Real Time Clock
A RTC or Real Time Clock is a build in time clock in electronic equipment such as an PC or an embedded processor. The RTC often has a battery power backup and the time are retained using a precision X-tal to minimize drift of time.
DS1307 RTC chip
A popular stand alone RTC chip is the DS1307 used by example by the popular Arduino[1] embedded system.
In the picture to the right you can see a DS1307 chip driven by the 32,768 KHz X-tal. The reason for chosing 32768 Hz is that 215 = 32768. The DS1307 contains a counter that repeatedly counts to 215. Each time the counter reaches 32768 the time clock counts one second forward. Battery power backup is provided by the battery just visible in top right corner.
Beside the RTC the DS1307 contains 112 Bytes of RAM often used for configuration and password information. The time and contents of RAM are lost if the chip losses power. (Loss of battery and external power)
Motorola MC146818
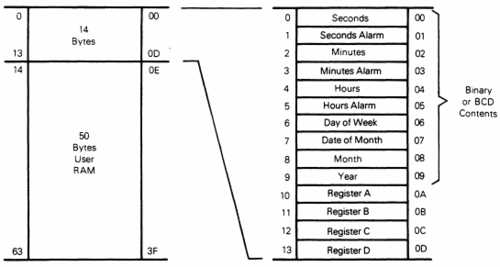
The most used RTC design was the Motorola MC146818 chip introduced in the PC/AT in 1984[2]. Today the RTC in is an integrated part of the PC mainboard chipset, but still emulating the MC146818.
| == MC146818 memory map ==
The MC146818 content are read- and writeable by the CPU using the IN or OUT instructions at port number 0x70 transferring the address to the MC146818. For example using the .... |
Modern day PC mainboards
In modern day mainboards the RTC is an integrated part of the chipset, but still emulating the MC146818. By example the popular desktop chipset from Intel P55 express chipset[3]
The battery backuped RAM typically contains the BIOS settings and optional passwords.
P55 express chipset
The P55 data sheets[4] RTC introduction states
P55 data sheet excerpt
The chipset contains a Motorola MC146818B-compatible real-time clock with 256 bytes of battery-backed RAM. The real-time clock performs two key functions: keeping track of the time of day and storing system data, even when the system is powered down. The RTC operates on a 32,768 KHz crystal and a 3 V battery.
The RTC also supports two lockable memory ranges. By setting bits in the configuration space, two 8-byte ranges can be locked to read and write accesses. This prevents unauthorized reading of passwords or other system security information.
The RTC also supports a date alarm that allows for scheduling a wake up event up to 30 days in advance, rather than just 24 hours in advance.