Difference between revisions of "CCDA - en"
m (→Sektioner i et Design dokument) |
m |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
*ISBN: 978-1-58720-177-6 | *ISBN: 978-1-58720-177-6 | ||
=== Part I - General Network Design === | === Part I - General Network Design === | ||
| − | *Chapter 1: [[ | + | *Chapter 1: [[/Network design methodology | Network design methodology]] |
| − | *Chapter 2: [[ | + | *Chapter 2: [[/Network Structure models | Network Structure models]] |
=== Part II - LAN and WAN design === | === Part II - LAN and WAN design === | ||
| − | *Chapter 3: [[ | + | *Chapter 3: [[/Enterprise LAN design | Enterprise LAN design]] |
| − | *Chapter 4: [[ | + | *Chapter 4: [[/Wireless LAN design | Wireless LAN design]] |
| − | *Chapter 5: [[ | + | *Chapter 5: [[/WAN Technologies WAN | Technologies]] |
| − | *Chapter 6: [[ | + | *Chapter 6: [[/WAN design | WAN design]] |
=== Part III - The Internet Protocol and Routing Protocols === | === Part III - The Internet Protocol and Routing Protocols === | ||
| − | *Chapter 7: [[ | + | *Chapter 7: [[/Internet Protocol version 4 | Internet Protocol version 4]] |
| − | *Chapter 8: [[ | + | *Chapter 8: [[/Internet Protocol version 6 | Internet Protocol version 6]] |
| − | *Chapter 9: [[ | + | *Chapter 9: [[/Routing Protocol Selection Criteria | Routing Protocol Selection Criteria]] |
| − | *Chapter 10: [[ | + | *Chapter 10: [[/RIP and EIGRP Characteristics and Design | RIP and EIGRP Characteristics and Design]] |
| − | *Chapter 11: [[ | + | *Chapter 11: [[/OSPF and IS-IS | OSPF and IS-IS]] |
| − | *Chapter 12: [[ | + | *Chapter 12: [[/Border Gateway Protocol, Route manipulation and IP Multicast | Border Gateway Protocol, Route manipulation and IP Multicast]] |
=== Part IV - Security, Convergence and Network Management === | === Part IV - Security, Convergence and Network Management === | ||
| − | *Chapter 13: [[ | + | *Chapter 13: [[/Security Management | Security Management]] |
| − | *Chapter 14: [[ | + | *Chapter 14: [[/Security Technologies and design | Security Technologies and design]] |
| − | *Chapter 15: [[ | + | *Chapter 15: [[/Traditional Voice Architectures and IP Telephony design | Traditional Voice Architectures and IP Telephony design]] |
| − | *Chapter 16: [[ | + | *Chapter 16: [[/Network Management protocols | Network Management protocols]] |
=== Part V - Comprehensive Scenarios === | === Part V - Comprehensive Scenarios === | ||
| − | *Chapter 17: [[ | + | *Chapter 17: [[/Comprehensive Scenarios | Comprehensive Scenarios]] |
= Summary = | = Summary = | ||
== IIN == | == IIN == | ||
Revision as of 07:48, 10 September 2013
Cisco Certified Design Associate
- Exam: 640-863
Strategic network design
Cisco Service-Oriented Network Architecure (SONA) describes a model for design of networks. Cisco updated their designmodel from Architecture for Voice, Video and Integrated Data(AVVID) to Intelligent Information Network (IIN).
There are three faces in the IIN design.
- Integrated transport: Voice, Video and Data are joined and transported together.
- Integrated services: For exampel Storage (SAN), voice
- Integrated Applications:
The Book
CCDA Official Exam Certification Guide
- ISBN: 978-1-58720-177-6
Part I - General Network Design
- Chapter 1: Network design methodology
- Chapter 2: Network Structure models
Part II - LAN and WAN design
- Chapter 3: Enterprise LAN design
- Chapter 4: Wireless LAN design
- Chapter 5: Technologies
- Chapter 6: WAN design
Part III - The Internet Protocol and Routing Protocols
- Chapter 7: Internet Protocol version 4
- Chapter 8: Internet Protocol version 6
- Chapter 9: Routing Protocol Selection Criteria
- Chapter 10: RIP and EIGRP Characteristics and Design
- Chapter 11: OSPF and IS-IS
- Chapter 12: Border Gateway Protocol, Route manipulation and IP Multicast
Part IV - Security, Convergence and Network Management
- Chapter 13: Security Management
- Chapter 14: Security Technologies and design
- Chapter 15: Traditional Voice Architectures and IP Telephony design
- Chapter 16: Network Management protocols
Part V - Comprehensive Scenarios
- Chapter 17: Comprehensive Scenarios
Summary
IIN
| IIN Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Integrated Transport | Joining voice, data and video in a transport network |
| Integrated Service | Ingegrate common services such as storage, virtualization of network systems |
| Integrated Application | The Network knows the applications, server virtualization |
SONA Lag
| SONA lag | Description |
|---|---|
| Network Infrastructure layer | Contains enterprise servers, storage and clients |
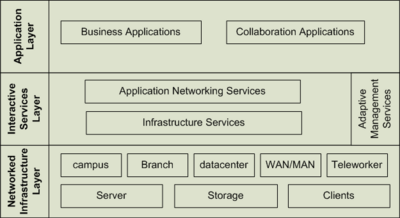
| Interactive Service Layer | Optimizationof communication between applications and services by utilizing intelligent network services such as security, Voice, Virtualization og QoS |
| Application layer | Business applications (Programs) and collaboration tools (mail, voice ...) |
SONA Infrastruktur services
| SONA lag | Description |
|---|---|
| Identity Services | Including AAA, NAC og NBAR |
| Mobility Services | Access to network services regardless of physical location |
| Storage Services | Storage of critical data |
| Compute Services | Enhancing compute resources (Virtualization) |
| Security Services | Security of all resources |
| Voice and collaboration Services | Shared services and programs |
PPDIOO
| PPDIOO aktivitet | Description |
|---|---|
| Prepare | DThe Prepare phase establishes organization and business requirements, develops a network
strategy, and proposes a high-level architecture to support the strategy. Technologies that support the architecture are identified. This phase creates a business case to establish a financial justification for a network strategy. |
| Plan | The Plan phase identifies the network requirements by characterizing and assessing the network,
performing a gap analysis against best-practice architectures, and looking at the operational environment. A project plan is developed to manage the tasks, responsible parties, milestones, and resources to do the design and implementation. This project plan is followed during all phases of the cycle. |
| Design | The network design is developed based on the technical and business requirements obtained from
the previous phases. The network design provides high availability, reliability, security, scalability, and performance. The design includes network diagrams and an equipment list. The project plan is updated with more granular information for implementation. After the Design phase is approved, the Implement phase begins. |
| Implement | New equipment is installed and configured in the Implement phase. New devices replace or
augment the existing infrastructure. The project plan is followed during this phase. Planned network changes should be communicated in change control meetings, with necessary approvals to proceed. Each step in the implementation should includes a description, detailed implementation guidelines, estimated time to implement, rollback steps in case of a failure, and any additional reference information. As changes are implemented they are also tested before moving to the Operate phase. |
| Operate | The Operate phase maintains the network’s day-to-day operational health. Operations include
managing and monitoring network components, routing maintenance, managing upgrades, managing performance, and identifying and correcting network faults. This phase is the design’s final test. During operation, network management stations should monitor the network’s general health and generate traps when certain thresholds are reached. |
| Optimize | The Optimize phase involves proactive network management by identifying and resolving issues
before they affect the network. The Optimize phase may create a modified network design if too many network problems arise, to improve performance issues, or to resolve application issues. The requirement for a modified network design leads to the network life cycle beginning. |
Top-down eller Bottom-up design
Top-down design
Incorporates the organization’s requirements. Provides the big picture. The design meets current and future requirements.
- Disadvantages:
- Time demanding
- Expensive short term.
Bottom-up design
The design is based on previous experience and allows for a quick solution.
- Disadvantages:
- May result in inappropriate design.
- Organizational requirements are not included.
Sektioner i et Design dokument
| Sektion | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | describes the project’s purpose and the reasons for the network design. |
| Design Requirements | lists the organization’s requirements, constraints, and goals. |
| Existing Network Infrastructure | includes logical (Layer 3) topology diagrams; physical topology diagrams; audit results; routing protocols; a summary of applications; a list of network routers, switches, and other devices; configurations; and a description of issues. |
| Design | contains the specific design information, such as logical and physical topology, IP
addressing, routing protocols, and security configurations. |
| Proof of Concept | results from live pilot or prototype testing. |
| Implementation plan | includes the detailed steps for the network staff to implement the new
installation and changes. |
| Appendixes | contains additional information and configurations. |
Optimering af kommunikationen mellem applikationer og services ved at anvende intelligente netværks services som for eksempel sikkerhed, virtualisering og QoS