Difference between revisions of "Multicast IPv6 Address"
m |
m (→Scope Field) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
|[[Image:Multicast IPv6 format.png|left|350px|Thumb|Format of IPv6 Multicast Address]] | |[[Image:Multicast IPv6 format.png|left|350px|Thumb|Format of IPv6 Multicast Address]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | ==Flag Field== | ||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |The flag field consists of four flags. || | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" border=1 | ||
| + | |+ | ||
| + | |- bgcolor=lightgrey | ||
| + | ! 0 !!R !!P !! T | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:center" border=1 | ||
| + | |+ Flags | ||
| + | |- bgcolor=lightgrey | ||
| + | ! Flag !!Explanation | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | T ||align="left"| | ||
| + | T = 0 indicates a permanently-assigned ("well-known") multicast address, assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). | ||
| + | |||
| + | T = 1 indicates a non-permanently-assigned ("transient" or "dynamically" assigned) multicast address. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | P ||align="left"| | ||
| + | P = 0 indicates a multicast address that is not assigned based on the network prefix. | ||
| + | |||
| + | P = 1 indicates a multicast address that is assigned based on the network prefix. See [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3306 rfc3306] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | R ||align="left"| | ||
| + | R = 0 indicates a multicast address that does not embed the address of the RP | ||
| + | |||
| + | R = 1 indicates a multicast address that embed an RP (Rendezvous Point) See [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3956 rfc3956] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | 0 ||align="left"| The high-order flag is reserved, and must be initialized to 0. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==Scope Field== | ==Scope Field== | ||
The Scope field is used to limit the Scope of the Multicast Group. | The Scope field is used to limit the Scope of the Multicast Group. | ||
| Line 45: | Line 80: | ||
::FF05::101 means all NTP servers in the same site as the sender. | ::FF05::101 means all NTP servers in the same site as the sender. | ||
::FF0E::101 means all NTP servers in the Internet. | ::FF0E::101 means all NTP servers in the Internet. | ||
| − | |||
=RFC's= | =RFC's= | ||
[http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4291 rfc4291] ''"IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture"'' defines new flags in [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3306 rfc3306] ''"Unicast-Prefix-based IPv6 Multicast Addresses"'' and [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3956 rfc3956] ''"Embedding the Rendezvous Point (RP) Address in an IPv6 Multicast Address"'' | [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4291 rfc4291] ''"IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture"'' defines new flags in [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3306 rfc3306] ''"Unicast-Prefix-based IPv6 Multicast Addresses"'' and [http://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc3956 rfc3956] ''"Embedding the Rendezvous Point (RP) Address in an IPv6 Multicast Address"'' | ||
Revision as of 15:16, 12 June 2011
| IPv6 Address Type: | Multicast |
| Prefix: | ff00::/8 |
| Local Routeable: | Yes and No |
| Global Routeable: | Yes and No |
| Global Unique: | Yes and No |
| Example: | FF0E::101 |
| IPv4 Equivalent: | 224.0.0.0/4 |
| Described in: | rfc4291 section 2.7 |
| # (Optional) |
These addresses are used to identify multicast groups. They should only be used as destination addresses, never as source addresses.
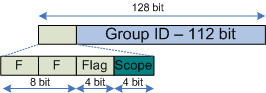
Multicast Address Format
The IPv6 Multicast addresses contains two fields describing which kind of Multicast it is. Flag and Scope.
Flag Field
| The flag field consists of four flags. |
|
| Flag | Explanation |
|---|---|
| T |
T = 0 indicates a permanently-assigned ("well-known") multicast address, assigned by the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority (IANA). T = 1 indicates a non-permanently-assigned ("transient" or "dynamically" assigned) multicast address. |
| P |
P = 0 indicates a multicast address that is not assigned based on the network prefix. P = 1 indicates a multicast address that is assigned based on the network prefix. See rfc3306 |
| R |
R = 0 indicates a multicast address that does not embed the address of the RP R = 1 indicates a multicast address that embed an RP (Rendezvous Point) See rfc3956 |
| 0 | The high-order flag is reserved, and must be initialized to 0. |
Scope Field
The Scope field is used to limit the Scope of the Multicast Group.
| Value | Scope | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Interface-Local | Interface-Local scope spans only a single interface on a node and is useful only for loopback transmission of multicast. |
| 2 | Link Local | Link-Local multicast scope spans the same topological region as the corresponding unicast scope. |
| 4 | Admin Local | Admin-Local scope is the smallest scope that must be administratively configured, i.e., not automatically derived from physical connectivity or other, non-multicast-related configuration. |
| 5 | Site Local | Site-Local scope is intended to span a single site. |
| 8 | Organization Local | Organization-Local scope is intended to span multiple sites belonging to a single organization. |
| E | Global | Global span. |
Permanent Assigned Multicast Address
The "meaning" of a permanently-assigned multicast address is independent of the scope value. For example, if the "NTP servers group" is assigned a permanent multicast address with a group ID of 101 (hex), then
- FF01::101 means all NTP servers on the same interface (i.e., the same node) as the sender.
- FF02::101 means all NTP servers on the same link as the sender.
- FF05::101 means all NTP servers in the same site as the sender.
- FF0E::101 means all NTP servers in the Internet.
RFC's
rfc4291 "IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture" defines new flags in rfc3306 "Unicast-Prefix-based IPv6 Multicast Addresses" and rfc3956 "Embedding the Rendezvous Point (RP) Address in an IPv6 Multicast Address"