CCNP SWITCH/Securing the Campus Infrastructure
Contents
 This article is under development....
This article is under development....
Securing the Campus Infrastructure
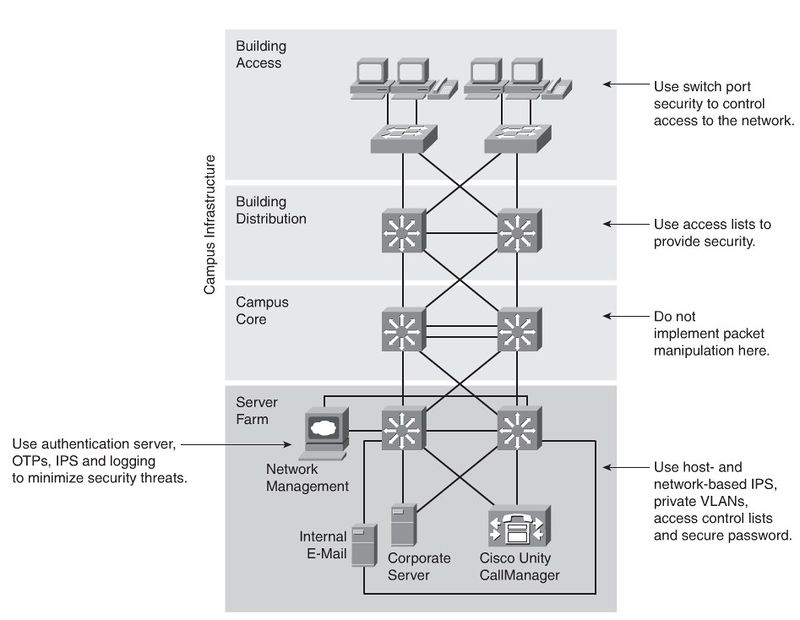
Security Infrastructure Services
Rouge Devices
Company employees sometimes plug inexpensive APs into company network devices to extend the network. But securing the wireless APs is not always a priority. Wired Rouge Devices could also be a problem, because of its nature.
Layer 2 Attack Categories
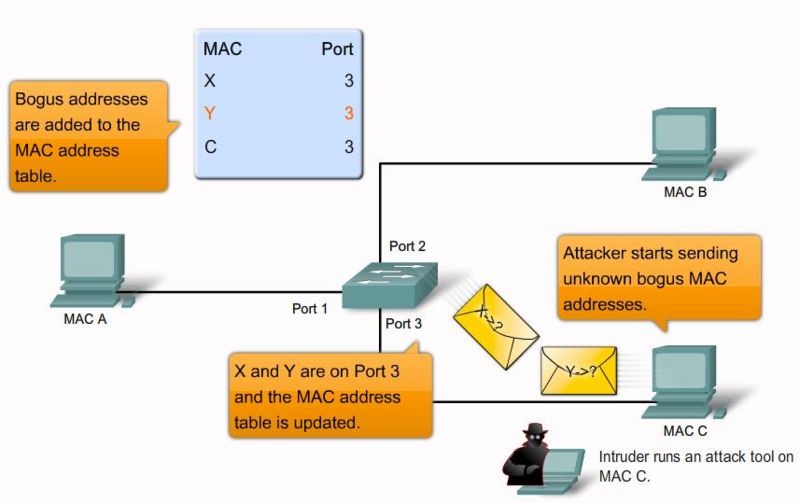
MAC Layer Attacks
MAC address flooding
Frames with unique, invalid source MAC addresses flood the switch, exhausting content addressable memory (CAM) table space, disallowing new entries from valid hosts. Traffic to valid hosts is subsequently flooded out all ports.
Mitigation:
Port security. MAC address VLAN access maps.
Switch(config-if)#<input>switchport port-security</input>
Switch(config-if)#<input>switchport port-security maximum <value></input>
Switch(config-if)#<input>switchport port-security <mac-addressmac-address></input>
Switch(config-if)#<input>switchport port-security violation{shutdown |restrict |
protect}</input>Debugging:
switch# <input>show port-security interface fastethernet0/1</input>
Port Security : Enabled
Port Status : Secure-up
Violation Mode : Restrict
Aging Time : <notice>60 mins</notice>
Aging Type : Inactivity
SecureStatic Address Aging : Enabled
Maximum MAC Addresses : 2
Total MAC Addresses : 1
Configured MAC Addresses : 0
Sticky MAC Addresses : 0
Last Source Address:Vlan : 001b.d513.2ad2:5
Security Violation Count : 0VLAN Attacks
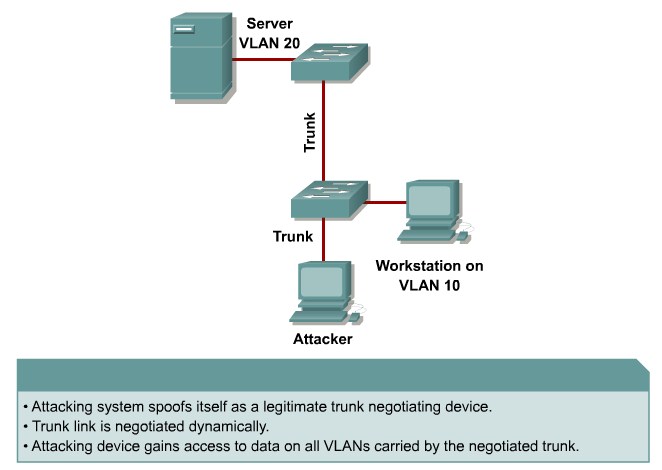
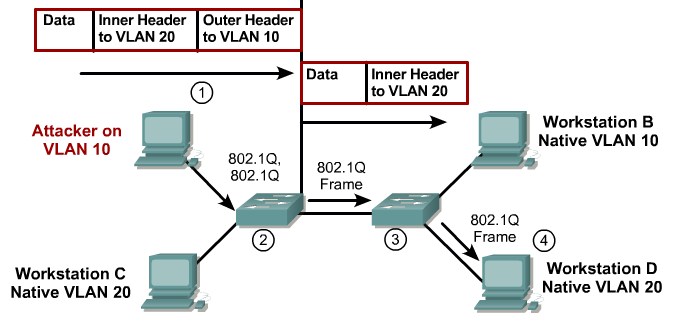
VLAN Hopping
By altering the VLAN ID on packets encapsulated for trunking, an attacking device can send or receive packets on various VLANs, bypassing Layer 3 security measures.
Mitigation:
Tighten up trunk configurations and the negotiation state of unused ports. Place unused ports in a common unused VLAN. Remember to protect against DTP attacks and VLAN hopping.
Attacks between devices on a common VLAN
Devices might need protection from one another, even though they are on a common VLAN. This is especially true on service-provider segments that support devices from multiple customers.
Mitigation:
Implement private VLANs (PVLAN).
Spoofing Attacks
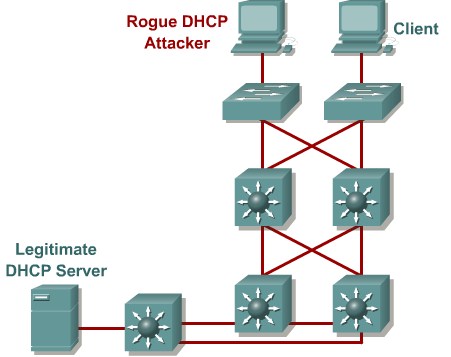
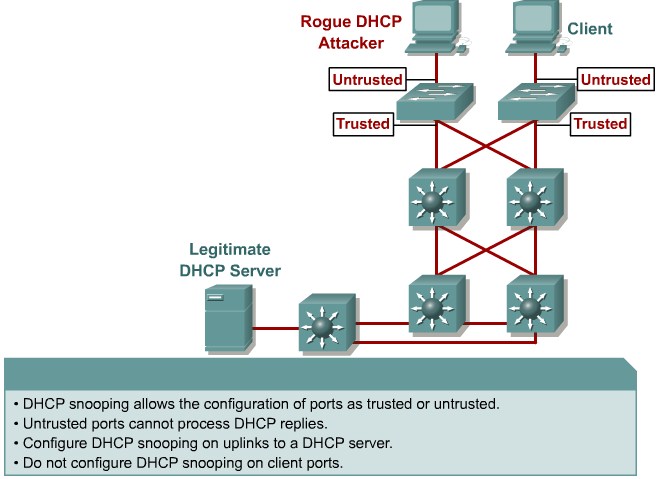
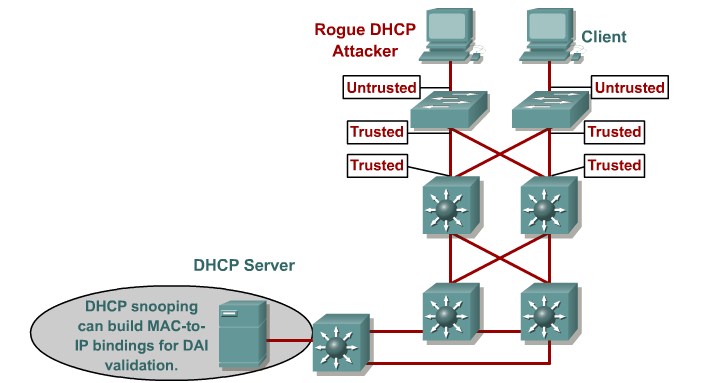
DHCP starvation and spoofing
An attacking device can exhaust the address space available to the DHCP servers for a period of time or establish itself as a DHCP server in man-in-the-middle attacks.
Mittigation:
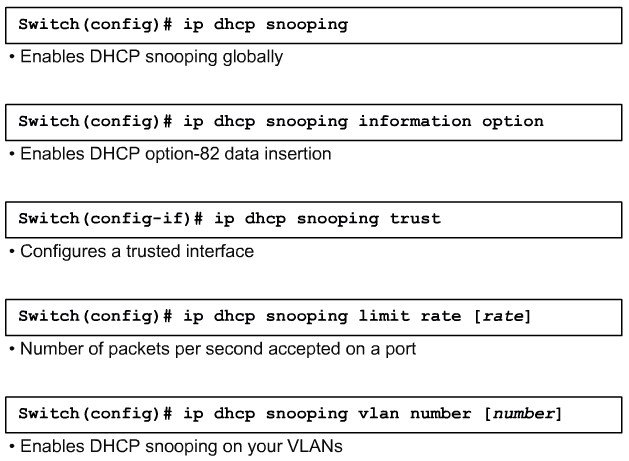
Use DHCP snooping
Configure DHCP Snooping
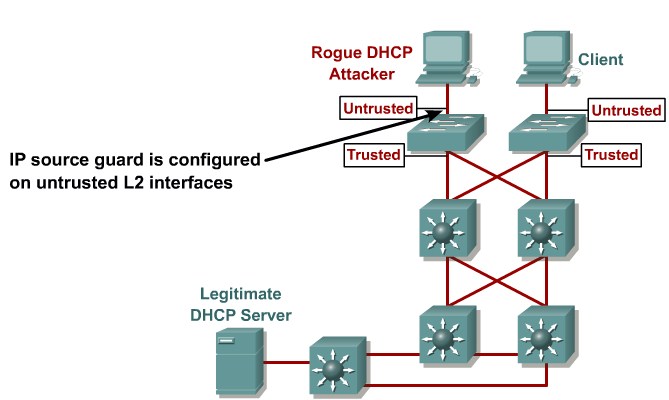
IP Source spoofing
Attacking devices spoof there source address to pretend to be someone else
Mittigation:
Enable IP Source Guard
Configure IP Source Guard
Spanning-tree compromises
Attacking device spoofs the root bridge in the STP topology. If successful, the network attacker cansee a variety of frames.
Mittigation:
Proactively configure the primary and backup root devices. Enable root guard.
MAC spoofing
Attacking device spoofs the MAC address of a valid host currently in the CAM table. The switch then forwards frames destined for the valid host to the attacking device.
Mittigation:
Use DHCP snooping, port security.
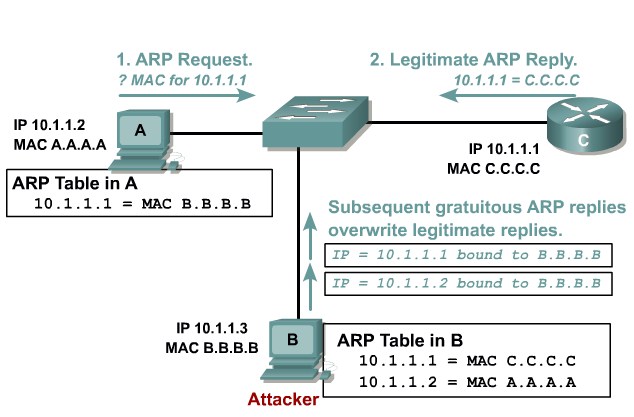
ARP spoofing
Attacking device crafts ARP replies intended for valid hosts. The attackingdevice’s MAC address thenbecomes the destination addressfound in the Layer 2 frames sent by the valid network device.
Mittigation:
Use Dynamic ARP Inspection. DHCP snooping, port security.
Switch# <input>configure terminal</input>
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Switch(config)# <input>ip arp inspection vlan 10</input>
Switch(config)# <input>interface gigabitEthernet 1/1</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>description Uplink Port</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>ip arp inspection trust</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>end</input>Switch Device Attacks
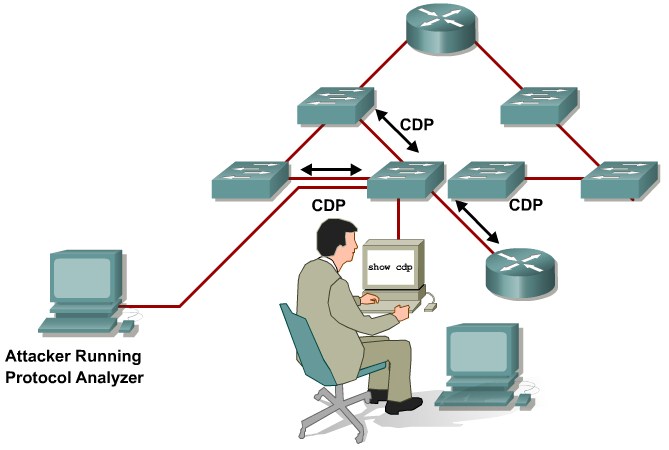
CDP manipulation
Information sent through CDP is transmitted in clear text and unauthenticated, allowing it to be captured and divulge network topology information.
Mittigation:
Disable CDP on all ports where it is not intentionally used.
Switch(config)# <input>no cdp run</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>no cdp enable</input>Configure LLDP
Switch(config)# <input>lldp run</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>lldp enable</input>
Switch(config-if)# <input>end</input>
switch# <input>show lldp neighbor</input>
Capability codes:
(R) Router, (B) Bridge, (T) Telephone, (C) DOCSIS Cable Device
(W) WLAN Access Point, (P) Repeater, (S) Station, (O) Other
Device ID Local Intf Hold-time Capability Port ID
c2960-8 Fa0/8 120 B Fa0/8
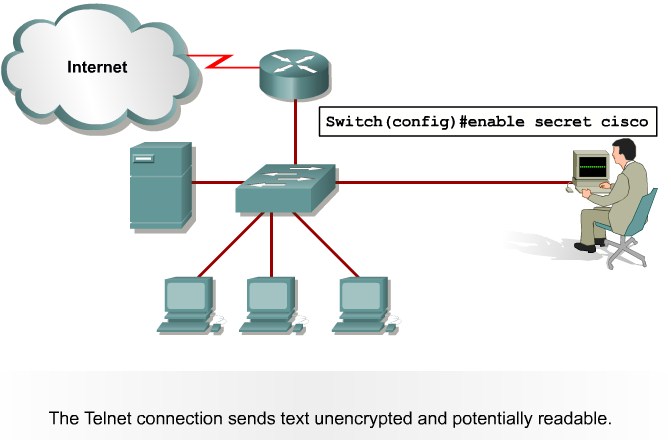
Total entries displayed: 1SSH and Telnet attacks
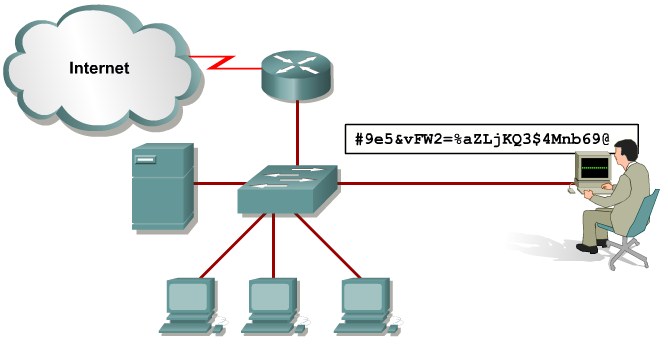
Telnet packets can be read in clear text. SSH is an option but has securityissues in version 1.
Mittigation:
Use SSH Version 2. Use telnet with VTY ACLs.
Switch(config)# <input>aaa new-model</input>
Switch(config)# <input>aaa authentication login default local</input>
Switch(config)# <input>username Joe password User</input>
Switch(config)# <input>ip domain-name sshtest.lab</input>
Switch(config)# <input>crypto key generate key</input>
Switch(config)# <input>line vty 0 15</input>
Switch(config-line)# <input>login local</input>
Switch(config-line)# <input>transport input ssh</input>VTY ACLs
Switch(config)# <input>access-list 100 permit ip 10.1.1.0.0.0.0.255 any</input>
Switch(config)# <input>line vty 0 15</input>
Switch(config-line)#<input> access-class 100 in</input>