Difference between revisions of "CCDA/Wireless LAN design"
m |
m (→ISM) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== ISM and UNII frequencies == | == ISM and UNII frequencies == | ||
=== ISM === | === ISM === | ||
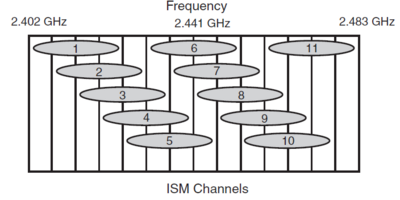
| − | [[Image:ISM.png|400px|thumb|right|Figure 1: Industrial Scientific and medical Frequencies in 2,4 Gbps area]] | + | [[Image:ISM.png|400px|thumb|right|Figure 1: Industrial Scientific and medical Frequencies in the 2,4 Gbps area]] |
ISM - Industrial, Scientific and medical - frequencies are set aside by ITU-R radio regulations 5.138 and 5.150. In the U.S., the Federal Communications Commission (15.247) specifies the ISM bands for unlicensed use. Several bands are specified in the following ranges: | ISM - Industrial, Scientific and medical - frequencies are set aside by ITU-R radio regulations 5.138 and 5.150. In the U.S., the Federal Communications Commission (15.247) specifies the ISM bands for unlicensed use. Several bands are specified in the following ranges: | ||
*900 to 928 MHz | *900 to 928 MHz | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
*5.75 to 5.875 GHz | *5.75 to 5.875 GHz | ||
Of these, channels located in the 2.4-GHz range are used for 802.11b and 802.11g. As shown in Figure 1, 11 overlapping channels are available for use. Each channel is 22 MHz wide. It is common to use channels 1, 6, and 11 in the same areas, because these three channels do not overlap. | Of these, channels located in the 2.4-GHz range are used for 802.11b and 802.11g. As shown in Figure 1, 11 overlapping channels are available for use. Each channel is 22 MHz wide. It is common to use channels 1, 6, and 11 in the same areas, because these three channels do not overlap. | ||
| + | |||
=== UNII === | === UNII === | ||
The UNII - Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure - radio bands were specified for use with 802.11a wireless. UNII operates over three ranges: | The UNII - Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure - radio bands were specified for use with 802.11a wireless. UNII operates over three ranges: | ||
Revision as of 08:45, 7 July 2009
ISM and UNII frequencies
ISM
ISM - Industrial, Scientific and medical - frequencies are set aside by ITU-R radio regulations 5.138 and 5.150. In the U.S., the Federal Communications Commission (15.247) specifies the ISM bands for unlicensed use. Several bands are specified in the following ranges:
- 900 to 928 MHz
- 2.4 to 2.5 GHz
- 5.75 to 5.875 GHz
Of these, channels located in the 2.4-GHz range are used for 802.11b and 802.11g. As shown in Figure 1, 11 overlapping channels are available for use. Each channel is 22 MHz wide. It is common to use channels 1, 6, and 11 in the same areas, because these three channels do not overlap.
UNII
The UNII - Unlicensed National Information Infrastructure - radio bands were specified for use with 802.11a wireless. UNII operates over three ranges:
- UNII 1—5.15 to 5.25 GHz and 5.25 to 5.35 GHz.
- UNII 2—5.47 to 5.725 GHz. This range is used by High Performance Radio LAN (HiperLAN) in Europe.
- UNII 3—5.725 to 5.875 GHz. This range overlaps with ISM.
UNII provides 12 nonoverlapping channels for 802.11a.
| IEEE Protocol | Release | Frequency | Typical Data rate | Max. Data Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Legacy | 1997 | ISM | 1 Mbps | 2 Mbps |
| 802.11a | 1999 | UNII | 25 Mbps | 54 Mbps |
| 802.11b | 1999 | ISM | 6,5 Mbps | 11 Mbps |
| 802.11g | 2003 | ISM | 25 Mbps | 54 Mbps |
| 802.11n | 2007 (Draft) | ISM or UNII | 200 Mbps | 540 Mbps |