Difference between revisions of "CCNA Explorer semester 2 kapitel 11"
m |
m |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
# If the router-id is not configured, the router chooses highest IP address of any of its loopback interfaces. | # If the router-id is not configured, the router chooses highest IP address of any of its loopback interfaces. | ||
# If no loopback interfaces are configured, the router chooses highest active IP address of any of its physical interfaces. | # If no loopback interfaces are configured, the router chooses highest active IP address of any of its physical interfaces. | ||
| − | + | {| | |
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 12.gif|800px|left|thumb|Der er ingen Loopback interfaces konfigureret]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ==Loopback interface OSPF eksempel == | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 13.gif|800px|left|thumb|Konfiguration af Loopback interfaces]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 14.gif|800px|left|thumb|Netværks tegning]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 15.gif|800px|left|thumb|Ny Router ID]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | = Verifying OSPF = | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 16.gif|800px|left|thumb|Verificer OSPF naboer]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | *'''Neighbor ID''' - The router ID of the neighboring router. | ||
| + | *'''Pri''' - The OSPF priority of the interface. This is discussed in a later section. | ||
| + | *'''State''' - The OSPF state of the interface. FULL state means that the router and its neighbor have identical OSPF link-state databases. OSPF states are discussed in CCNP. | ||
| + | *'''Dead Time''' - The amount of time remaining that the router will wait to receive an OSPF Hello packet from the neighbor before declaring the neighbor down. This value is reset when the interface receives a Hello packet. | ||
| + | *'''Address''' - The IP address of the neighbor's interface to which this router is directly connected. | ||
| + | *'''Interface''' - The interface on which this router has formed adjacency with the neighbor. | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 17.gif|800px|left|thumb|show ip protocols]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 18.gif|800px|left|thumb|show ip ospf]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 19.gif|800px|left|thumb|show ip ospf interface]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | =Route tabellen= | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 20.gif|800px|left|thumb|R1]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 21.gif|800px|left|thumb|R2]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:Ccna explorer 2 chap 11 23.gif|800px|left|thumb|R3]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
[[Category:CCNA]] | [[Category:CCNA]] | ||
Revision as of 08:00, 18 April 2010
Contents
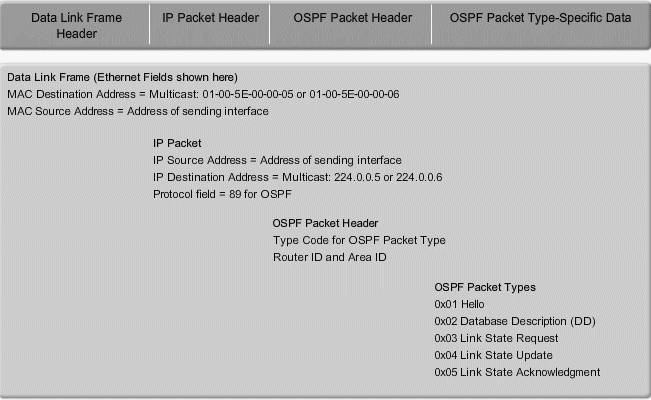
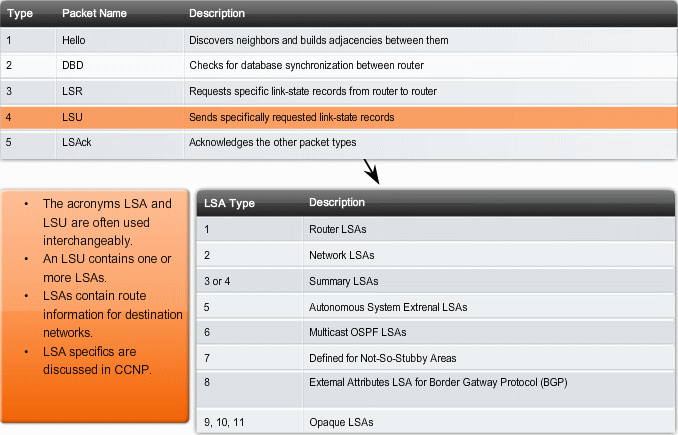
OSPF Pakketyper
1. Hello - Hello packets are used to establish and maintain adjacency with other OSPF routers. The hello protocol is discussed in detail in the next topic.
2. DBD - The Database Description (DBD) packet contains an abbreviated list of the sending router's link-state database and is used by receiving routers to check against the local link-state database.
3. LSR - Receiving routers can then request more information about any entry in the DBD by sending a Link-State Request (LSR).
4. LSU - Link-State Update (LSU) packets are used to reply to LSRs as well as to announce new information. LSUs contain seven different types of Link-State Advertisements (LSAs). LSUs and LSAs are briefly discussed in a later topic.
5. LSAck - When an LSU is received, the router sends a Link-State Acknowledgement (LSAck) to confirm receipt of the LSU.
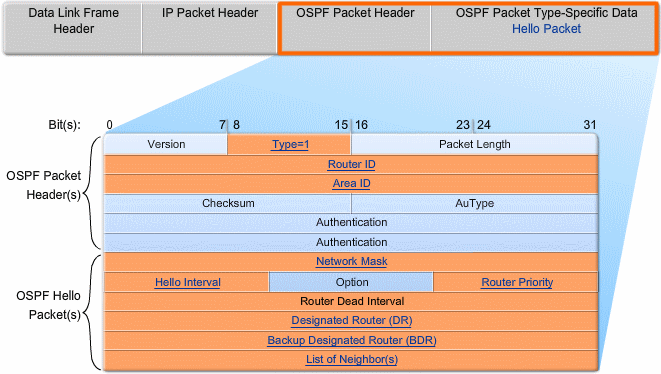
HELLO protocol
- Type: OSPF Packet Type: Hello (1), DD (2), LS Request (3), LS Update (4), LS ACK (5)
- Router ID: ID of the originating router
- Area ID: area from which the packet originated
- Network Mask: Subnet mask associated with the sending interface
- Hello Interval: number of seconds between the sending router's hellos
- Router Priority: Used in DR/BDR election (discussed later)
- Designated Router (DR): Router ID of the DR, if any
- Backup Designated Router (BDR): Router ID of the BDR, if any
- List of Neighbors: lists the OSPF Router ID of the neighboring router(s)
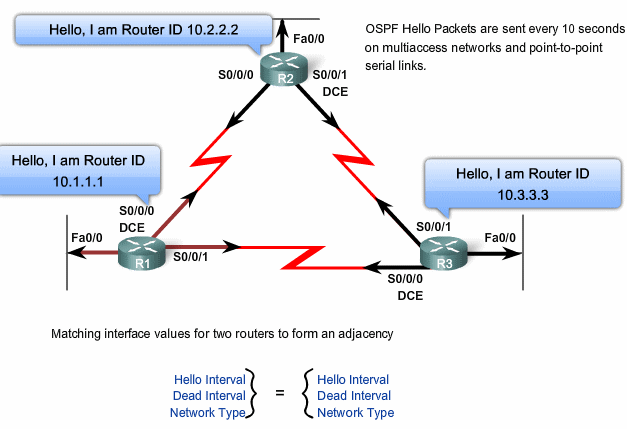
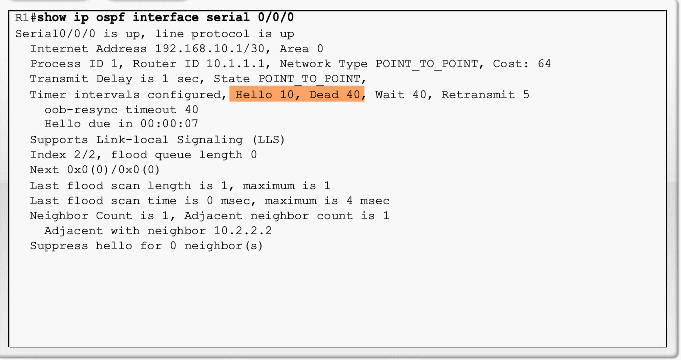
Mismatch OSPF timere
Hvis HELLO interval og DEAD interval ikke er ens på naboerne kan der ikke laves et adjacencie.
Link State Updates
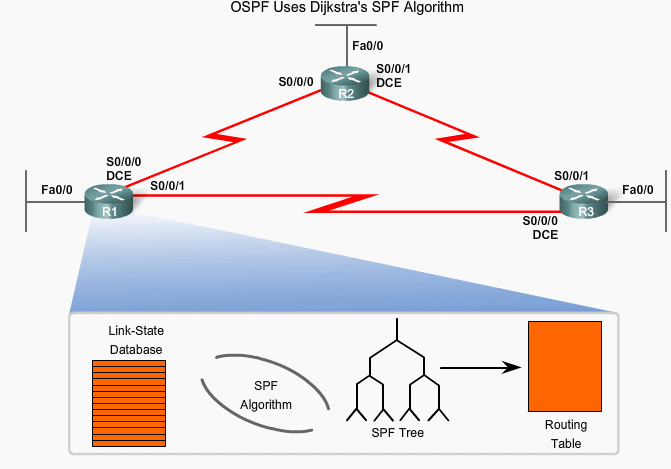
OSPF algoritmen
OSPF eksempel
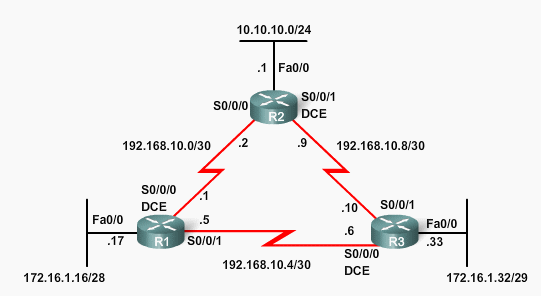
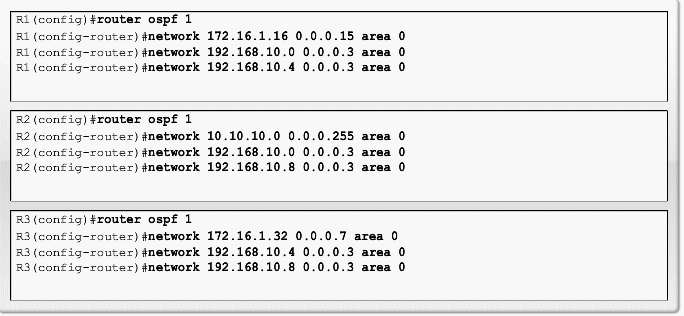
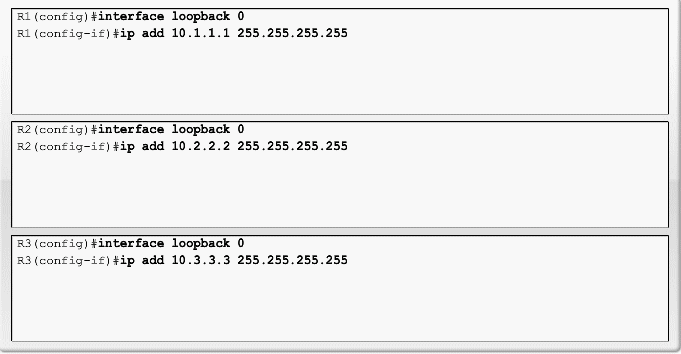
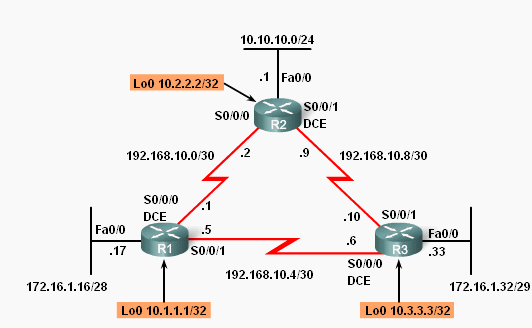
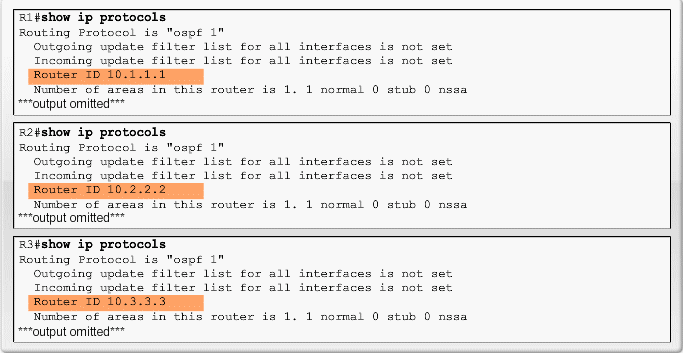
OSPF Router ID
- Use the IP address configured with the OSPF router-id command.
- If the router-id is not configured, the router chooses highest IP address of any of its loopback interfaces.
- If no loopback interfaces are configured, the router chooses highest active IP address of any of its physical interfaces.
Loopback interface OSPF eksempel
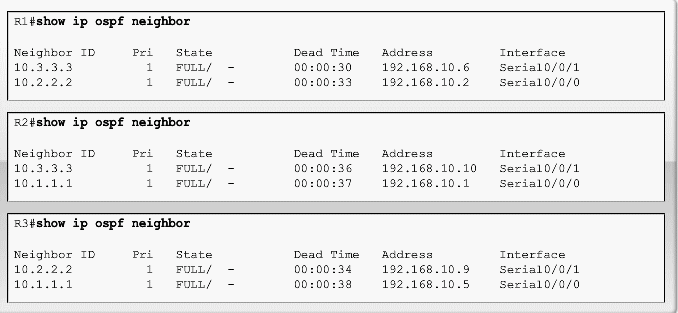
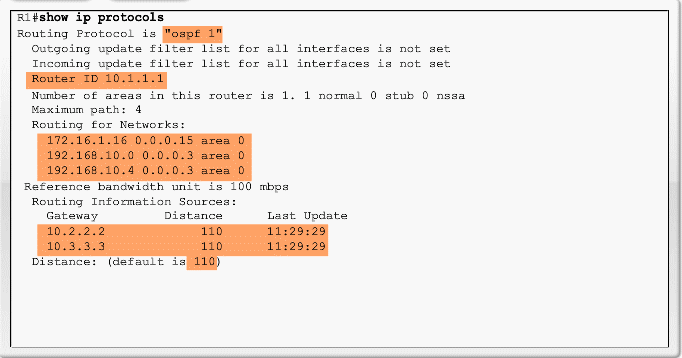
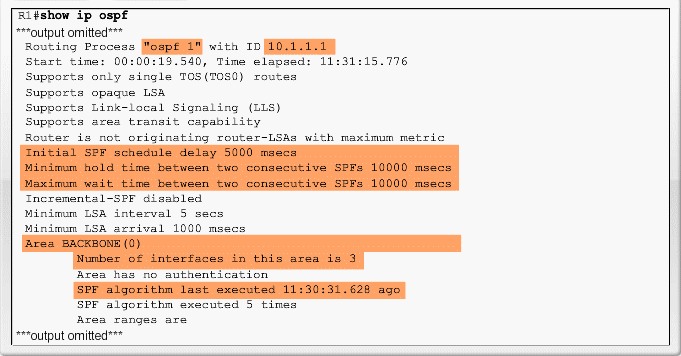
Verifying OSPF
- Neighbor ID - The router ID of the neighboring router.
- Pri - The OSPF priority of the interface. This is discussed in a later section.
- State - The OSPF state of the interface. FULL state means that the router and its neighbor have identical OSPF link-state databases. OSPF states are discussed in CCNP.
- Dead Time - The amount of time remaining that the router will wait to receive an OSPF Hello packet from the neighbor before declaring the neighbor down. This value is reset when the interface receives a Hello packet.
- Address - The IP address of the neighbor's interface to which this router is directly connected.
- Interface - The interface on which this router has formed adjacency with the neighbor.