Difference between revisions of "IS-IS"
m (→Level 1-2 Routers) |
m (→Point-to-point link Adjacencies) |
||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== Point-to-point link Adjacencies == | == Point-to-point link Adjacencies == | ||
If a Point-to-Point link connects two Routers the Routers are neighbors and each side send a CSNP - Complete Sequence Number Packet - which is a packets containing the Link State database to each other. | If a Point-to-Point link connects two Routers the Routers are neighbors and each side send a CSNP - Complete Sequence Number Packet - which is a packets containing the Link State database to each other. | ||
| − | == | + | == Broadcast links Adjacencies == |
| + | On broadcast link medias, for example Ethernet, all Routers receive receive LSP - link State packets - from one router the DIS - Designated Intermediate system. The DIS Router has the responsibility to flood LSP's to all connected IS-IS Routers. | ||
[[category:Network]][[Category:Cisco]] | [[category:Network]][[Category:Cisco]] | ||
Revision as of 11:34, 24 March 2009
Contents
Intermediate-System to Intermediate-System
IS-IS is a link state Routing protocol which are also used in IP network. Here it is called integrated IS-IS. IS-IS is often used by providers as an IGP.
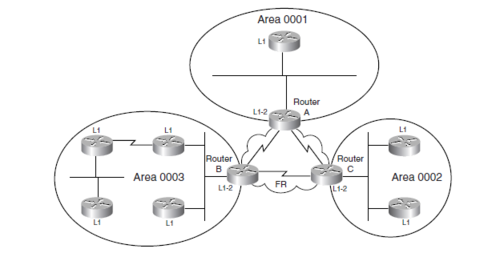
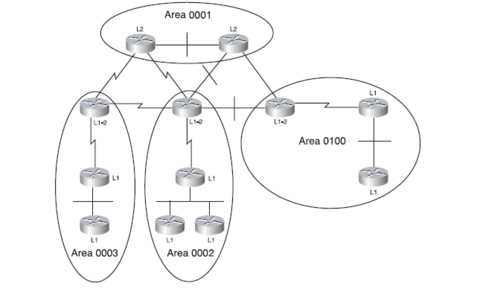
Level 1 Routing
A level 1 Router only knows about the area in which it is located. Like a stub Router in OSPF. It has no knowledge of other areas. A level 1 Router only knows a default Route to the nearest level 2 Router if Routing between areas is necessary. Every Level 1 Router in that area has the same link State Database containing information about that area.
Level 1 Routers are referred to as Intra-area Routers
Level 2 Routing
A Level 2 Router routes between areas and are referred to as Backbone Routers. The backbone must be contiguous because all Level 2 Routers share the same Link-State Database which contain prefixes from all areas. If the backbone is fractured Routing information will not be the same on all Level 2 Routers.
Level 2 Routers are referred to as Inter-area Routers
Level 1-2 Routers
The Level 1-2 Router has both the Level 1 Link-state database containing information about the area in which it participates and Level 2 Link-state database containing information about all areas.
Point-to-point link Adjacencies
If a Point-to-Point link connects two Routers the Routers are neighbors and each side send a CSNP - Complete Sequence Number Packet - which is a packets containing the Link State database to each other.
Broadcast links Adjacencies
On broadcast link medias, for example Ethernet, all Routers receive receive LSP - link State packets - from one router the DIS - Designated Intermediate system. The DIS Router has the responsibility to flood LSP's to all connected IS-IS Routers.