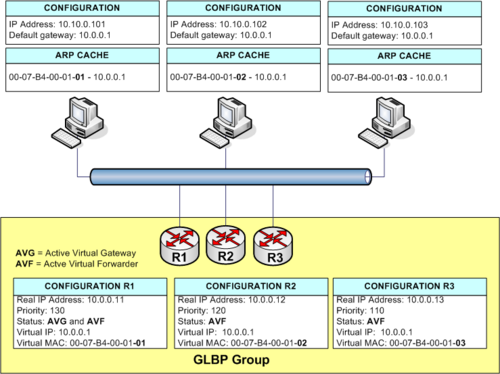
- Active virtual gateway (AVG): Members of a GLBP group elect one gateway to be the AVG for that group. Other group members provide backup for the AVG if the AVG becomes unavailable. The AVG assigns a virtual MAC address to each member of the group.
- Active virtual forwarder (AVF): Each gateway assumes responsibility for forwarding packets sent to the virtual MAC address assigned to it by the AVG. These gateways are known as AVFs for their virtual MAC address.
- Communication: GLBP members communicate with each other using hello messages sent every 3 seconds to the multicast address 224.0.0.102, User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port 3222.
GLBP features
- Load sharing: Traffic from LAN clients can be shared by multiple routers.
- Multiple virtual routers: Up to 1,024 virtual routers (GLBP groups) can be on each physical interface of a router, and there can be up to four virtual forwarders per group.
- Preemption: You can preempt an AVG with a higher priority backup virtual gateway. Forwarder preemption works in a similar way, except that it uses weighting instead of priority and is enabled by default.
- Efficient resource utilization: Any router in a group can serve as a backup, which eliminates the need for a dedicated backup router because all available routers can support network traffic.
How does GLBP work
GLBP RolesAVG - Active Virtual GatewayThe Router with the highest priority is chosen as the AVG. The AVG has the responsebility of assigning MAC addresses to the AVF Routers. AVF - Active Virtual ForwarderThe AVF Routers Route traffic from the connected clients. Each AVF is assigned its own MAC-Address. The MAC-Address is assigned from the AVG. Load BalancingWhen the clients broadcast ARP requests to get the MAC Address of the default gateway - 10.0.0.1 - the AVG responds with a MAC-Address of one of the AVF's. load balancing can be either
TimersDefault the hello time for GLBP is 3 seconds and holdtime is 10 seconds. In the example hello time is set to 0.25 second and holdtime is 0.7 second. |
hostname R1 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 10.0.0.11 255.0.0.0 glbp 7 ip 10.0.0.1 glbp 7 priority 130 glbp 7 timers msec 200 msec 700 |
hostname R2 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 10.0.0.12 255.0.0.0 glbp 7 ip 10.0.0.1 glbp 7 priority 120 glbp 7 timers msec 200 msec 700 |
hostname R3 ! interface FastEthernet1/0 ip address 10.0.0.13 255.0.0.0 glbp 7 ip 10.0.0.1 glbp 7 priority 110 glbp 7 timers msec 200 msec 700 |