From Teknologisk videncenter
STP
Redundant Layer 2 Topologies
Redundancy
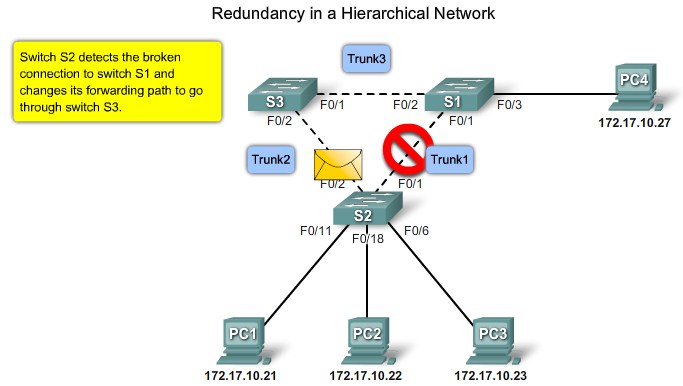 Simple network VLAN mangement |
|
|
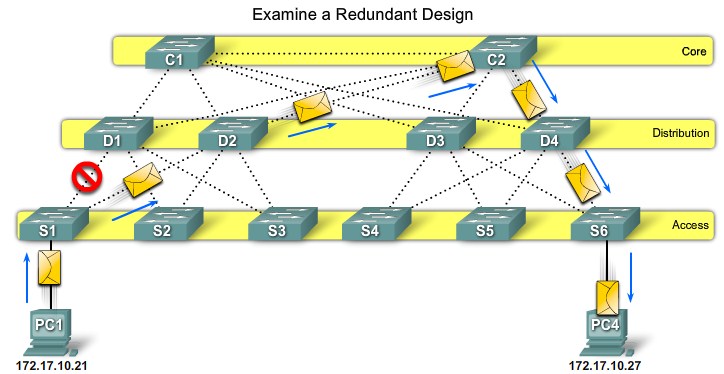 Path Failure - Access to Distribution |
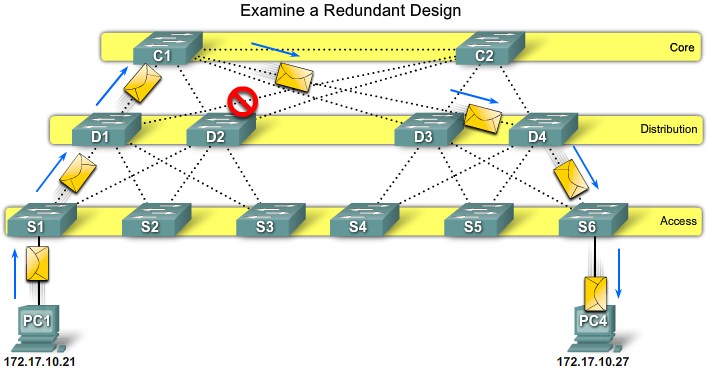 Path Failure - Distribution to Core |
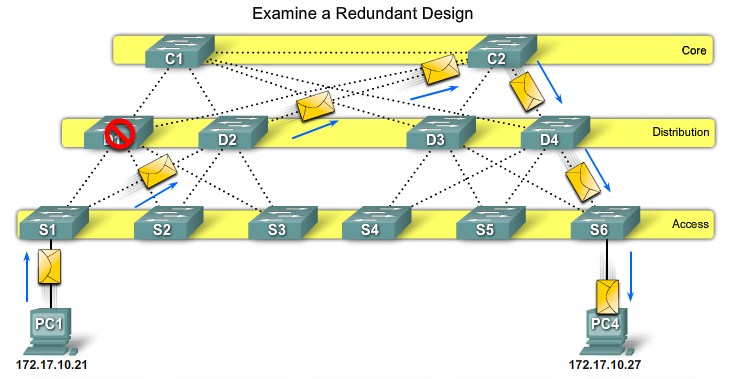 Switch Failure - Distribution layer |
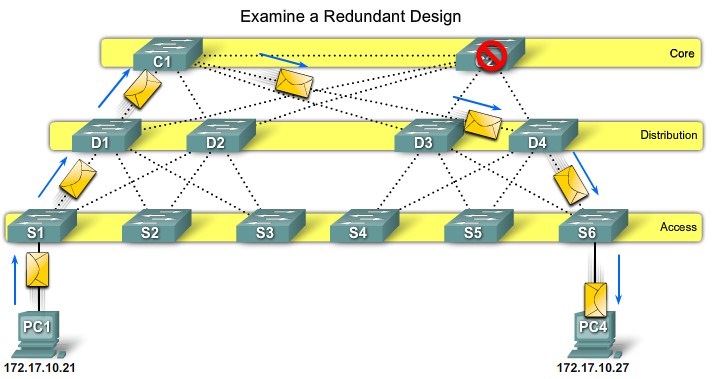 Switch Failure - Core layer |
Issues with Redundancy
|
|
|
|
Real-world Redundancy Issues
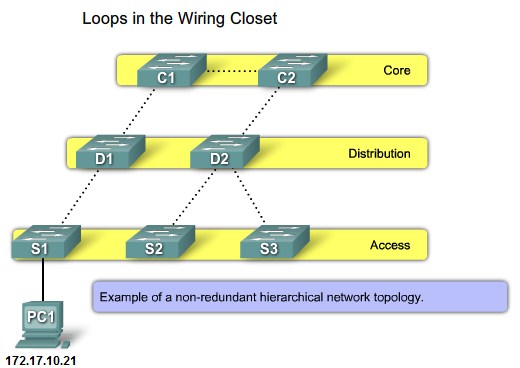 Non-Redundant network topology |
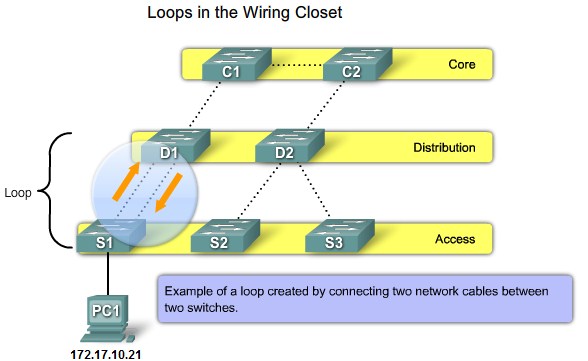 Loops from 2 connections in the same switch |
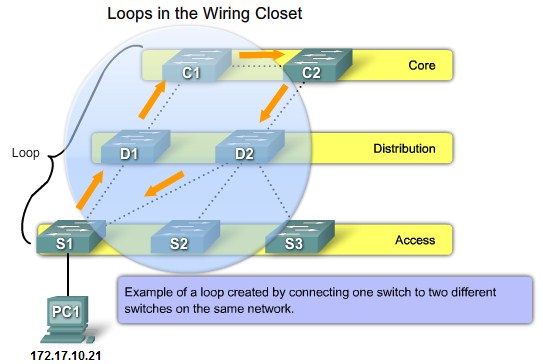 Loops from connections to a second switch |
|
|
Introduction to STP
The Spanning Tree Algorithm
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Root ports - Switch ports closest to the root bridge.
Designated ports - All non-root ports that are still permitted to forward traffic on the network.
Non-designated ports - All ports configured to be in a blocking state to prevent loops.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
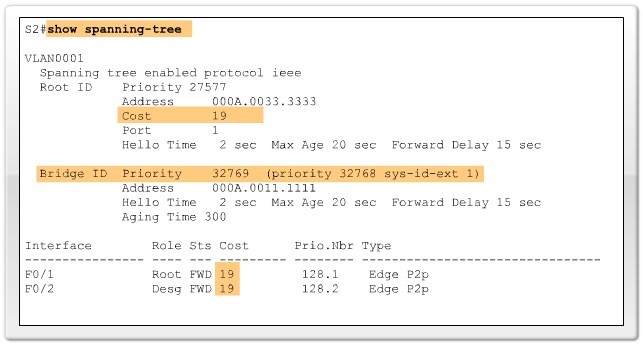 Verify port and path costs |
STP BPDU
|
|
|
Version - The version field indicates the version of the protocol, This field contains the value zero.
Message type - The message type field indicated the type of message, this field contains the value zero.
Flags - The flags field includes one of the following: Topology change(TC) bit, which signals a topology change in the event a path to the root bridge has been disrupted. Topology change acknowledgment(TCA) bit, which is set to acknowledge receipt of a configuration messege with the TC bit set.
Root ID - The Root ID field indicates the root bridge by listing its 2-byte prority followed by its 6-byte MAC address ID.
Bridge ID - The Bridge ID field indicates the priority and MAC address ID of the bridge sending the message
Port ID - The Port ID field indicates the port number from which the configuration message was sent.
Forward Delay - The Forward delay field indicates the length of time that bridges should wait before transitioning to a new state after topology change.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bridge ID
|
|
|
|
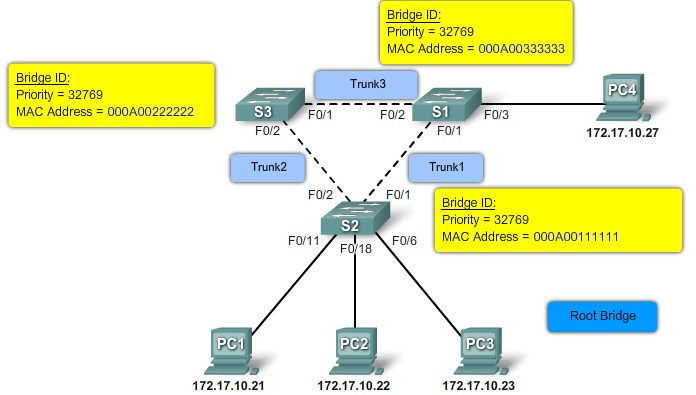 MAC Address-based desicions |
|
|
|
|
Port Roles
- Root Port
- The root port exists on non-root bridges and is the switch port with the best path to the root bridge.
- Designated Port
- The designated port exists on root and non-root bridges. For root bridges, all switch ports are designated ports. Only one designated port is allowed per segment. Designated ports are capable of populating the MAC table.
- Non-designated Port
- The non-designated port is a switch port that is blocked, so it is not forwarding data frames and not populating the MAC address table with source addresses.
- Disabled Port
- The disabled port is a switch port that is administratively shut down.
|
|
|
|
|
|
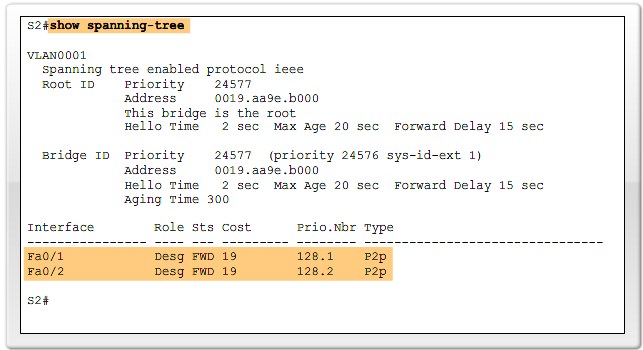 Verify Port Roles and Priority |
STP Port States and BPDU Timers
|
|
|
|
|
|
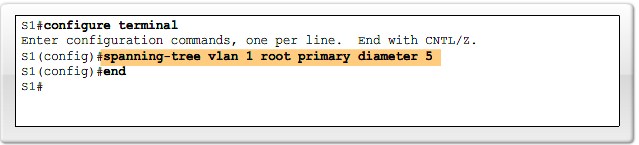 Configure network diameter |
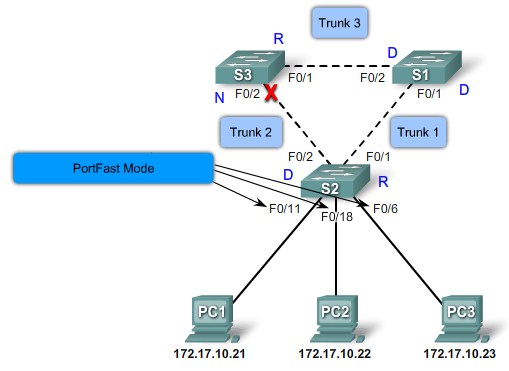 Cisco Portfast technology |
|
|
|
|
STP Convergence
STP Convergence
|
|
Step 1. Electing A Root Bridge
|
|
Step 2. Elect Root Ports
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Step 3. Electing Desgnated Ports and Non-Designated Ports
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
STP Topology Change
|
|
| Topology change notification(TCN) messages are flooded out the root port, until it reaches the root bridge.
|
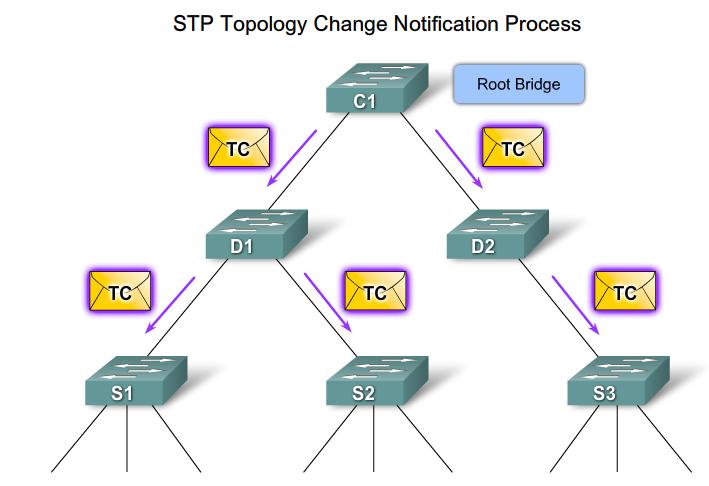 STP Broadcast notification |
| The Root Bridge broadcasts Topology change messages
|
PVST+, RSTP and Rapid-PVST+
Cisco and STP Variants
|
|
PVST+
|
|
|
|
|
|
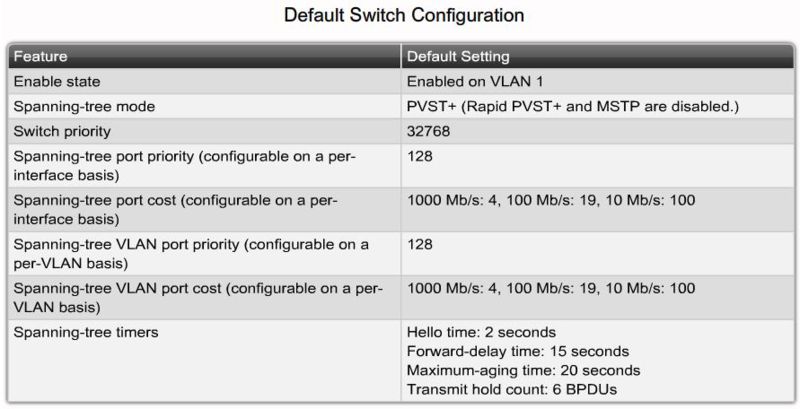 Default PVST+ configuration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RSTP
|
|
|
|
|
|
Edge Ports
|
|
Link Types
|
|
|
Point-to-point Link Type - Links attaches to switch ports that are operating in full-duplex mode
Shared Link Type - This link is attached to a port that is operating in half-duplex mode
|
RSTP Port States and Port Roles
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Configure Rapid-PVST+
|
|
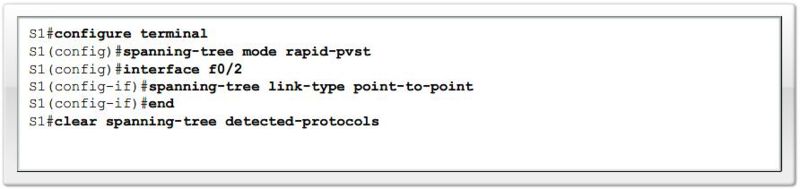 Rapid-PVST+ Example configuration |
|
|
Design STP for Trouble Avoidance
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Troubleshoot STP Operation
|
|
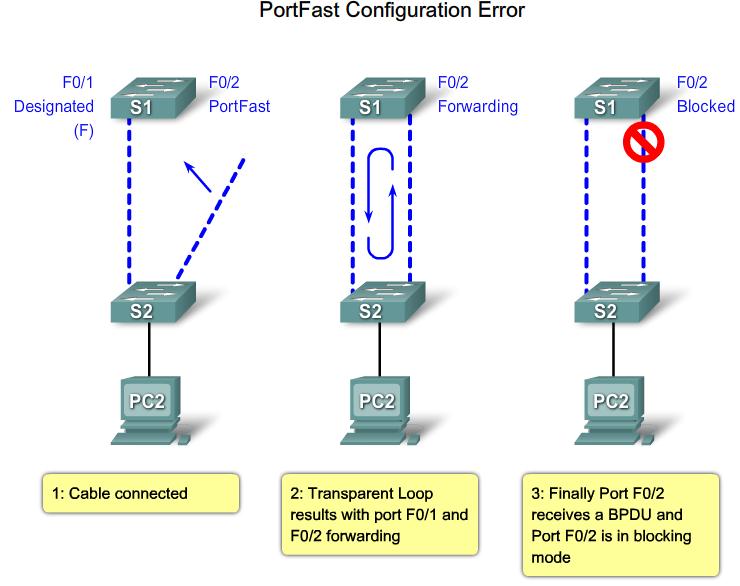 PortFast configuration error |
|
|
Chapter Summary
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|