Difference between revisions of "CCNP TSHOOT 642-832/Chapter 2"
From Teknologisk videncenter
m (→Popular Troubleshooting Methods) |
m (→Examine Collected information) |
||
| Line 49: | Line 49: | ||
Fin a balance between | Fin a balance between | ||
*What ''is'' occurring on the network? | *What ''is'' occurring on the network? | ||
| − | *what ''should be''occurring on the network? | + | *what ''should be'' occurring on the network? |
| + | |||
=== Eliminate Potential Causes=== | === Eliminate Potential Causes=== | ||
*Is OSPF running etc. | *Is OSPF running etc. | ||
Revision as of 11:34, 6 June 2010
Introduction to Troubleshooting Processes
Contents
Troubleshooting Methods
Defining Troubleshooting
- Step 1: Problem Report
- Step 2: Problem Diagnosis
- Step 3: Problem resolution
Diagnosing a Problem
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Collect Information | A problem report often lacks sufficient information. Collect additional information from. fx. Network Management tolls or interviewing the user. |
| Examine Collected Information | Examine collected information. Fx. comparing to baseline information. |
| Eliminate Potential causes | Based on knowledge of network and collected information - start to eliminate causes. |
| Hypothesize Underlying Cause | After eliminating causes hypothesize the most likely cause of the problem. |
| Verify Hypothesis | Test if the hypothesize resolve the problem |
The Value of a Structured Troubleshooting Approach
Popular Troubleshooting Methods
Structured Troubleshooting Procedure
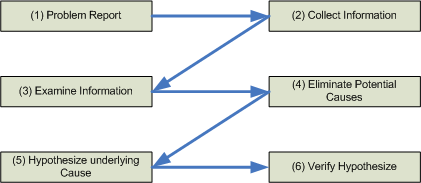
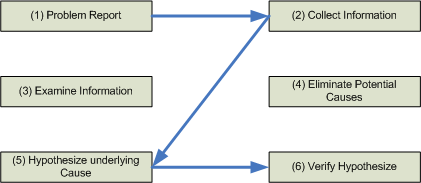
By combining the previously mentioned Three-step troubleshooting procedure and the subprocesses of Problem Diagnosis steps you get
- Problem Report
- Collect Information
- Examine Collected Information
- Eliminate Potential Causes
- Hypothesize Underlying Cause
- Verify Hypothesize
- Problem resolution
Problem Report
- Often lacks information
- Are you authorized to resolve the problem or need to forward it.
- Interview the user who reported the problem.
Collect Information
- Collect information from routers and switches... (show debug commands, log, NMS etc)
Examine Collected information
- Identify indicators pointing to the underlying cause of the problem
- Find evidence that can be used to eliminate potential causes
Fin a balance between
- What is occurring on the network?
- what should be occurring on the network?
Eliminate Potential Causes
- Is OSPF running etc.
Hypothesize Underlying Cause
- If problem can't be resolved (Lack of authority, devices) a temporary fix could resolve the problem here and now.
Verify Hypothesis
- Implementing the fix. (Make a plan)
Problem resolution
- Document the resolved problem.