Difference between revisions of "CentOS Cluster Configuration"
m (→active-passive example) |
m (→active-passive example) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|valign="top"| | |valign="top"| | ||
| + | ===== Picture 1 - Normal operation ===== | ||
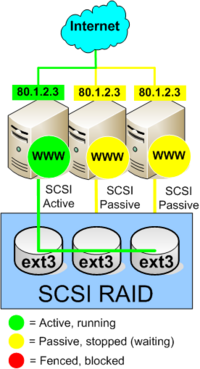
#Filesystem: The filesystem is a [[ext3]] filesystem which can only be mounted on one node at a time. In Picture 1 below the left node has mounted the shared filesystem on the SCSI-raid controllers. The other servers has not mounted the shared filesystem. | #Filesystem: The filesystem is a [[ext3]] filesystem which can only be mounted on one node at a time. In Picture 1 below the left node has mounted the shared filesystem on the SCSI-raid controllers. The other servers has not mounted the shared filesystem. | ||
#Service: The Apache WEB-server service is running on the left node, and using the resources from the shared SCSI filesystem delivering WEB-content to the Internet. The Apache service on the other nodes are stopped. | #Service: The Apache WEB-server service is running on the left node, and using the resources from the shared SCSI filesystem delivering WEB-content to the Internet. The Apache service on the other nodes are stopped. | ||
#IP address: The left server is answering request for the shared IP address 80.1.2.3. The other nodes ignores 80.1.2.3. | #IP address: The left server is answering request for the shared IP address 80.1.2.3. The other nodes ignores 80.1.2.3. | ||
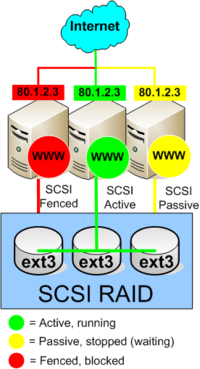
| + | ===== Picture 2 - Fault in left node ===== | ||
| + | When an error is discovered by the ''rgmanager'' on the failing node, ''rgmanager'' communicates with the ''rgmanager'' on the other nodes and decide which other node should transition from ''passive'' to ''active''. In the example on Picture 2, the middle node goes to active and continues to server WEB-requests to 80.1.2.3. | ||
| + | ====== Transition steps in example ====== | ||
|valign="top"| | |valign="top"| | ||
|[[Image:Cluster active-passive.png|200px|thumb|Picture 1: Active-passive example]] | |[[Image:Cluster active-passive.png|200px|thumb|Picture 1: Active-passive example]] | ||
Revision as of 11:24, 5 April 2009
Contents
cluster.conf configuration file
Configuration file for:
- cman - Cluster configuration
- fence - Fence configuration for disabling nodes with errors
- dlm - Distributed Lock Manager Configuration. Rules for access to shared resources
- gfs - Global file System configuration. Shared file systems among nodes.
- rgmanager - Resource Group manager configuration. Fx. apache service setup on cluster.
cman - Basci cluster config
fence - Fencing nodes
dlm - lock management
gfs - global file system
rgmanager - resource config
Resource Group manager is a High Availability service. Rgmanager can start and stop services on nodes. If a service is failing on one node it will be started on another node. Rgmanager monitor the services and make sure they are actually runnning.
Service Groups
A Service Group is a group of nodes on which a specified service can be started or stopped by rgmanager. Not all nodes in a cluster need to be member of a Service Group. There can be many Service Groups in a cluster.If a service fails, a script is called to automatically restart the service. If a node fails, the service may be relocated to a different node in the service group.
What is a Cluster-service
A Cluster-service is a resource that are shared among nodes. For example a apache WEB-service. This service can be run in two different ways.
active-passive Cluster-service
An active-passive Cluster-service is a service running on one node at a time. If the node running the service fails the service is started on another node in the Service Group.
active-passive example
Two front-end-nodes have the responsibility of delivering a high-availability WEB-service. In the image below there are three services
Picture 1 - Normal operation
Picture 2 - Fault in left nodeWhen an error is discovered by the rgmanager on the failing node, rgmanager communicates with the rgmanager on the other nodes and decide which other node should transition from passive to active. In the example on Picture 2, the middle node goes to active and continues to server WEB-requests to 80.1.2.3. Transition steps in example |
files and programs
- /usr/share/cluster - here lives the rgmanager scripts
- /etc/cluster/cluster.conf - rgmanager configuration
- clustat - See cluster and service status clustat -s SERVICE_NAME -l
- RedHAT rgmanager FAQ